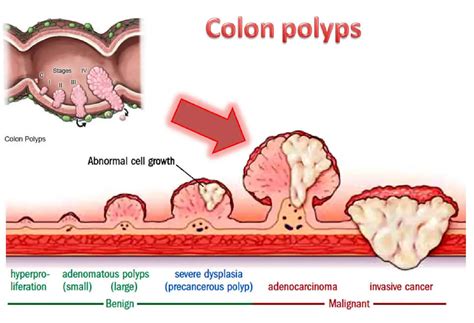
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the large intestine (colon) or the rectum. It is one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, and it is estimated that over 100,000 new cases of colon cancer will be diagnosed in the coming year. One of the primary ways that colon cancer develops is through the formation of polyps, which are small growths on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. In this article, we will explore the relationship between colon cancer and polyps, and provide information on the different types of polyps, their symptoms, and treatment options.
Key Points
- Colon cancer is a type of cancer that affects the large intestine (colon) or the rectum
- Polyps are small growths on the inner lining of the colon or rectum that can develop into cancer
- There are several types of polyps, including adenomatous polyps, hyperplastic polyps, and inflammatory polyps
- Symptoms of colon cancer include blood in the stool, changes in bowel movements, and abdominal pain
- Treatment options for colon cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy
What are Polyps?
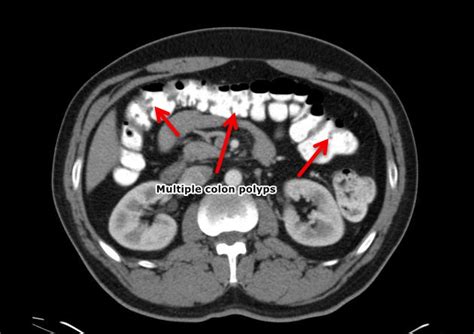
Polyps are small growths on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. They are usually benign (non-cancerous), but they can develop into cancer over time. There are several types of polyps, including:
- Adenomatous polyps: These are the most common type of polyp and have the potential to develop into cancer
- Hyperplastic polyps: These are small and usually harmless, but can sometimes develop into cancer
- Inflammatory polyps: These are caused by inflammation in the colon or rectum and are usually harmless
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of colon cancer is not known, but there are several risk factors that can increase a person’s chance of developing the disease. These include:
- Age: The risk of colon cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 50
- Family history: Having a family history of colon cancer or polyps can increase a person’s risk
- Diet: A diet that is high in red meat and low in fiber can increase the risk of colon cancer
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of colon cancer
- Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of colon cancer
| Type of Polyp | Description |
|---|---|
| Adenomatous Polyp | A type of polyp that has the potential to develop into cancer |
| Hyperplastic Polyp | A small, usually harmless polyp that can sometimes develop into cancer |
| Inflammatory Polyp | A type of polyp caused by inflammation in the colon or rectum |
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
The symptoms of colon cancer can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor. Common symptoms include:
- Blood in the stool: This can be a sign of colon cancer, especially if the blood is mixed with stool or if there is a significant amount of blood
- Changes in bowel movements: Colon cancer can cause changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the abdomen can be a symptom of colon cancer, especially if the pain is severe or persistent
- Weakness or fatigue: Colon cancer can cause weakness or fatigue, especially if the cancer is advanced
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of colon cancer
Treatment Options
Treatment options for colon cancer depend on the stage and location of the cancer. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgery is often the first line of treatment for colon cancer, and can involve removing the tumor and surrounding tissue
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy can be used to treat colon cancer that has spread to other parts of the body
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy can be used to treat colon cancer that has spread to other parts of the body
What is the best way to prevent colon cancer?
+The best way to prevent colon cancer is through regular screening and removal of polyps. A healthy diet and regular exercise can also help reduce the risk of colon cancer.
What are the symptoms of colon cancer?
+The symptoms of colon cancer can include blood in the stool, changes in bowel movements, abdominal pain, weakness or fatigue, and weight loss.
How is colon cancer diagnosed?
+Colon cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of tests, including a colonoscopy, blood tests, and imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI.
Meta Description: Learn about the relationship between colon cancer and polyps, including the different types of polyps, symptoms, and treatment options. Understand the importance of regular screening and removal of polyps to prevent colon cancer.