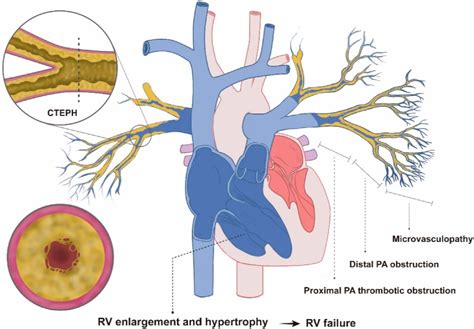
The medical abbreviation "CTEPH" stands for Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. It is a condition characterized by the presence of chronic blood clots in the pulmonary arteries, which can lead to increased blood pressure in the lungs and potentially life-threatening complications. CTEPH is a rare and underdiagnosed condition, affecting approximately 3-5% of patients who have experienced a pulmonary embolism.
Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation
CTEPH occurs when blood clots in the pulmonary arteries fail to dissolve, leading to the formation of chronic thrombi. This can cause a range of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and coughing. In severe cases, CTEPH can lead to right heart failure, which can manifest as swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, as well as abdominal distension. The diagnosis of CTEPH is often delayed due to its non-specific symptoms and the lack of awareness among healthcare professionals.
Diagnostic Criteria and Evaluation
The diagnosis of CTEPH is based on a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and hemodynamic measurements. The diagnostic criteria include the presence of chronic thrombi in the pulmonary arteries, as confirmed by imaging studies such as ventilation-perfusion scanning or pulmonary angiography. Additionally, patients must have a mean pulmonary artery pressure of at least 25 mmHg, as measured by right heart catheterization. The evaluation of CTEPH also involves the assessment of right ventricular function, using techniques such as echocardiography or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
| Diagnostic Criterion | Description |
|---|---|
| Chronic thrombi | Persistent blood clots in the pulmonary arteries |
| Mean pulmonary artery pressure | ≥ 25 mmHg, as measured by right heart catheterization |
| Right ventricular function | Assessed using echocardiography or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging |
Treatment Options and Management
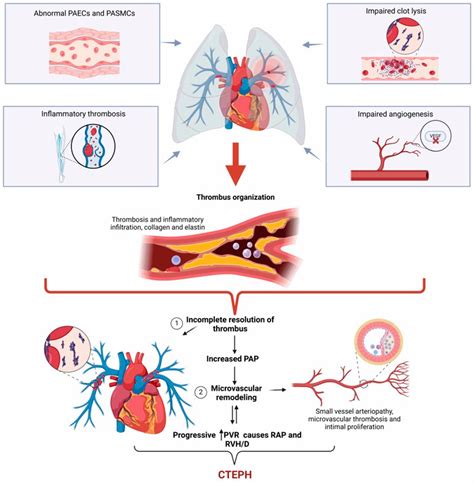
The treatment of CTEPH is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms, improving quality of life, and preventing disease progression. Medical therapy, including anticoagulation and pulmonary vasodilators, is the mainstay of treatment. In selected patients, surgical thromboendarterectomy or balloon pulmonary angioplasty may be considered. These procedures involve the removal or dilation of chronic thrombi in the pulmonary arteries, with the goal of improving blood flow and reducing pulmonary artery pressure.
Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy
Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of chronic thrombi from the pulmonary arteries. This procedure is typically performed in patients with severe CTEPH, who have failed medical therapy or have significant symptoms. The surgery is performed under cardiopulmonary bypass, and involves the removal of thrombi from the pulmonary arteries, using a combination of surgical and endoscopic techniques.
Key Points
- CTEPH is a rare and underdiagnosed condition, characterized by chronic blood clots in the pulmonary arteries
- The diagnosis of CTEPH requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and hemodynamic measurements
- Treatment options include medical therapy, surgical thromboendarterectomy, and balloon pulmonary angioplasty
- Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of chronic thrombi from the pulmonary arteries
- A multidisciplinary approach is essential for the accurate diagnosis and management of CTEPH
In conclusion, CTEPH is a complex and challenging condition, requiring a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and management. By understanding the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment options for CTEPH, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
What is the primary cause of CTEPH?
+The primary cause of CTEPH is the presence of chronic blood clots in the pulmonary arteries, which can occur after a pulmonary embolism.
How is CTEPH diagnosed?
+CTEPH is diagnosed using a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and hemodynamic measurements, including right heart catheterization and pulmonary angiography.
What are the treatment options for CTEPH?
+Treatment options for CTEPH include medical therapy, surgical thromboendarterectomy, and balloon pulmonary angioplasty, aimed at reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.