When it comes to higher education, one of the most fundamental concepts is the credit hour. Essentially, a credit hour is a unit of measurement that represents the amount of time a student spends in a particular course or activity. The concept of credit hours is crucial in understanding how academic programs are structured, how student progress is tracked, and how institutions of higher learning operate. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of credit hours, exploring how they are earned, calculated, and utilized in various academic contexts.
Key Points
- Credit hours are a standardized measure of academic work, representing one hour of classroom instruction and two hours of outside work per week.
- Students can earn credit hours through various means, including coursework, internships, and examinations.
- The calculation of credit hours involves considering factors such as classroom time, outside work, and faculty instruction.
- Credit hours play a crucial role in determining student progress, academic standing, and graduation eligibility.
- Institutions of higher learning have varying policies regarding credit hour requirements, transfer credits, and course equivalencies.
Understanding Credit Hours: A Fundamental Concept

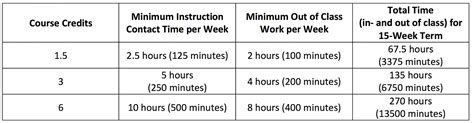
Credit hours are the building blocks of academic programs, allowing students to progress through their studies in a structured and organized manner. The concept of credit hours is based on the idea that students should spend a certain amount of time engaged in academic activities, including attending classes, completing assignments, and participating in discussions. Generally, one credit hour represents one hour of classroom instruction and two hours of outside work per week, totaling three hours of academic engagement per week. This standardization enables institutions to ensure that students are meeting the necessary academic requirements and making satisfactory progress towards their degree.
Credit Hour Calculation and Earned Credits
The calculation of credit hours involves considering several factors, including classroom time, outside work, and faculty instruction. For example, a course that meets for three hours of classroom instruction per week and requires an additional six hours of outside work per week would typically be worth three credit hours. Students can earn credit hours through various means, including coursework, internships, and examinations. The number of credit hours earned per course or activity is usually determined by the institution and is based on the amount of academic work required.
| Credit Hour Category | Definition | Credit Hour Value |
|---|---|---|
| Lecture | Classroom instruction | 1-3 credit hours |
| Lab | Hands-on experimentation or practice | 1-2 credit hours |
| Internship | Practical work experience | 1-6 credit hours |
| Exam | Assessment of knowledge or skills | 1-3 credit hours |

Credit Hours and Academic Progress

Credit hours play a crucial role in determining student progress, academic standing, and graduation eligibility. Students typically need to earn a minimum number of credit hours to progress through their academic program, with most institutions requiring a minimum of 120 credit hours for a bachelor’s degree. The accumulation of credit hours also helps institutions track student progress, identify areas where students may need additional support, and ensure that students are meeting the necessary academic requirements.
Transfer Credits and Course Equivalencies
Institutions of higher learning have varying policies regarding credit hour requirements, transfer credits, and course equivalencies. Students who transfer from one institution to another may be able to transfer some or all of their earned credit hours, depending on the policies of the receiving institution. Course equivalencies, on the other hand, refer to the process of determining whether a course taken at one institution is equivalent to a course offered at another institution. This process helps ensure that students are not required to repeat coursework and can progress through their academic program efficiently.
How are credit hours calculated?
+Credit hours are calculated based on the amount of academic work required, including classroom instruction and outside work. Generally, one credit hour represents one hour of classroom instruction and two hours of outside work per week.
Can credit hours be transferred between institutions?
+Yes, credit hours can be transferred between institutions, depending on the policies of the receiving institution. Students should check with the receiving institution to determine which credit hours are transferable and how they will be applied to their academic program.
How do credit hours affect academic progress?
+Credit hours play a crucial role in determining student progress, academic standing, and graduation eligibility. Students typically need to earn a minimum number of credit hours to progress through their academic program and meet the necessary academic requirements.
In conclusion, credit hours are a fundamental concept in higher education, representing a standardized measure of academic work and progress. By understanding how credit hours are earned, calculated, and utilized, students and institutions can work together to ensure that academic programs are structured, delivered, and completed in a way that meets the needs of all stakeholders. As the higher education landscape continues to evolve, the concept of credit hours will remain a critical component of academic programs, providing a framework for measuring student progress, academic achievement, and institutional effectiveness.