Density Functional Theory (DFT) is a computational method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the behavior of many-electron systems. It's a powerful tool for understanding the properties of molecules and solids, and has become a cornerstone of modern materials science and quantum chemistry. In this article, we'll delve into the principles and applications of DFT, exploring its strengths and limitations, and examining the ways in which it has revolutionized our understanding of the physical world.
Key Points
- Density Functional Theory is a computational method for studying many-electron systems
- DFT is based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which relate the density of a system to its external potential
- The Kohn-Sham equations are a key component of DFT, allowing for the calculation of the density and energy of a system
- DFT has a wide range of applications, including materials science, quantum chemistry, and condensed matter physics
- While DFT has many strengths, it also has limitations, including the need for approximate exchange-correlation functionals
Introduction to Density Functional Theory

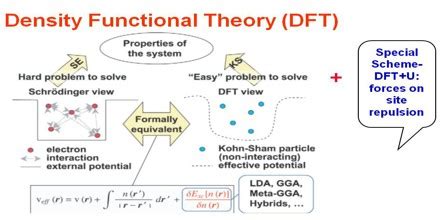
DFT is based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which were formulated in the 1960s. These theorems state that the density of a system determines its external potential, and that the density is a unique functional of the external potential. This means that, in principle, it’s possible to calculate the properties of a system using only its density, rather than its wavefunction. The Hohenberg-Kohn theorems provide a foundation for DFT, and have been widely used to develop new methods and approximations.
The Kohn-Sham Equations
The Kohn-Sham equations are a key component of DFT. These equations are a set of single-particle equations that describe the behavior of a system of non-interacting electrons in an effective potential. The effective potential includes the external potential, as well as the Hartree potential, which describes the electrostatic interactions between the electrons. The exchange-correlation potential is also included, which accounts for the many-electron effects that are not included in the Hartree potential. The Kohn-Sham equations are solved self-consistently, meaning that the density and potential are iteratively updated until convergence is reached.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Density | The density of a system is a measure of the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space |
| External Potential | The external potential is the potential experienced by an electron due to the presence of nuclei and other external fields |
| Exchange-Correlation Potential | The exchange-correlation potential accounts for the many-electron effects that are not included in the Hartree potential |
Applications of Density Functional Theory
DFT has a wide range of applications, including materials science, quantum chemistry, and condensed matter physics. It’s used to study the properties of molecules and solids, and has been instrumental in the development of new materials and technologies. For example, DFT has been used to study the properties of graphene, a material that has potential applications in electronics and energy storage. It’s also been used to study the behavior of molecules in solution, and has been used to develop new catalysts and drugs.
Materials Science Applications
DFT is widely used in materials science to study the properties of solids and surfaces. It’s used to calculate the band structure and density of states of materials, and has been used to study the behavior of defects and impurities. DFT has also been used to study the properties of nanostructures, such as nanoparticles and nanowires. These systems have unique properties that are not seen in bulk materials, and DFT is essential for understanding their behavior.
For example, DFT has been used to study the properties of transition metal oxides, which have potential applications in energy storage and conversion. It's also been used to study the behavior of topological insulators, which have unique properties that make them useful for quantum computing and other applications.
Limitations of Density Functional Theory
While DFT has many strengths, it also has limitations. One of the key limitations is the need for approximate exchange-correlation functionals. These functionals are used to approximate the exchange-correlation potential, and are essential for obtaining accurate results. However, the development of new functionals is an active area of research, and there is still much to be learned about the behavior of many-electron systems.
Exchange-Correlation Functionals
Exchange-correlation functionals are a key component of DFT, and are used to approximate the exchange-correlation potential. These functionals are typically based on the local density approximation (LDA), which assumes that the exchange-correlation potential is a function of the local density. However, the LDA is not always accurate, and more sophisticated functionals are often needed to obtain accurate results.
What is the main advantage of using DFT?
+The main advantage of using DFT is that it allows for the calculation of the properties of many-electron systems using only the density, rather than the wavefunction. This makes it a much more efficient method than traditional wavefunction-based methods, and allows for the study of larger systems.
What is the main limitation of DFT?
+The main limitation of DFT is the need for approximate exchange-correlation functionals. These functionals are used to approximate the exchange-correlation potential, and are essential for obtaining accurate results. However, the development of new functionals is an active area of research, and there is still much to be learned about the behavior of many-electron systems.
What are some common applications of DFT?
+DFT has a wide range of applications, including materials science, quantum chemistry, and condensed matter physics. It's used to study the properties of molecules and solids, and has been instrumental in the development of new materials and technologies.
In conclusion, DFT is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of many-electron systems. It’s based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, and uses the Kohn-Sham equations to calculate the density and energy of a system. While DFT has many strengths, it also has limitations, including the need for approximate exchange-correlation functionals. However, the development of new functionals is an active area of research, and DFT remains a widely used and essential tool in materials science, quantum chemistry, and condensed matter physics.