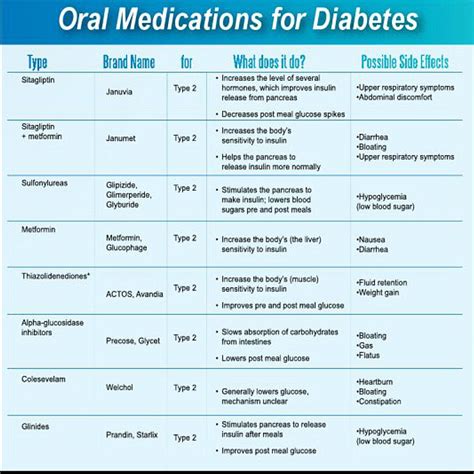
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing it effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. With numerous medications available to treat diabetes, it can be overwhelming for patients and healthcare providers to navigate the various options. A diabetes medications chart can be a valuable tool in helping individuals understand the different types of medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects.
Key Points
- There are several classes of diabetes medications, including metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Each class of medication has a unique mechanism of action and potential side effects.
- A diabetes medications chart can help patients and healthcare providers compare and contrast different medications.
- Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, are also crucial in managing diabetes.
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and medication adjustments can help individuals with diabetes achieve optimal glycemic control.
Classes of Diabetes Medications
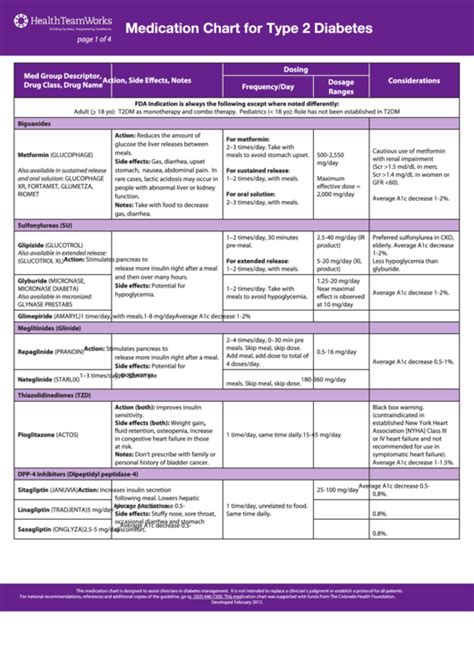
There are several classes of diabetes medications, each with its own unique mechanism of action and potential side effects. The main classes of diabetes medications include:
Metformin
Metformin is a biguanide that works by decreasing glucose production in the liver and increasing insulin sensitivity. It is often the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes and is available in both immediate-release and extended-release formulations. Common side effects of metformin include gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas are a class of medications that stimulate insulin release from the pancreas. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including glimepiride, glyburide, and glipizide. Common side effects of sulfonylureas include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal upset.
Meglitinides
Meglitinides are a class of medications that also stimulate insulin release from the pancreas. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including repaglinide and nateglinide. Common side effects of meglitinides include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal upset.
Thiazolidinediones
Thiazolidinediones are a class of medications that increase insulin sensitivity and decrease glucose production in the liver. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including pioglitazone and rosiglitazone. Common side effects of thiazolidinediones include weight gain, edema, and increased risk of heart failure.
DPP-4 Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors are a class of medications that work by increasing the levels of incretin hormones in the body, which in turn increase insulin release and decrease glucose production. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. Common side effects of DPP-4 inhibitors include gastrointestinal upset, headache, and increased risk of pancreatitis.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that work by increasing the levels of incretin hormones in the body, which in turn increase insulin release and decrease glucose production. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide. Common side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists include gastrointestinal upset, nausea, and increased risk of pancreatitis.
SGLT2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications that work by decreasing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, which in turn increases glucose excretion in the urine. They are often used to treat type 2 diabetes and are available in several different formulations, including canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin. Common side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include increased risk of urinary tract infections, genital mycotic infections, and decreased blood pressure.
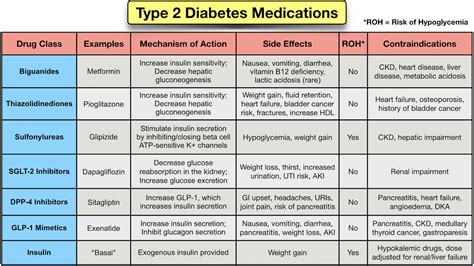
| Medication Class | Examples | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Glucophage, Fortamet | Decreases glucose production in liver, increases insulin sensitivity | Gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Sulfonylureas | Glimepiride, Glyburide, Glipizide | Stimulates insulin release from pancreas | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, gastrointestinal upset |
| Meglitinides | Repaglinide, Nateglinide | Stimulates insulin release from pancreas | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, gastrointestinal upset |
| Thiazolidinediones | Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone | Increases insulin sensitivity, decreases glucose production in liver | Weight gain, edema, increased risk of heart failure |
| DPP-4 Inhibitors | Sitagliptin, Saxagliptin, Linagliptin | Increases incretin hormones, increases insulin release and decreases glucose production | Gastrointestinal upset, headache, increased risk of pancreatitis |
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Exenatide, Liraglutide, Dulaglutide | Increases incretin hormones, increases insulin release and decreases glucose production | Gastrointestinal upset, nausea, increased risk of pancreatitis |
| SGLT2 Inhibitors | Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, Empagliflozin | Decreases glucose reabsorption in kidneys, increases glucose excretion in urine | Increased risk of urinary tract infections, genital mycotic infections, decreased blood pressure |
Conclusion
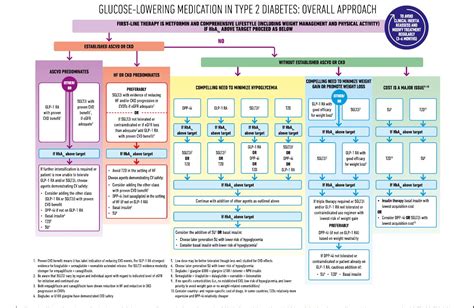
In conclusion, managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. A diabetes medications chart can be a valuable tool in helping patients and healthcare providers navigate the various medication options and develop personalized treatment plans. By understanding the different classes of diabetes medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects, individuals with diabetes can achieve optimal glycemic control and improve their overall health outcomes.
What is the primary mechanism of action of metformin?
+Metformin works by decreasing glucose production in the liver and increasing insulin sensitivity.
What are the common side effects of sulfonylureas?
+Common side effects of sulfonylureas include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal upset.
How do DPP-4 inhibitors work?
+DPP-4 inhibitors work by increasing the levels of incretin hormones in the body, which in turn increase insulin release and decrease glucose production.
What is the primary benefit of using a diabetes medications chart?
+A diabetes medications chart can help patients and healthcare providers compare and contrast different medications, develop personalized treatment plans, and achieve optimal glycemic control.
What are the potential side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors?
+Potential side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include increased risk of urinary tract infections, genital mycotic infections, and decreased blood pressure.
Meta description: Learn about the different classes of diabetes medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects. A comprehensive diabetes medications chart can help patients and healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans and achieve optimal glycemic control. (147 characters)