The Delta G Rxn formula, also known as the Gibbs free energy change equation, is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics and chemistry. It is used to determine the spontaneity of a chemical reaction, which is essential in understanding the feasibility and direction of a reaction. The Delta G Rxn formula is expressed as: ΔG = ΔH - TΔS, where ΔG is the change in Gibbs free energy, ΔH is the change in enthalpy, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and ΔS is the change in entropy.
The Delta G Rxn formula is a measure of the energy available to do work in a system. A negative ΔG value indicates that a reaction is spontaneous, meaning it will proceed on its own without external input. On the other hand, a positive ΔG value indicates that a reaction is non-spontaneous, requiring energy input to proceed. The formula takes into account the enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS) changes of a reaction, as well as the temperature (T) at which the reaction occurs.
Key Points
- The Delta G Rxn formula is used to determine the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.
- A negative ΔG value indicates a spontaneous reaction, while a positive ΔG value indicates a non-spontaneous reaction.
- The formula takes into account the enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS) changes of a reaction, as well as the temperature (T) at which the reaction occurs.
- ΔG is a measure of the energy available to do work in a system.
- The Delta G Rxn formula is essential in understanding the feasibility and direction of a chemical reaction.
Understanding the Components of the Delta G Rxn Formula
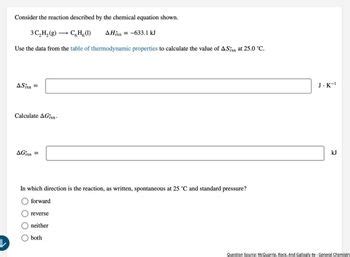
The Delta G Rxn formula consists of three main components: ΔH, ΔS, and T. The change in enthalpy (ΔH) is a measure of the energy change associated with the formation or breaking of chemical bonds. The change in entropy (ΔS) is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. Temperature (T) is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system.
A reaction with a negative ΔH value is exothermic, releasing energy into the surroundings. On the other hand, a reaction with a positive ΔH value is endothermic, absorbing energy from the surroundings. The change in entropy (ΔS) can also be positive or negative. A reaction with a positive ΔS value is one in which the disorder or randomness of the system increases, while a reaction with a negative ΔS value is one in which the disorder or randomness of the system decreases.
Calculating the Delta G Rxn Formula
The Delta G Rxn formula can be calculated using the following equation: ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. To calculate ΔG, we need to know the values of ΔH, ΔS, and T. The units of ΔG are typically expressed in joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ). The units of ΔH and ΔS are typically expressed in joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ) per mole, while the units of T are typically expressed in Kelvin (K).
| Component | Unit |
|---|---|
| ΔG | joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ) |
| ΔH | joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ) per mole |
| ΔS | joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ) per mole per Kelvin (K) |
| T | Kelvin (K) |
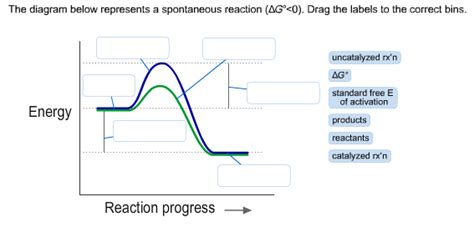
Applications of the Delta G Rxn Formula

The Delta G Rxn formula has numerous applications in chemistry and biology. It is used to predict the spontaneity of a chemical reaction, which is essential in understanding the feasibility and direction of a reaction. The formula is also used to calculate the equilibrium constant (K) of a reaction, which provides information about the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium.
In biology, the Delta G Rxn formula is used to understand the energy changes associated with metabolic pathways. It is also used to predict the spontaneity of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, which is essential in understanding the mechanisms of enzymatic reactions.
Limitations of the Delta G Rxn Formula
While the Delta G Rxn formula is a powerful tool for predicting the spontaneity of a chemical reaction, it has some limitations. The formula assumes that the reaction is at equilibrium, which may not always be the case. Additionally, the formula does not provide information about the rate of a reaction, which is influenced by other factors, such as the concentration of reactants and the presence of catalysts.
What is the Delta G Rxn formula used for?
+The Delta G Rxn formula is used to determine the spontaneity of a chemical reaction, which is essential in understanding the feasibility and direction of a reaction.
What are the components of the Delta G Rxn formula?
+The Delta G Rxn formula consists of three main components: ΔH, ΔS, and T.
What are the units of the Delta G Rxn formula?
+The units of ΔG are typically expressed in joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ), while the units of ΔH and ΔS are typically expressed in joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ) per mole, and the units of T are typically expressed in Kelvin (K).
In conclusion, the Delta G Rxn formula is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics and chemistry. It is used to determine the spontaneity of a chemical reaction, which is essential in understanding the feasibility and direction of a reaction. The formula consists of three main components: ΔH, ΔS, and T, and it has numerous applications in chemistry and biology. While the formula has some limitations, it is a powerful tool for predicting the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.