The commutative property is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and arithmetic, which states that the order of the numbers being added or multiplied does not change the result. This property is crucial for understanding and simplifying various mathematical expressions and equations. In this article, we will delve into the commutative property, its definition, examples, and significance in different mathematical operations.
Key Points
- The commutative property applies to addition and multiplication, stating that the order of the numbers does not affect the result.
- For addition, the commutative property can be represented as a + b = b + a, where a and b are any real numbers.
- For multiplication, the property is represented as a * b = b * a, where a and b are any real numbers.
- The commutative property does not apply to subtraction or division, as the order of numbers changes the result in these operations.
- Understanding and applying the commutative property is essential for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
Commutative Property of Addition
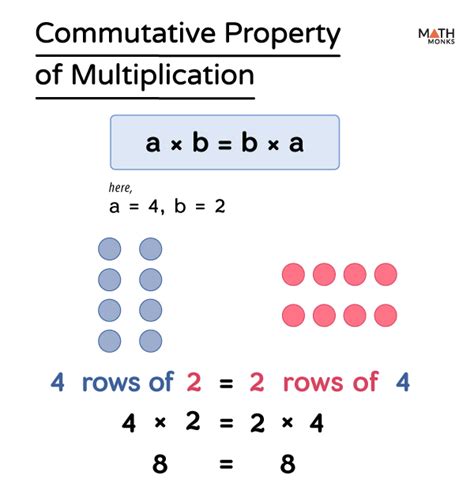
The commutative property of addition states that when we add two numbers, the order in which we add them does not change the result. This can be mathematically represented as a + b = b + a. For example, if we take the numbers 3 and 5, according to the commutative property of addition, 3 + 5 = 5 + 3, both resulting in 8. This property helps in simplifying addition problems by allowing the flexibility to add numbers in any order that makes the calculation easier.
Real-World Application of Commutative Property in Addition
In everyday life, the commutative property of addition is applied naturally without much thought. For instance, if you have 3 boxes of pens and your friend gives you 5 more boxes, the total number of boxes you have is the same regardless of how you count them. You can either start with the 3 boxes you already have and add the 5 your friend gave you (3 + 5), or you can start with the 5 boxes your friend gave you and then add the 3 you already had (5 + 3). In both cases, you end up with 8 boxes of pens, demonstrating the commutative property in a real-world scenario.
| Numbers | Operation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 3, 5 | 3 + 5 | 8 |
| 3, 5 | 5 + 3 | 8 |

Commutative Property of Multiplication
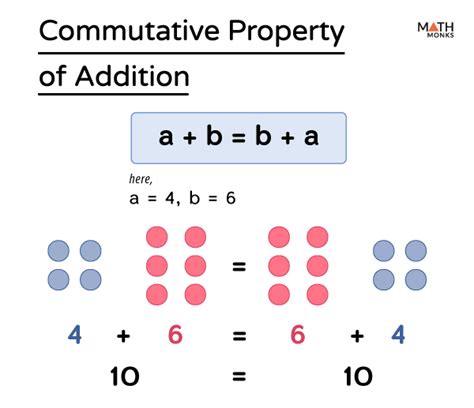
Similarly, the commutative property of multiplication states that the order in which we multiply numbers does not affect the product. Mathematically, this is represented as a * b = b * a. For example, using the numbers 4 and 6, we have 4 * 6 = 6 * 4, both resulting in 24. This property is particularly useful in algebra and in simplifying expressions involving multiplication.
Importance of Commutative Property in Algebra
In algebra, the commutative property of multiplication is essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations. It allows for the regrouping of terms in a way that makes the calculation simpler. For instance, when simplifying the expression 2x * 3y, we can rearrange it to 3y * 2x without changing the result, thanks to the commutative property. This flexibility is crucial in manipulating algebraic expressions to solve for unknown variables.
Limitations of the Commutative Property
While the commutative property is useful for addition and multiplication, it does not apply to subtraction or division. For these operations, the order of the numbers does change the result. For example, 10 - 3 is not equal to 3 - 10, and 10 / 2 is not the same as 2 / 10. This limitation highlights the importance of understanding the specific properties of each mathematical operation to apply them correctly.
What is the commutative property in mathematics?
+The commutative property is a mathematical principle that states the order of the numbers being added or multiplied does not change the result. It applies to addition and multiplication but not to subtraction or division.
Can the commutative property be applied to all mathematical operations?
+No, the commutative property only applies to addition and multiplication. It does not apply to subtraction or division, as the order of numbers changes the result in these operations.
What is an example of the commutative property in real life?
+A simple example is combining boxes of items. If you have 3 boxes of one item and receive 5 more, the total number of boxes is the same whether you count the ones you have first and then add the new ones (3 + 5) or start with the new ones and add the ones you already have (5 + 3), both resulting in 8 boxes.
In conclusion, the commutative property is a foundational principle in mathematics that underpins many arithmetic and algebraic operations. By understanding and applying this property, individuals can simplify complex expressions, solve equations more efficiently, and develop a deeper appreciation for the structure of mathematics. Its relevance extends beyond academic contexts, influencing how we approach problems and think about quantities in everyday life.