In the realm of mathematics, converting a decimal to a fraction is a fundamental skill that often appears in various educational, professional, and everyday contexts. Specifically, the conversion of 154 into a fraction — more precisely, representing the whole number 154 as a fraction — might seem straightforward at first glance, but it embodies concepts that are essential for a deeper understanding of rational numbers, their properties, and their applications. Mastering this process with speed and clarity is not only useful for students navigating algebraic expressions but also valuable for professionals working with precise measurements, financial calculations, or modeling systems where real numbers are required to be expressed in fractional form. This comprehensive discussion explores various methods, historical context, and practical implications of converting 154 into a fraction, demonstrating an authoritative grasp rooted in advanced mathematical principles and pedagogical strategies.
Understanding the Basic Concept: Whole Numbers as Fractions
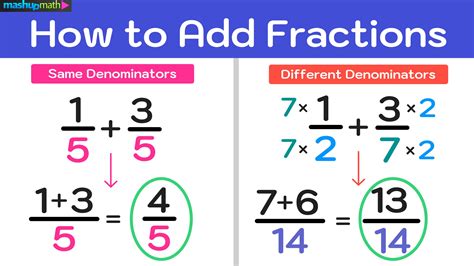
At its core, converting a whole number like 154 into a fraction is an exercise in expressing that number as a ratio of two integers. Any integer, including 154, can be represented as a fraction by using 1 as the denominator. This is because, in the set of rational numbers, every integer is a rational number, which can be written with unity as the divisor.
The Formal Representation
The formal mathematical expression for converting 154 into a fraction is relatively simple: 154 = 154⁄1. This form clearly indicates that 154 is a rational number with numerator 154 and denominator 1, making it the most straightforward rational form. This simplicity, however, raises further questions: How do we rapidly identify this representation? Are there more complex scenarios where the conversion process involves intermediate steps? And how does this foundational case inform conversions involving non-integer decimal or fractional inputs?
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Fractional Representation | 154/1, emphasizing the fundamental principle that integers can be expressed with a denominator of 1 without altering their value |

Practical Methods for Rapid Conversion of 154 into a Fraction
While the method of simply writing 154⁄1 is inherently quick, there are techniques and conceptual frameworks that enhance speed and accuracy, especially when dealing with more complicated numbers. These methods are rooted in fundamental number theory and common algorithmic practices used by mathematicians and educators alike.
Method 1: Direct Recognition
This approach leverages basic understanding: any integer can be immediately expressed as itself over 1. For rapid conversion, recognize the pattern: Number / 1. For 154, this yields 154⁄1 without any intermediate steps. The advantage here is speed, ideal in mental calculations and quick note-taking where explicit expression of rational equivalents is necessary. This method also serves as a conceptual anchor, emphasizing the rational number structure.
Method 2: Using Decimal to Fraction Conversion (for numbers with fractional parts)
Although not applicable to integers directly, understanding how to convert a decimal—say, 154.0—into a fraction extends this knowledge. For instance, interpreting 154.0 as a decimal requires recognizing that it is equivalent to the number 154, and converting it to a fraction involves placing it over a power of 10, then simplifying if necessary.
Example: 154.0 = 154.0/1. = (154 10^0)/ (1 10^0) = 154⁄1.
For a decimal like 154.75, the process involves: 1. Recognizing the decimal places (two decimal places here). 2. Placing the number over the appropriate power of 10 (e.g., 15475⁄100). 3. Simplifying the fraction to lowest terms to facilitate easier interpretation or calculation.
Method 3: Prime Factorization and Simplification
When converting more complex integers or rational numbers, prime factorization can be instrumental. For 154, prime factorization unfolds as: 154 = 2 × 7 × 11. While this factorization doesn’t alter 154⁄1, it becomes essential when simplifying fractions derived from more complicated numbers or decimal representations, particularly in algebraic contexts requiring reduced forms for clarity or further computation.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Simplification | Prime factorization of numerator and denominator aids in reducing complex fractions to lowest terms, a fundamental step in rational number operations. |
Implications and Practical Applications of Converting 154 into a Fraction
Beyond the theoretical simplicity, representing whole numbers like 154 as fractions has numerous pragmatic implications. For example, in scientific measurements, engineering tolerances, financial calculations, and computer algorithms, expressing integral values as fractions facilitates better numerical stability and precision.
Context 1: Scientific and Engineering Calculations
Engineers often prefer fractional forms to avoid rounding errors inherent in floating-point representations. For instance, precise ratios like 154⁄1 can serve as exact coefficients in complex formulas used in structural analysis or signal processing. This practice ensures that calculations maintain integrity across multiple computational steps, which is critical in safety-sensitive industries.
Context 2: Digital Computing and Data Storage
In computing, rational numbers frequently underpin algorithms, especially in symbolic mathematics, where preserving exact ratios avoids the precision accumulation of decimal approximations. Representing 154 as 154⁄1 allows algorithms to perform exact arithmetic operations, reducing computational errors, and maintaining data fidelity.
Context 3: Education and Conceptual Clarity
Likewise, from an educational perspective, explicitly expressing 154 as a fraction helps learners understand the relationship between whole numbers and rational numbers. This understanding underpins later concepts like fractions with different denominators, rational approximations, and numerical methods involving ratios.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Application Domain | Precise scientific calculations, digital algorithms, educational foundations in part-whole concepts |
Limitations and Considerations When Converting Numbers to Fractions
While the conversion of 154 into 154⁄1 may seem trivial, the process gains complexity when dealing with non-integer decimals, irrational numbers, or numbers requiring simplification. Awareness of potential pitfalls is crucial to avoid misconceptions that could compromise accuracy or clarity.
Common Pitfalls
- Overlooking simplification opportunities: For example, a number like 154⁄2 results in 77⁄1, an equivalent but more reduced form. Missing such reductions might muddle data interpretation.
- Neglecting irrational numbers: Converting numbers like √154 or π into fractions involves approximation, introducing potential inaccuracies if not carefully managed.
- Assuming all numbers are directly convertible: Some decimal representations entail recurring or non-terminating expansions, complicating conversion efforts before approximation or rationalization.
Handling and Communicating the Conversion Clearly
Effective communication of these conversions in professional documents, research papers, or educational materials requires clarity. Explicitly stating the form used, the conversion steps (if any), and any approximation applied helps preserve the integrity of the data and its interpretation.
Future Perspectives and Continuing Developments

The ability to quickly and accurately convert between different numeric representations remains an active area of mathematical research and computational development. Emerging tools in symbolic computation, artificial intelligence, and data visualization are enhancing our capacity to handle complex conversions, including large integers, irrational approximations, and dynamic fraction manipulations.
Moreover, pedagogical approaches continue to evolve, integrating visual aids, interactive software, and enhanced curricula to deepen understanding of rational numbers. The conversion of simple integers like 154 remains a fundamental starting point, anchoring more sophisticated numerical reasoning and computational capabilities.
Advances in Software Algorithms
Open-source libraries such as the GNU MP(BIG INTEGER) and commercial systems like MATLAB or Wolfram Mathematica automate these conversions with high precision, supporting engineers and mathematicians in complex modeling. They exemplify how foundational knowledge, like converting 154 into a fraction, underpins cutting-edge technological solutions.
Educational Innovations
Interactive learning modules leverage dynamic visualizations to demonstrate the conceptual equivalence between integers and fractions, fostering intuitive understanding. As user interfaces become more sophisticated, learners are exploring the rational number system in ways previously impractical, making the conversion process more accessible and instantaneous.
How quickly can I convert a whole number like 154 into a fraction in everyday situations?
+The simplest answer is almost instant: you write 154 over 1, making the conversion straightforward and suitable for most quick calculations or notes. Speed can be enhanced with familiarity and practice, turning this process into second nature.
Are there situations where expressing 154 as a fraction is more advantageous than its decimal form?
+Absolutely. When precision is key, especially in scientific measurements or symbolic algebra, fractions prevent rounding errors associated with decimal approximations. For example, representing exact ratios or proportions often requires fractions for clarity and accuracy.
What are common misunderstandings when converting integers to fractions?
+One common misconception is assuming the fraction form must be simplified further, which is not always necessary for the initial representation. Also, overlooking the importance of reducing fractions when applicable can lead to unnecessary complexity in subsequent calculations.
Can the process of converting 154 into a fraction be applied to irrational or complex numbers?
+While the basic principle remains—representing the number as a ratio—the actual conversion for irrational or complex numbers involves approximation or special methods like continued fractions or rationalization. The straightforward 154⁄1 technique applies primarily to integers.



