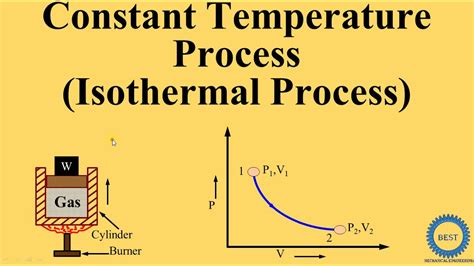
Constant temperature is a crucial factor in various industries, including science, engineering, and healthcare. Maintaining a consistent temperature is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experiments, manufacturing processes, and medical treatments. In this article, we will explore 5 ways constant temperature is used in different fields, highlighting its importance and applications.
Key Points
- Constant temperature is essential for scientific research and experimentation
- Temperature control is critical in manufacturing processes, such as pharmaceutical production
- Constant temperature is used in medical treatments, including cancer therapy and vaccine storage
- Temperature-controlled environments are necessary for food storage and transportation
- Constant temperature is used in engineering applications, such as materials testing and calibration
Scientific Research and Experimentation
In scientific research, constant temperature is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experiments. Many chemical reactions and biological processes are temperature-dependent, and even small changes in temperature can affect the outcome of an experiment. For example, in molecular biology, enzymes are highly sensitive to temperature, and a constant temperature is necessary for optimal enzyme activity. In addition, many scientific instruments, such as spectrophotometers and microscopes, require a constant temperature to function accurately.
Temperature control is also essential in materials science, where the properties of materials can change significantly with temperature. For instance, the strength and conductivity of metals can vary greatly with temperature, and a constant temperature is necessary for accurate testing and characterization. Furthermore, in nanotechnology, temperature control is critical for the synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles, which are highly sensitive to temperature.
Temperature Control in Scientific Instruments
Many scientific instruments, such as thermometers, calorimeters, and spectrometers, require a constant temperature to function accurately. These instruments are designed to measure physical properties, such as temperature, heat capacity, and spectral absorbance, and a constant temperature is necessary for reliable measurements. In addition, some instruments, such as cryostats and incubators, are designed to maintain a constant temperature over a wide range, from cryogenic temperatures to elevated temperatures.
| Instrument | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Thermometer | -200°C to 1000°C |
| Calorimeter | -100°C to 500°C |
| Spectrometer | -50°C to 200°C |

Manufacturing Processes
In manufacturing processes, temperature control is critical for ensuring the quality and consistency of products. Many industrial processes, such as chemical synthesis, polymerization, and metal casting, require a constant temperature to produce high-quality products. For example, in pharmaceutical production, temperature control is essential for ensuring the stability and efficacy of drugs. In addition, in food processing, temperature control is necessary for preventing spoilage and ensuring food safety.
Temperature control is also important in materials processing, such as metalworking and ceramics production. In these processes, temperature control is necessary for controlling the microstructure and properties of materials, which can affect their strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Furthermore, in electronics manufacturing, temperature control is critical for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic components, such as semiconductors and circuits.
Temperature Control in Pharmaceutical Production
In pharmaceutical production, temperature control is essential for ensuring the stability and efficacy of drugs. Many pharmaceuticals are sensitive to temperature, and even small changes in temperature can affect their potency and shelf life. For example, vaccines are highly sensitive to temperature, and a constant temperature is necessary for maintaining their potency and preventing degradation. In addition, some pharmaceuticals, such as insulin and antibiotics, require a constant temperature to prevent degradation and ensure their efficacy.
Medical Treatments
In medical treatments, constant temperature is used to prevent infection, promote healing, and improve patient outcomes. For example, in cancer therapy, hyperthermia (elevated temperature) is used to kill cancer cells, while hypothermia (reduced temperature) is used to prevent tissue damage during surgery. In addition, in vaccine storage, a constant temperature is necessary for maintaining the potency and preventing degradation of vaccines.
Temperature control is also important in medical imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). These imaging modalities require a constant temperature to function accurately and produce high-quality images. Furthermore, in medical devices, such as pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, temperature control is critical for ensuring their reliability and performance.
Temperature Control in Cancer Therapy
In cancer therapy, hyperthermia is used to kill cancer cells, while hypothermia is used to prevent tissue damage during surgery. Hyperthermia involves heating the tumor to a high temperature, typically above 40°C, to kill cancer cells, while hypothermia involves cooling the tumor to a low temperature, typically below 20°C, to prevent tissue damage. Temperature control is critical in these treatments, as excessive heat or cold can cause tissue damage and affect patient outcomes.
| Treatment | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Hyperthermia | 40°C to 45°C |
| Hypothermia | 20°C to 30°C |
Food Storage and Transportation
In food storage and transportation, temperature control is necessary for preventing spoilage and ensuring food safety. Many foods, such as meat, dairy products, and fruits, are sensitive to temperature, and even small changes in temperature can affect their quality and safety. For example, in refrigerated transportation, a constant temperature is necessary for maintaining the quality and safety of perishable foods, such as meat and dairy products.
Temperature control is also important in food processing, such as canning and freezing. In these processes, temperature control is necessary for preventing spoilage and ensuring food safety. Furthermore, in food storage, temperature control is critical for maintaining the quality and safety of foods, such as grains, nuts, and dried fruits.
Temperature Control in Food Storage
In food storage, temperature control is necessary for maintaining the quality and safety of foods. Many foods, such as grains, nuts, and dried fruits, are sensitive to temperature, and even small changes in temperature can affect their quality and safety. For example, in grain storage, a constant temperature is necessary for preventing moisture accumulation and spoilage, while in nut storage, a constant temperature is necessary for preventing oil oxidation and rancidity.
What is the importance of constant temperature in scientific research?
+Constant temperature is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experiments, as many chemical reactions and biological processes are temperature-dependent.
How is temperature control used in manufacturing processes?
+Temperature control is critical in manufacturing processes, such as chemical synthesis, polymerization, and metal casting, to produce high-quality products.
What is the role of constant temperature in medical treatments?
+Constant temperature is used in medical treatments, such as cancer therapy and vaccine storage, to prevent infection, promote healing, and improve patient outcomes.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the importance of constant temperature in various industries, including scientific research, manufacturing processes, medical treatments, food storage, and transportation. Learn how temperature control is critical for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and quality of products and treatments.”