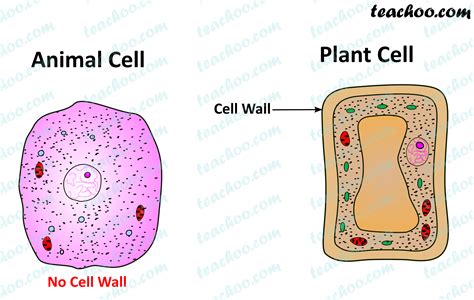
One of the fundamental characteristics that distinguish plants and some other organisms from animals is the presence of cell walls. Cell walls are rigid structures that provide support, protection, and shape to cells, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of tissues and organs. However, the statement "animals have cell walls" is not entirely accurate, as it depends on the specific type of animal being referred to. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell biology and explore the characteristics of cell walls in different organisms, including animals.
Cell Walls in Plants and Fungi
Plants and fungi are two groups of organisms that are well-known for having cell walls. Plant cell walls are composed of a tough, flexible material called cellulose, which provides support and structure to the cell. Fungal cell walls, on the other hand, are composed of a tough, flexible material called chitin. Both cellulose and chitin are polysaccharides, which are long chains of sugar molecules that are linked together to form a strong and rigid structure. The presence of cell walls in plants and fungi allows them to maintain their shape and withstand external pressures, and they play a crucial role in the development and function of these organisms.
Cell Walls in Bacteria
Bacteria are a group of single-celled microorganisms that also have cell walls. Bacterial cell walls are composed of a layer of peptidoglycan, which is a molecule that is composed of sugar and amino acid molecules. The peptidoglycan layer provides support and protection to the cell, and it helps to maintain the cell’s shape and structure. Some bacteria also have an additional layer of lipopolysaccharides or lipoteichoic acids, which provide extra protection and help to regulate the cell’s interactions with its environment.
Key Points
- Cell walls are rigid structures that provide support, protection, and shape to cells.
- Plants and fungi have cell walls composed of cellulose and chitin, respectively.
- Bacteria have cell walls composed of peptidoglycan.
- Animals do not have cell walls, with the exception of some invertebrates.
- The absence of cell walls in animals allows for greater flexibility and mobility.
Cell Walls in Animals
Animals, on the other hand, do not have cell walls. Instead, their cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that regulates the cell’s interactions with its environment. The absence of cell walls in animals allows for greater flexibility and mobility, as their cells can change shape and move more easily. However, some invertebrate animals, such as sponges and cnidarians, do have cell walls that are composed of a tough, flexible material called collagen. These cell walls provide support and structure to the cells, and they help to maintain the integrity and function of the tissues and organs.
| Organism | Cell Wall Composition |
|---|---|
| Plants | Cellulose |
| Fungi | Chitin |
| Bacteria | Peptidoglycan |
| Animals (most) | No cell wall |
| Some invertebrates (e.g. sponges, cnidarians) | Collagen |
Evolutionary Implications
The evolution of cell walls has had a significant impact on the development and diversity of life on Earth. The presence of cell walls in plants and fungi has allowed these organisms to thrive in a wide range of environments, from the freezing tundra to the hottest deserts. The absence of cell walls in animals, on the other hand, has allowed them to develop greater flexibility and mobility, which has enabled them to colonize a wide range of habitats and exploit new resources. The evolution of cell walls has also had significant implications for the development of complex tissues and organs, as it has allowed for the formation of rigid structures that can provide support and protection to cells and tissues.
In conclusion, the statement "animals have cell walls" is not entirely accurate, as it depends on the specific type of animal being referred to. While some invertebrate animals do have cell walls, most animals do not. The presence or absence of cell walls is a key characteristic that distinguishes different groups of organisms, and understanding the composition and function of cell walls is essential for understanding the biology and ecology of these organisms.
What is the main function of cell walls in organisms?
+The main function of cell walls is to provide support, protection, and shape to cells. They help to maintain the cell's integrity and function, and they play a crucial role in the development and ecology of organisms.
Which organisms have cell walls composed of cellulose?
+Plants have cell walls composed of cellulose. Cellulose is a tough, flexible material that provides support and structure to plant cells.
Do all animals have cell walls?
+No, most animals do not have cell walls. However, some invertebrate animals, such as sponges and cnidarians, do have cell walls that are composed of collagen.
Meta Description: Learn about the composition and function of cell walls in different organisms, including plants, fungi, bacteria, and animals. Discover the evolutionary implications of cell walls and how they have shaped the diversity of life on Earth. (149 characters)