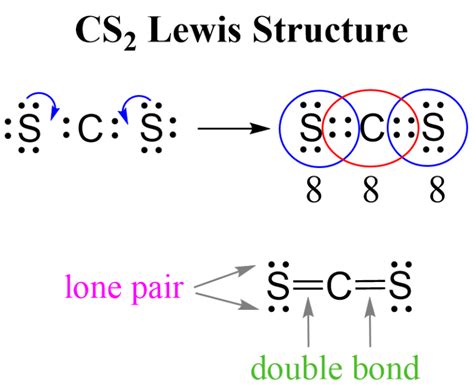
Understanding the Lewis structure of CS2 (carbon disulfide) is crucial for grasping its chemical properties and reactivity. The Lewis structure is a graphical representation of the molecule's valence electrons and bonding. Here are five key tips for drawing the Lewis structure of CS2:
Tip 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
To begin drawing the Lewis structure of CS2, we first need to calculate the total number of valence electrons. Carbon © has 4 valence electrons, and each sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons. Since there are two sulfur atoms, we multiply the number of valence electrons in one sulfur atom by 2. The total number of valence electrons is 4 (from C) + 6*2 (from the two S atoms) = 4 + 12 = 16 valence electrons.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which participate in chemical bonding. In the case of CS2, the valence electrons of carbon and sulfur are involved in forming the covalent bonds that hold the molecule together.
| Atom | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 4 |
| Sulfur (S) | 6 |
Tip 2: Draw the Skeleton of the Molecule
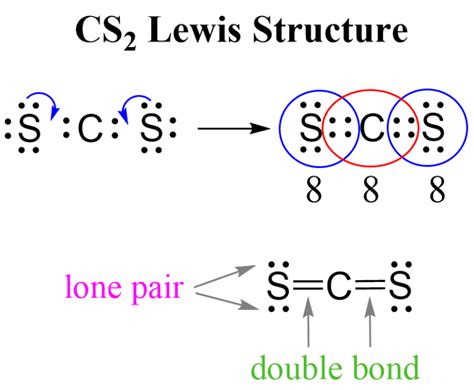
With the total number of valence electrons in mind, the next step is to draw the skeleton of the CS2 molecule. The carbon atom is typically placed at the center, and the two sulfur atoms are arranged around it. In CS2, the carbon forms double bonds with each sulfur atom, resulting in a linear molecule.
Skeleton Structure
The skeleton structure of CS2, with carbon at the center and sulfur atoms on either side, provides a foundation for distributing the valence electrons. Given the linear geometry, the molecule’s shape is influenced by the double bonds between carbon and sulfur.
Linear Geometry: The arrangement of atoms in CS2, with carbon bonded to two sulfur atoms, leads to a linear shape. This geometry minimizes electron pair repulsions and is consistent with the molecule's observed properties.
Tip 3: Distribute the Valence Electrons
Distributing the valence electrons around the atoms in the CS2 molecule is crucial for completing the Lewis structure. Each atom must have an octet (eight electrons in its valence shell) to achieve stability, except for hydrogen, which seeks two electrons. In CS2, the carbon forms two double bonds with the sulfur atoms to fulfill this requirement.
Distributing Electrons
The distribution of electrons in CS2 involves placing four electrons in each of the double bonds between carbon and sulfur. This leaves each sulfur atom with a lone pair of electrons, satisfying the octet rule for both sulfur atoms and the carbon atom.
| Atom | Bonding Electrons | Lone Pair Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 8 (4 in double bonds) | 0 |
| Sulfur (S) | 4 (in double bond) | 4 |
Key Points
- The Lewis structure of CS2 involves a central carbon atom bonded to two sulfur atoms via double bonds.
- Each sulfur atom has a lone pair of electrons in addition to the double bond with carbon.
- The molecule's linear geometry minimizes electron pair repulsions.
- The distribution of valence electrons satisfies the octet rule for all atoms in the molecule.
- Understanding the Lewis structure of CS2 is essential for predicting its chemical behavior and properties.
Tip 4: Check for Octet Rule Satisfaction
After distributing the electrons, it’s crucial to verify that each atom in the CS2 molecule satisfies the octet rule. The carbon atom, with its four bonds (two double bonds), and each sulfur atom, with its four bonds (one double bond and two lone pairs), must have eight electrons in their valence shells.
Octet Rule Satisfaction
The octet rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry stating that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to have eight electrons in their valence shell, thereby achieving the electron configuration of a noble gas. In CS2, the satisfaction of the octet rule by all atoms indicates a stable molecule.
Stability: The stability of the CS2 molecule is reflected in its ability to satisfy the octet rule for all atoms involved. This stability is a key factor in the molecule's chemical properties and reactivity.
Tip 5: Consider Formal Charges
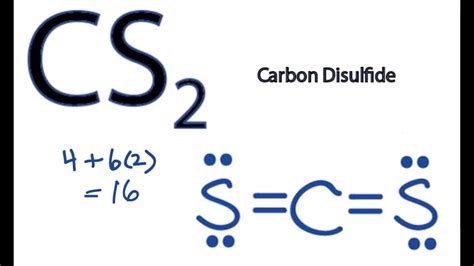
Finally, when drawing the Lewis structure of CS2, consider the formal charges on each atom. Formal charge is calculated by subtracting the number of non-bonding electrons and half the number of bonding electrons from the total number of valence electrons of an atom. In an ideal situation, the formal charge on each atom should be as close to zero as possible.
Formal Charges in CS2
In the case of CS2, the formal charges can be calculated for each atom. The goal is to have a structure where the formal charges are minimized, ideally zero, to represent the most stable and realistic distribution of electrons.
What is the significance of the Lewis structure in understanding CS2?
+The Lewis structure of CS2 provides insight into the molecule's bonding, shape, and chemical properties. It helps in understanding how the valence electrons are distributed and how the molecule behaves in different chemical environments.
How does the linear geometry of CS2 affect its properties?
+The linear geometry of CS2, resulting from the double bonds between carbon and sulfur, influences the molecule's polarity, reactivity, and physical properties such as its boiling point and solubility.
What role do lone pairs play in the Lewis structure of CS2?
+Lone pairs on the sulfur atoms in CS2 contribute to the molecule's stability by fulfilling the octet rule for sulfur. They also play a role in the molecule's reactivity and its ability to form bonds with other molecules.
In conclusion, drawing the Lewis structure of CS2 involves several key steps, from calculating the total number of valence electrons to considering formal charges. Understanding the Lewis structure is essential for predicting the chemical behavior and properties of CS2, making it a fundamental concept in chemistry.