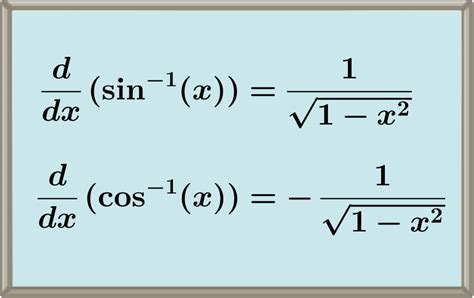The derivative of inverse sine, also known as arcsine, is a fundamental concept in calculus. It is used to find the rate of change of the inverse sine function with respect to its input. The inverse sine function, denoted as sin^(-1)(x) or arcsin(x), is the inverse of the sine function. It returns the angle whose sine is a given number. In this article, we will explore five ways to find the derivative of inverse sine, including the definition of a derivative, implicit differentiation, and geometric interpretation.
Key Points
- The derivative of inverse sine is 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2), which can be derived using the definition of a derivative.
- Implicit differentiation can be used to find the derivative of inverse sine by differentiating both sides of the equation y = sin^(-1)(x).
- The geometric interpretation of the derivative of inverse sine involves finding the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the inverse sine function.
- The derivative of inverse sine has many applications in physics, engineering, and computer science, including optimization problems and signal processing.
- Using the chain rule and the derivative of inverse sine, we can find the derivatives of more complex functions involving inverse sine.
Definition of a Derivative
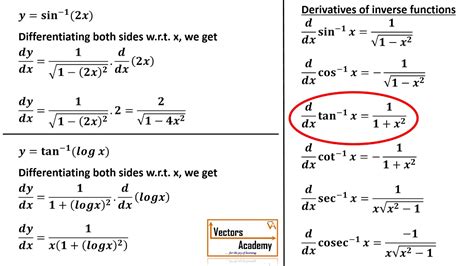
The derivative of a function f(x) is defined as the limit of the difference quotient as the change in x approaches zero. For the inverse sine function, we can use this definition to find its derivative. Let f(x) = sin^(-1)(x). Then, the derivative of f(x) is given by f’(x) = lim(h -> 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)]/h. By using the addition formula for sine and simplifying the expression, we can show that f’(x) = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2).
Implicit Differentiation
Implicit differentiation is a technique used to find the derivative of a function that is defined implicitly. For the inverse sine function, we can use implicit differentiation to find its derivative. Let y = sin^(-1)(x). Then, sin(y) = x. Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get cos(y) * dy/dx = 1. Solving for dy/dx, we find that dy/dx = 1 / cos(y). Using the identity cos(y) = sqrt(1 - sin^2(y)) and substituting sin(y) = x, we can simplify this expression to dy/dx = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2).
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| sin^(-1)(x) | 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) |
| cos^(-1)(x) | -1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) |
| tan^(-1)(x) | 1 / (1 + x^2) |
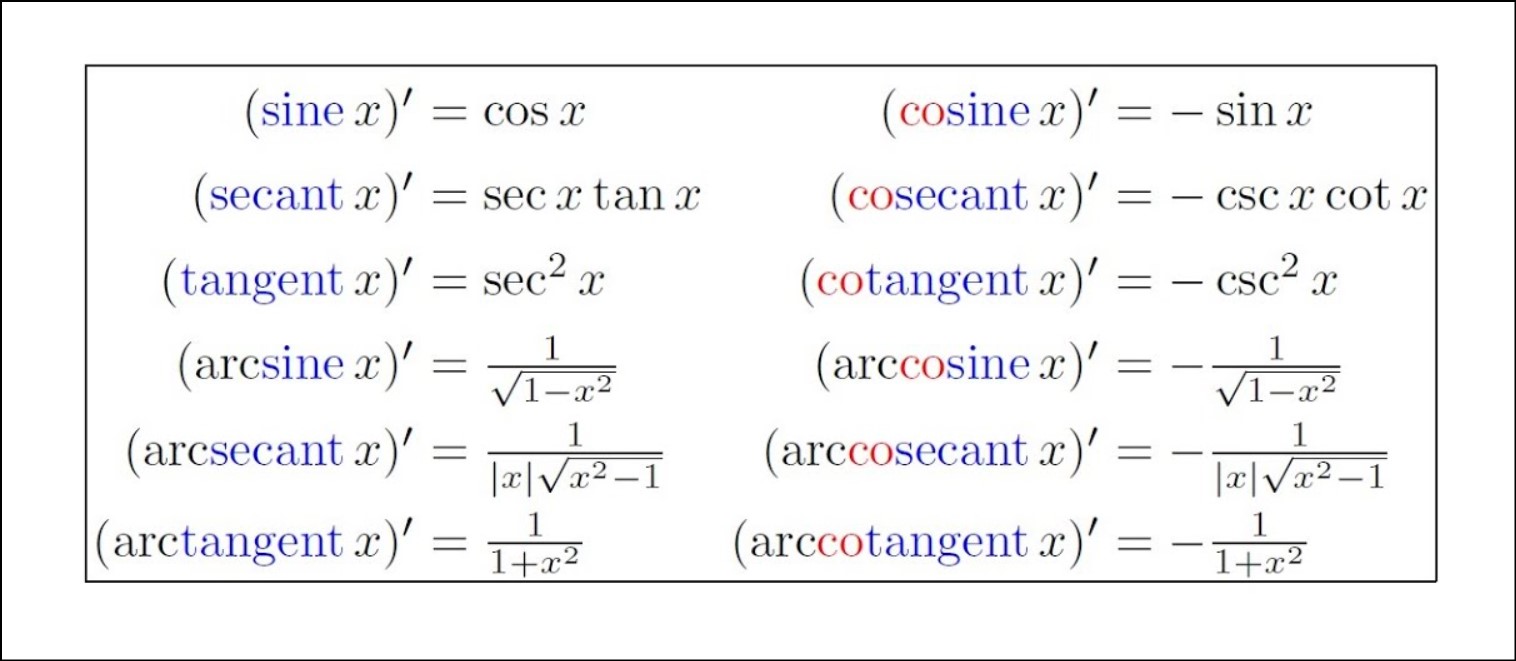
Geometric Interpretation
The geometric interpretation of the derivative of inverse sine involves finding the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the inverse sine function. The graph of the inverse sine function is a curve that passes through the points (0, 0) and (1, pi/2). The slope of the tangent line to this curve at any point (x, y) is given by the derivative of the inverse sine function at that point. Using the definition of a derivative, we can show that the slope of the tangent line is 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2). This result can be verified geometrically by drawing the graph of the inverse sine function and finding the slope of the tangent line at different points.
Applications
The derivative of inverse sine has many applications in physics, engineering, and computer science. One of the most common applications is in optimization problems, where we need to find the maximum or minimum of a function subject to certain constraints. The derivative of inverse sine can be used to find the critical points of the function, which are the points where the function has a maximum or minimum. Another application is in signal processing, where the derivative of inverse sine can be used to filter out noise from a signal. The derivative of inverse sine can also be used in computer graphics to create smooth curves and surfaces.
What is the derivative of inverse sine?
+The derivative of inverse sine is 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2).
How can we find the derivative of inverse sine using implicit differentiation?
+We can find the derivative of inverse sine using implicit differentiation by differentiating both sides of the equation y = sin^(-1)(x) and solving for dy/dx.
What are some applications of the derivative of inverse sine?
+The derivative of inverse sine has many applications in physics, engineering, and computer science, including optimization problems, signal processing, and computer graphics.
In conclusion, the derivative of inverse sine is a fundamental concept in calculus that has many applications in physics, engineering, and computer science. Understanding the different ways to find this derivative, including the definition of a derivative, implicit differentiation, and geometric interpretation, can help you develop a deeper appreciation for the subject and improve your problem-solving skills. By applying the derivative of inverse sine to real-world problems, you can create innovative solutions and make meaningful contributions to your field.