The debate between digital and analog signals has been a longstanding one, with each having its own set of advantages and disadvantages. In the realm of signal processing, the choice between digital and analog signals is crucial, as it can significantly impact the quality, efficiency, and reliability of the signal transmission. In this article, we will delve into the world of digital and analog signals, exploring their fundamental differences, applications, and the trade-offs involved in choosing one over the other.
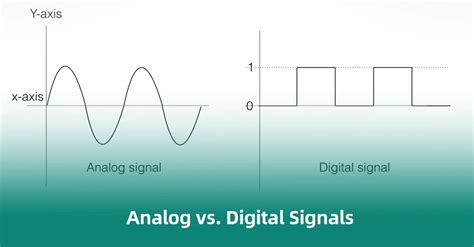
At its core, a signal is a representation of information, such as sound, image, or data, that is transmitted through a medium, like air, wire, or fiber optic cable. The primary distinction between digital and analog signals lies in the way they represent this information. Analog signals are continuous, meaning they can take on any value within a given range, whereas digital signals are discrete, consisting of a series of binary digits (0s and 1s) that represent the information. This fundamental difference has far-reaching implications for signal processing, transmission, and storage.
Key Points
- Digital signals offer higher resistance to noise and interference, making them more reliable for long-distance transmission.
- Analog signals provide a more nuanced representation of information, but are more susceptible to degradation and distortion.
- Digital signals require more complex processing and encoding, but enable more efficient data compression and error correction.
- Analog signals are often used in applications where high fidelity and dynamic range are critical, such as audio and image processing.
- The choice between digital and analog signals ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, including signal quality, transmission distance, and processing complexity.
Digital Signal Characteristics

Digital signals are composed of a series of binary digits, which can be represented as a sequence of electrical pulses or light signals. This discrete nature of digital signals provides several advantages, including higher resistance to noise and interference, improved reliability, and enhanced security. Digital signals can be easily encoded, decoded, and processed using digital circuits and algorithms, making them well-suited for applications such as computer networks, digital communication systems, and data storage devices.
One of the primary benefits of digital signals is their ability to withstand noise and interference. Since digital signals are composed of discrete values, they can be easily distinguished from noise, which is typically continuous. This allows digital signals to maintain their integrity over long distances, making them ideal for applications such as satellite communication, fiber optic transmission, and wireless networking. Additionally, digital signals can be compressed and encoded using various algorithms, reducing the amount of bandwidth required for transmission and increasing the overall efficiency of the system.
Digital Signal Processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is a critical component of modern digital systems, enabling the manipulation and analysis of digital signals in real-time. DSP techniques, such as filtering, modulation, and demodulation, allow digital signals to be processed and transformed in a variety of ways, enabling applications such as audio and image processing, data compression, and error correction. The use of digital signal processing algorithms and techniques has revolutionized the field of signal processing, enabling the development of sophisticated systems that can efficiently process and transmit large amounts of data.
| Signal Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Digital | Higher resistance to noise, improved reliability, enhanced security | More complex processing, higher power consumption |
| Analog | More nuanced representation of information, lower power consumption | More susceptible to degradation and distortion, lower reliability |
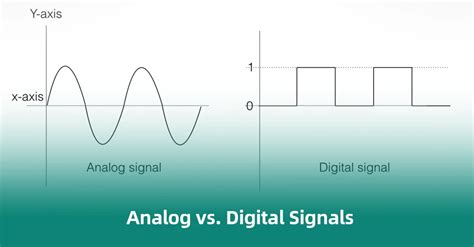
Analog Signal Characteristics
Analog signals, on the other hand, are continuous, meaning they can take on any value within a given range. This continuous nature of analog signals provides a more nuanced representation of information, making them well-suited for applications such as audio and image processing, where high fidelity and dynamic range are critical. Analog signals can be represented as a continuous waveform, which can be manipulated and processed using various analog circuits and techniques.
One of the primary advantages of analog signals is their ability to provide a more accurate representation of the original information. Since analog signals are continuous, they can capture the subtle nuances and variations in the information, making them ideal for applications such as music and image processing. Additionally, analog signals typically require less power to transmit and process, making them more energy-efficient than digital signals.
Analog Signal Processing
Analog signal processing (ASP) is a critical component of modern analog systems, enabling the manipulation and analysis of analog signals in real-time. ASP techniques, such as amplification, filtering, and modulation, allow analog signals to be processed and transformed in a variety of ways, enabling applications such as audio and image processing, data transmission, and control systems. The use of analog signal processing algorithms and techniques has been instrumental in the development of sophisticated systems that can efficiently process and transmit analog information.
Comparison of Digital and Analog Signals
In conclusion, digital and analog signals have distinct characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Digital signals offer higher resistance to noise and interference, improved reliability, and enhanced security, making them ideal for applications such as computer networks, digital communication systems, and data storage devices. Analog signals, on the other hand, provide a more nuanced representation of information, making them well-suited for applications such as audio and image processing, where high fidelity and dynamic range are critical.
When choosing between digital and analog signals, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including signal quality, transmission distance, and processing complexity. By understanding the trade-offs involved in using digital and analog signals, engineers and system designers can make informed decisions about which type of signal to use, enabling the development of more efficient, reliable, and effective systems.
What is the primary advantage of digital signals over analog signals?
+The primary advantage of digital signals over analog signals is their higher resistance to noise and interference, making them more reliable for long-distance transmission.
What is the primary disadvantage of digital signals compared to analog signals?
+The primary disadvantage of digital signals compared to analog signals is their more complex processing and encoding requirements, which can increase power consumption and reduce efficiency.
What are some common applications of analog signals?
+Analog signals are commonly used in applications such as audio and image processing, where high fidelity and dynamic range are critical. They are also used in control systems, data transmission, and medical devices.
As technology continues to evolve, the distinction between digital and analog signals will become increasingly blurred. The development of new technologies, such as quantum computing and neuromorphic processing, will enable the creation of more sophisticated systems that can efficiently process and transmit both digital and analog information. By understanding the fundamental differences between digital and analog signals, engineers and system designers can create more efficient, reliable, and effective systems that can meet the demands of an increasingly complex and interconnected world.



