The concepts of radius and diameter are fundamental in geometry, particularly when dealing with circles and spheres. Understanding the difference between these two terms and how they relate to each other is crucial for solving problems in mathematics, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the world of circles and explore five essential tips that highlight the relationship between radius and diameter, helping you to grasp these concepts more effectively.
Key Points
- Understanding the definitions of radius and diameter and their relationship
- Learning how to calculate the diameter from the radius and vice versa
- Applying the concepts to real-world problems and geometric shapes
- Recognizing the importance of precision in measurements and calculations
- Practicing with examples to reinforce understanding and build problem-solving skills
Tip 1: Definitions and Relationship

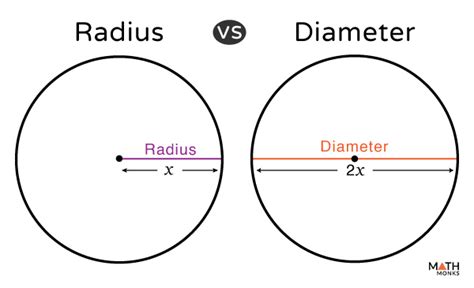
A radius of a circle is a line segment that connects the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. The diameter, on the other hand, is a line segment that passes through the center of the circle and connects two points on the circumference. A critical relationship between the radius and diameter is that the diameter is twice the length of the radius. This can be expressed as d = 2r, where d is the diameter and r is the radius. Understanding this relationship is key to solving many geometric problems.
Calculating Diameter from Radius and Vice Versa
Given the formula d = 2r, calculating the diameter from the radius is straightforward. For example, if the radius of a circle is 4 cm, the diameter would be 2 * 4 = 8 cm. Conversely, to find the radius from the diameter, you divide the diameter by 2. So, if the diameter is 10 cm, the radius would be 10 / 2 = 5 cm. This simple yet crucial calculation is the foundation of many geometric and trigonometric applications.
Tip 2: Real-World Applications

The concepts of radius and diameter have numerous real-world applications. For instance, in architecture, understanding the radius and diameter of circular columns or domes is essential for designing structures that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound. In mechanical engineering, the radius and diameter of gears, axles, and other circular components are critical for ensuring the proper functioning of machines. Moreover, in physics, the radius of the Earth and other celestial bodies is a fundamental parameter in calculating their circumferences, surface areas, and volumes.
Importance of Precision
Precision is paramount when working with measurements of radius and diameter. Small discrepancies can lead to significant errors in calculations, especially in applications where exactness is critical, such as in the manufacturing of parts for machinery or in the construction of large-scale structures. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that all measurements are taken accurately and that calculations are performed meticulously to avoid compounded errors.
Tip 3: Geometric Shapes and Formulas
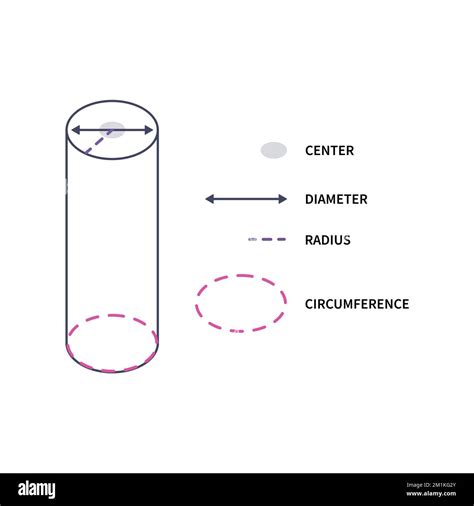
Beyond the basic circle, understanding radius and diameter is essential for working with other geometric shapes, such as spheres, cylinders, and cones. For a sphere, the radius is the distance from the center to any point on its surface, and the diameter is the longest possible distance within the sphere, passing through its center. For cylinders and cones, the radius of the base and the height are critical dimensions that require precise measurement and calculation. Familiarity with the formulas related to these shapes, such as the volume and surface area formulas, further emphasizes the importance of grasping radius and diameter concepts.
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sphere Volume | V = (4/3)πr^3 |
| Cylinder Volume | V = πr^2h |
| Cone Volume | V = (1/3)πr^2h |
Tip 4: Practice and Reinforcement
Practice is essential for reinforcing the understanding of radius and diameter concepts. Solving problems that involve calculating the radius from the diameter, and vice versa, helps in solidifying the relationship between these two parameters. Moreover, applying these concepts to real-world scenarios and geometric shapes makes the learning process more engaging and relevant. Utilizing online resources, textbooks, and educational software can provide a plethora of practice problems and interactive exercises to help learners at all levels.
Recognizing Mistakes and Limitations
It’s also important to recognize common mistakes and limitations in calculations involving radius and diameter. For instance, forgetting to divide by 2 when calculating the radius from the diameter, or incorrectly applying formulas for different geometric shapes, can lead to significant errors. Being aware of these potential pitfalls and double-checking calculations can prevent misunderstandings and miscalculations.
Tip 5: Advanced Applications and Future Directions
In advanced fields such as astronomy and aerospace engineering, the concepts of radius and diameter are applied on a cosmic scale. The radius of the Earth, the diameter of the Sun, and the distances between celestial bodies are all critical measurements for understanding our universe. As technology advances and our ability to measure and explore space improves, the precision and accuracy of these measurements will become even more crucial. For those interested in pursuing careers in these fields, a deep understanding of geometric principles, including radius and diameter, will be essential.
What is the difference between the radius and diameter of a circle?
+The radius is a line segment from the center to any point on the circumference, while the diameter is a line segment that passes through the center and connects two points on the circumference. The diameter is twice the length of the radius.
How do you calculate the diameter from the radius?
+The diameter is calculated by multiplying the radius by 2. This can be expressed as d = 2r, where d is the diameter and r is the radius.
What are some real-world applications of radius and diameter?
+Radius and diameter have applications in architecture, mechanical engineering, physics, and astronomy. They are used in designing structures, machines, and in calculating distances and sizes of celestial bodies.