The CL2 Lewis structure, also known as the chlorine molecule, is a covalently bonded molecule consisting of two chlorine atoms. Drawing the Lewis structure for CL2 requires a basic understanding of chemistry and the rules for drawing Lewis structures. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to draw the CL2 Lewis structure using five different methods.
Key Points
- Determine the total number of valence electrons in the CL2 molecule
- Draw the basic structure of the molecule with the two chlorine atoms
- Distribute the valence electrons around the atoms to satisfy the octet rule
- Form a covalent bond between the two chlorine atoms
- Verify that the Lewis structure is stable and satisfies the octet rule for both atoms
Method 1: Using the Octet Rule
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level, which typically consists of eight electrons. To draw the CL2 Lewis structure using the octet rule, start by determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Chlorine has seven valence electrons, so the total number of valence electrons in CL2 is 7 + 7 = 14.
Next, draw the basic structure of the molecule with the two chlorine atoms. Distribute the valence electrons around the atoms, making sure that each atom has eight electrons in its outer energy level. Since chlorine has seven valence electrons, each atom will have three lone pairs and one pair of electrons shared with the other atom.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Lone Pairs | Shared Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 7 | 3 | 1 |
| Cl | 7 | 3 | 1 |
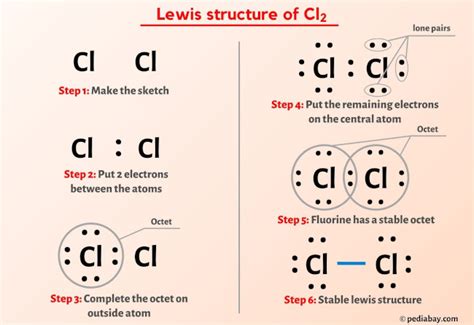
Forming the Covalent Bond
To form a covalent bond between the two chlorine atoms, share one pair of electrons between the atoms. This will result in a single bond between the two atoms, satisfying the octet rule for both chlorine atoms.
Method 2: Using the Total Valence Electrons
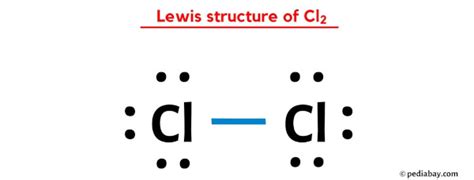
Another way to draw the CL2 Lewis structure is to use the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Start by calculating the total number of valence electrons, which is 14 for CL2. Then, draw the basic structure of the molecule with the two chlorine atoms.
Distribute the valence electrons around the atoms, making sure that each atom has eight electrons in its outer energy level. Since there are 14 valence electrons, each atom will have three lone pairs and one pair of electrons shared with the other atom.
Determining the Bond Order
The bond order of the CL2 molecule can be determined by calculating the number of electrons involved in bonding. Since there is one pair of shared electrons, the bond order is 1.
This method is similar to the first method, but it focuses on the total number of valence electrons rather than the octet rule.
Method 3: Using the Molecular Orbital Theory
The molecular orbital theory provides a more detailed description of the bonding in the CL2 molecule. According to this theory, the atomic orbitals of the individual atoms combine to form molecular orbitals.
The CL2 molecule has a sigma (σ) bonding orbital and a sigma (σ*) antibonding orbital. The sigma bonding orbital is formed by the combination of the two 3p atomic orbitals, resulting in a single bond between the two chlorine atoms.
Interpretation of Molecular Orbitals
The molecular orbital theory provides a more detailed understanding of the bonding in the CL2 molecule. The sigma bonding orbital is responsible for the single covalent bond between the two chlorine atoms.
Method 4: Using the Valence Bond Theory
The valence bond theory provides a description of the bonding in the CL2 molecule in terms of hybridization and overlapping atomic orbitals. According to this theory, the atomic orbitals of the individual atoms hybridize to form sp3 hybrid orbitals.
The sp3 hybrid orbitals overlap to form a single bond between the two chlorine atoms, resulting in a sigma (σ) bond.
Hybridization and Bonding
The valence bond theory provides a detailed description of the hybridization and bonding in the CL2 molecule. The sp3 hybrid orbitals are responsible for the single covalent bond between the two chlorine atoms.
Method 5: Using Chemistry Software
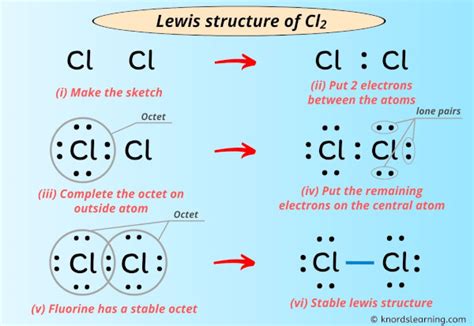
Chemistry software can be used to draw the CL2 Lewis structure and provide a detailed description of the bonding and molecular orbitals. These programs use algorithms to calculate the molecular structure and provide a visual representation of the molecule.
Some popular chemistry software programs include ChemDraw, Chem3D, and Gaussian. These programs can be used to draw the CL2 Lewis structure and provide a detailed understanding of the molecular structure and bonding.
What is the bond order of the CL2 molecule?
+The bond order of the CL2 molecule is 1, indicating a single covalent bond between the two chlorine atoms.
What is the molecular orbital theory?
+The molecular orbital theory provides a detailed description of the bonding in molecules, describing the combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals.
What is the valence bond theory?
+The valence bond theory provides a description of the bonding in molecules in terms of hybridization and overlapping atomic orbitals.
Meta description: Learn how to draw the CL2 Lewis structure using five different methods, including the octet rule, total valence electrons, molecular orbital theory, valence bond theory, and chemistry software.



