When working with chemicals, it's essential to prioritize hand protection to prevent skin irritation, burns, and other injuries. Chemical gloves are a crucial component of personal protective equipment (PPE) in various industries, including laboratories, manufacturing, and healthcare. In this article, we will explore five tips for selecting and using chemical gloves effectively, ensuring a safe working environment and preventing potential hazards.
Understanding Chemical Resistance and Glove Materials

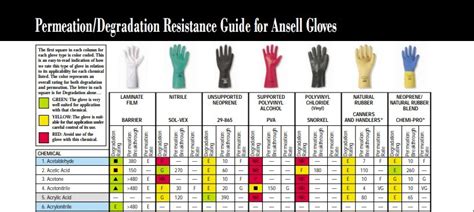
The first step in selecting the right chemical gloves is to understand the types of chemicals you will be working with and their potential hazards. Different glove materials offer varying levels of resistance to chemicals, including latex, nitrile, butyl rubber, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). For example, nitrile gloves are highly resistant to oils, fuels, and many organic solvents, making them an excellent choice for workers in the automotive and aerospace industries. On the other hand, butyl rubber gloves provide superior resistance to highly corrosive substances like acetone and methyl ethyl ketone.
Assessing Glove Thickness and Dexterity
Glove thickness and dexterity are critical factors to consider when selecting chemical gloves. Thicker gloves generally provide better protection against chemicals, but they can compromise dexterity and tactile sensitivity. For tasks requiring precision, such as laboratory work or handling small parts, thinner gloves with enhanced dexterity may be more suitable. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between protection and dexterity to ensure safe and efficient work practices.
| Glove Material | Chemical Resistance | Dexterity |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrile | Excellent resistance to oils and organic solvents | Medium to high |
| Butyl Rubber | Superior resistance to corrosive substances | Medium |
| Latex | Good resistance to water and mild chemicals | High |

Inspection and Maintenance of Chemical Gloves
Regular inspection and maintenance of chemical gloves are crucial to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. Before each use, inspect the gloves for signs of wear, cracks, or punctures, which can compromise their protective properties. After use, clean and dry the gloves according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent the accumulation of chemicals and contaminants. Regularly replacing gloves that are damaged or show signs of degradation is also essential to maintain a safe working environment.
Training and Education on Chemical Glove Use
Proper training and education on chemical glove use are vital to ensure that workers understand the importance of hand protection and how to use gloves effectively. Employers should provide comprehensive training programs that cover the selection, use, and maintenance of chemical gloves, as well as the potential hazards associated with chemical exposure. Workers should also be aware of the limitations of chemical gloves and the need for additional protective equipment, such as goggles and face shields, in certain situations.
Key Points
- Understand the types of chemicals and their potential hazards to select the right glove material
- Assess glove thickness and dexterity to balance protection and efficiency
- Regularly inspect and maintain chemical gloves to ensure their effectiveness
- Provide comprehensive training and education on chemical glove use and safety
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for use, maintenance, and disposal of chemical gloves
Future Developments in Chemical Glove Technology
The development of chemical glove technology is continuously evolving, with manufacturers focusing on creating gloves that offer improved protection, dexterity, and comfort. Advances in materials science have led to the creation of gloves with enhanced chemical resistance, such as gloves coated with nanomaterials or treated with specialized chemical-resistant agents. Additionally, the integration of smart technology, such as sensors and monitoring systems, is being explored to enhance worker safety and provide real-time feedback on glove performance.
In conclusion, selecting and using chemical gloves effectively requires a deep understanding of the chemicals involved, the types of glove materials, and the importance of regular inspection and maintenance. By following these tips and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in chemical glove technology, workers can minimize the risks associated with chemical exposure and ensure a safe working environment.
What are the most common types of chemical gloves?
+The most common types of chemical gloves include nitrile, butyl rubber, latex, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) gloves, each offering varying levels of resistance to different chemicals.
How often should chemical gloves be replaced?
+Chemical gloves should be replaced regularly, depending on the frequency of use, the type of chemicals handled, and the manufacturer's recommendations. Damaged or degraded gloves should be replaced immediately to ensure worker safety.
Can chemical gloves be reused?
+While some chemical gloves can be reused, it's essential to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for cleaning, disinfecting, and reusing gloves. Improper reuse can compromise the protective properties of the gloves and pose a risk to worker safety.
Meta Description: Learn how to select and use chemical gloves effectively to prevent skin irritation and injuries in the workplace. Discover the importance of glove material, thickness, and dexterity, as well as tips for inspection, maintenance, and training.