The concept of electron charge is fundamental to understanding the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level. Electrons, which are among the most basic constituents of matter, carry a negative charge. This characteristic is crucial for the formation of atoms, molecules, and ultimately, all physical substances. Here are five key facts about electron charge that highlight its significance and properties:
Introduction to Electron Charge

Electron charge is a fundamental property of electrons, which are subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. The charge carried by an electron is negative, denoted as -1 elementary charge (e), and it plays a pivotal role in the chemical and physical properties of elements. Understanding electron charge is essential for grasping how atoms interact with each other, including the formation of chemical bonds and the conduction of electricity.
Quantization of Electron Charge
A critical aspect of electron charge is its quantization. The charge of an electron is not variable; it is a fixed quantity, approximately equal to -1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs. This quantization is a cornerstone of quantum mechanics and explains why matter exhibits discrete properties rather than continuous variations. The fixed charge of electrons also underlies the concept of electric current, where the flow of electrons (each carrying a discrete charge) through a conductor enables the transmission of electrical energy.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Charge of an Electron | -1.602 x 10^-19 C |
| Mass of an Electron | 9.109 x 10^-31 kg |
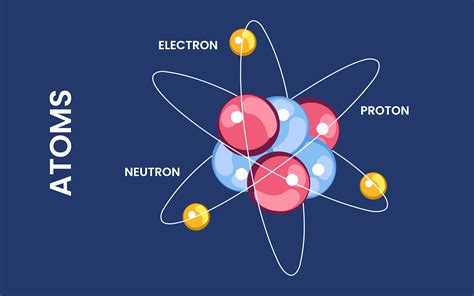
Electron Charge and Atomic Structure
The arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom is determined by their charge. The negative charge of electrons causes them to be attracted to the positively charged nucleus, leading to the formation of electron shells or orbitals. The number of electrons in an atom equals the number of protons in the nucleus, ensuring the atom is electrically neutral. This balance of charges is crucial for the stability of atoms and, by extension, molecules and solids.
Electron Charge in Chemical Bonding
Electron charge plays a central role in chemical bonding, the process by which atoms share or exchange electrons to form molecules. The transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges, leads to ionic bonds. Similarly, the sharing of electron pairs between atoms gives rise to covalent bonds. The polarity of molecules, which affects their physical and chemical properties, is also a consequence of the distribution of electron charge within the molecule.
Key Points
- The electron charge is a fundamental property that determines the chemical and physical behavior of atoms and molecules.
- The quantization of electron charge underlies the discrete nature of matter and energy.
- The arrangement of electrons around the nucleus and their charge determines atomic structure and stability.
- Electron charge is central to the formation of chemical bonds and the polarity of molecules.
- Understanding electron charge is essential for advancing technologies related to electronics, materials science, and chemistry.
Implications of Electron Charge for Technology and Science
The study of electron charge has profound implications for both science and technology. In electronics, the flow of electrons (electric current) is harnessed to power devices and transmit information. The design of materials with specific electrical properties, such as conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, relies on understanding how electron charge affects their behavior. Furthermore, advancements in fields like quantum computing and nanotechnology depend on precise control over electron charge and spin, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of computational power and material properties.
In conclusion, the electron charge is a foundational concept in physics and chemistry, influencing the structure of atoms, the formation of chemical bonds, and the properties of materials. Its quantization and negative value are critical for understanding the discrete nature of matter and the behavior of electrons in various contexts. As science and technology continue to evolve, the importance of electron charge in advancing our understanding of the physical world and developing new technologies will only continue to grow.
What is the significance of the quantization of electron charge?
+The quantization of electron charge means that electrons have a discrete, fixed charge, which is essential for understanding the discrete properties of matter and the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules.
How does electron charge affect chemical bonding?
+Electron charge is central to chemical bonding. The transfer or sharing of electrons between atoms, due to their negative charge, leads to the formation of ionic and covalent bonds, respectively.
What role does electron charge play in the design of electronic devices?
+Understanding electron charge is crucial for the design of electronic devices. The flow of electrons (electric current) is the basis of electronics, and controlling the behavior of electrons in different materials (conductors, semiconductors, insulators) is key to developing functional devices.



