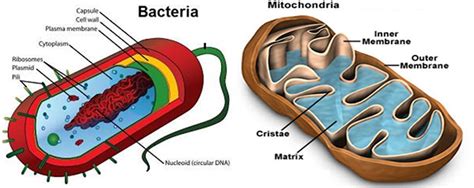
The existence of mitochondria in bacteria has been a topic of debate among scientists for many years. While it is widely accepted that mitochondria are a characteristic feature of eukaryotic cells, recent research has challenged this notion by suggesting that some bacteria may also possess mitochondria-like structures. In this article, we will delve into the world of bacterial cell biology and explore the concept of mitochondria in bacteria, examining the evidence, implications, and potential applications of this fascinating area of research.
Key Points
- Some bacteria, such as Rickettsia and Chlamydia, have been found to possess mitochondria-like structures
- These structures, known as mitochondria-derived organelles, are thought to have evolved from ancient mitochondrial endosymbionts
- The presence of mitochondria in bacteria has significant implications for our understanding of cellular evolution and the origins of eukaryotic cells
- Research into bacterial mitochondria may also have practical applications, such as the development of new antimicrobial therapies
- However, more research is needed to fully understand the function and significance of mitochondria in bacteria
The Discovery of Mitochondria in Bacteria

The discovery of mitochondria in bacteria was first reported in the 1960s, when scientists observed mitochondria-like structures in certain species of Rickettsia and Chlamydia. These structures, which were later termed mitochondria-derived organelles, were found to be similar in appearance and function to the mitochondria found in eukaryotic cells. Since then, numerous studies have confirmed the presence of mitochondria in various species of bacteria, including Parachlamydia, Simkania, and Waddlia.
Characteristics of Bacterial Mitochondria
Studies have shown that the mitochondria-like structures found in bacteria share many characteristics with eukaryotic mitochondria. For example, they are surrounded by a double membrane, have a similar morphology, and are capable of generating energy through the process of cellular respiration. However, bacterial mitochondria also exhibit some significant differences, such as the absence of mitochondrial DNA and the presence of unique protein complexes. Table 1 summarizes some of the key characteristics of bacterial mitochondria.
| Characteristic | Bacterial Mitochondria | Eukaryotic Mitochondria |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane structure | Double membrane | Double membrane |
| Mitochondrial DNA | Absent | Present |
| Energy generation | Cellular respiration | Cellular respiration |
| Protein complexes | Unique protein complexes | Standard protein complexes |
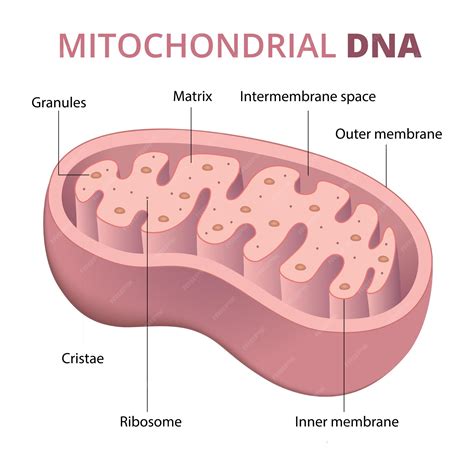
Implications and Applications
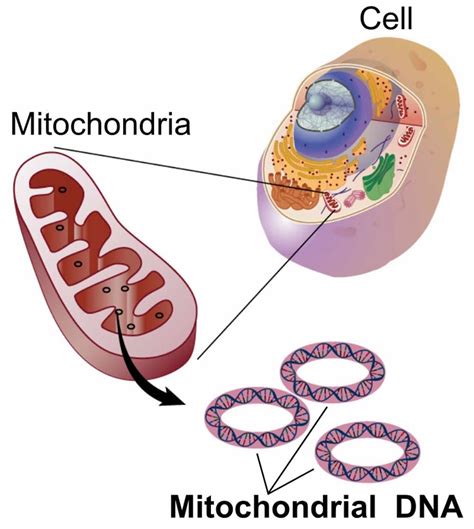
The discovery of mitochondria in bacteria has significant implications for our understanding of cellular evolution and the origins of eukaryotic cells. It also raises important questions about the evolution of cellular complexity and the role of endosymbiosis in shaping the diversity of life on Earth. Furthermore, research into bacterial mitochondria may have practical applications, such as the development of new antimicrobial therapies that target the unique characteristics of bacterial mitochondria.
Future Directions
While the discovery of mitochondria in bacteria is a significant breakthrough, more research is needed to fully understand the function and significance of these structures. Future studies should focus on characterizing the mitochondrial proteome, exploring the metabolic processes that occur within bacterial mitochondria, and investigating the evolutionary relationships between bacterial and eukaryotic mitochondria. Figure 1 illustrates the potential areas of research in this field.
In conclusion, the presence of mitochondria in bacteria is a fascinating area of research that challenges our current understanding of cellular biology and evolution. As we continue to explore this topic, we may uncover new insights into the origins of life on Earth and the diversity of cellular complexity. By combining cutting-edge techniques and interdisciplinary approaches, scientists can shed light on the function and significance of bacterial mitochondria, ultimately advancing our knowledge of the microbial world and its many secrets.
What are the implications of mitochondria in bacteria for our understanding of cellular evolution?
+The presence of mitochondria in bacteria suggests that the endosymbiotic theory, which proposes that mitochondria originated from ancient bacterial endosymbionts, may be more complex than previously thought. It also raises important questions about the evolution of cellular complexity and the role of endosymbiosis in shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
What are the potential applications of research into bacterial mitochondria?
+Research into bacterial mitochondria may have practical applications, such as the development of new antimicrobial therapies that target the unique characteristics of bacterial mitochondria. It may also provide insights into the development of new treatments for mitochondrial diseases in humans.
What are the future directions for research into bacterial mitochondria?
+Future studies should focus on characterizing the mitochondrial proteome, exploring the metabolic processes that occur within bacterial mitochondria, and investigating the evolutionary relationships between bacterial and eukaryotic mitochondria. This research will help to shed light on the function and significance of bacterial mitochondria and their potential applications.