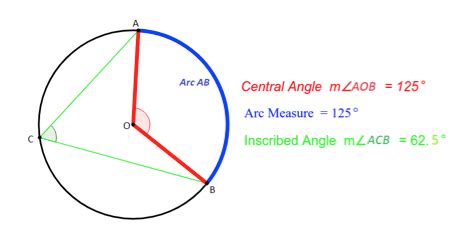
The concept of central angle is a fundamental principle in geometry, particularly in the study of circles and angles. A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle, and its sides pass through the endpoints of an arc. Understanding central angles is crucial for various applications in mathematics, engineering, and design. In this article, we will delve into the significance of central angles, exploring five key aspects that highlight their importance and versatility.
Key Points
- Definition and properties of central angles, including their relationship with arcs and sectors.
- Measurement of central angles in degrees, radians, and gradians, with conversion methods between units.
- Applications of central angles in trigonometry, particularly in solving problems involving right triangles and circular functions.
- Role of central angles in geometry, including the calculation of sector areas, arc lengths, and the properties of inscribed and circumscribed polygons.
- Real-world applications of central angles in engineering, architecture, and design, such as in the construction of bridges, buildings, and mechanical systems.
Understanding Central Angles: Definition and Properties
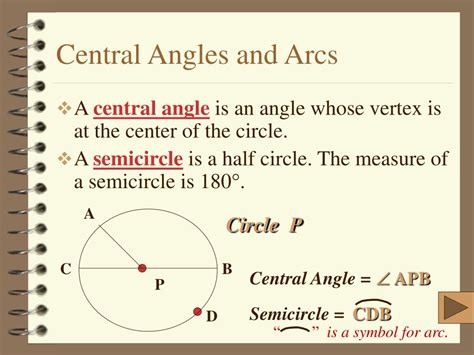
A central angle is defined as an angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle. The sides of the angle intersect the circle at two points, forming an arc. The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc. Central angles are crucial for understanding the properties of circles and sectors. For instance, the area of a sector can be calculated using the formula: Area = (θ/360) * πr^2, where θ is the central angle in degrees, and r is the radius of the circle.
Measurement of Central Angles
Central angles can be measured in degrees, radians, or gradians. The degree is the most common unit, where a full circle is 360 degrees. Radians are used in more advanced mathematical contexts, where 2π radians equal a full circle. Gradians are less commonly used but are based on dividing the circle into 400 equal parts. Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for solving problems involving central angles. For example, to convert degrees to radians, we use the formula: radians = degrees * π / 180.
| Unit | Full Circle Measurement |
|---|---|
| Degree | 360 degrees |
| Radian | 2π radians |
| Gradian | 400 gradians |

Applications in Trigonometry and Geometry
Central angles play a pivotal role in trigonometry, particularly in solving problems involving right triangles and circular functions. The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are defined in terms of the ratios of the sides of a right triangle, which can be related to central angles. In geometry, central angles are used to calculate sector areas, arc lengths, and to understand the properties of inscribed and circumscribed polygons. For instance, the formula for the area of a triangle given two sides and the included angle (Area = 0.5ab*sin©) relies on the concept of central angles.
Real-World Applications
Beyond theoretical mathematics, central angles have numerous practical applications. In engineering, the design of gears, motors, and other mechanical systems relies on the understanding of central angles and circular motion. Architects use central angles to design symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing structures. In navigation, central angles are crucial for determining directions and distances between locations on the Earth’s surface, which is essentially a sphere. Understanding central angles is also vital in the construction of bridges, where the shape and stability of the structure depend on the precise calculation of angles and stresses.
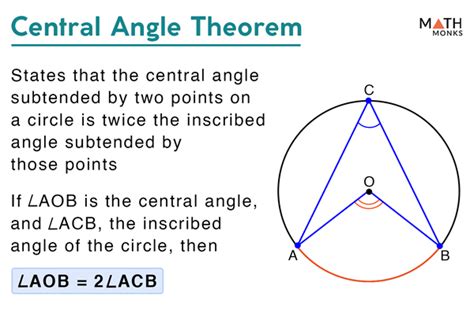
What is the difference between a central angle and an inscribed angle?
+A central angle is formed by two radii of a circle, while an inscribed angle is formed by two chords or secants that intersect on the circle. The central angle is twice the measure of the inscribed angle that intercepts the same arc.
How are central angles used in engineering?
+Central angles are used in the design of mechanical systems, such as gears and motors, where understanding circular motion and angular relationships is critical. They are also applied in the construction of buildings and bridges, where precise angular measurements are necessary for structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
What is the formula for converting degrees to radians?
+The formula to convert degrees to radians is: radians = degrees * π / 180. This conversion is essential for solving problems that involve circular functions and trigonometry in calculus and advanced mathematics.
In conclusion, central angles are a fundamental concept in geometry and trigonometry, with far-reaching applications in various fields. Understanding the definition, properties, and measurement of central angles, as well as their applications in trigonometry, geometry, and real-world scenarios, is essential for advancing in mathematical and scientific studies. By grasping these concepts, individuals can better appreciate the intricacies of circular motion, the design of mechanical systems, and the beauty of geometric shapes that surround us.