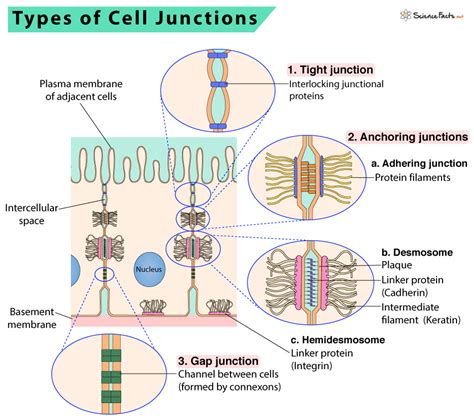
Cell-cell junctions are complex structures that play a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity and facilitating communication between adjacent cells. These junctions are essential for the proper functioning of various tissues and organs, and their dysregulation has been implicated in numerous diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell-cell junctions, exploring their types, functions, and significance in human health and disease.
Cell-cell junctions are specialized regions of the plasma membrane where cells interact with each other, and they can be broadly classified into three main categories: tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions. Each type of junction has distinct structural and functional characteristics, and they work together to maintain tissue homeostasis. Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions, are the most apical junctions and are responsible for maintaining the barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues. Adherens junctions, on the other hand, are involved in cell-cell adhesion and are critical for maintaining tissue structure and organization. Gap junctions, which are composed of connexin proteins, allow for the direct exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between adjacent cells.
Key Points
- Cell-cell junctions are essential for maintaining tissue integrity and facilitating communication between adjacent cells.
- Tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions are the three main types of cell-cell junctions, each with distinct structural and functional characteristics.
- Cell-cell junctions play a critical role in maintaining the barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues, as well as facilitating the exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between cells.
- Dysregulation of cell-cell junctions has been implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders.
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms and regulation of cell-cell junctions is crucial for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of various diseases.
Types of Cell-Cell Junctions
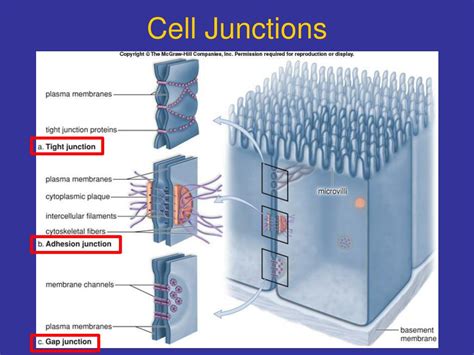
As mentioned earlier, there are three main types of cell-cell junctions: tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions. Tight junctions are the most apical junctions and are responsible for maintaining the barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues. They are composed of a complex network of proteins, including occludin, claudin, and zonulin, which form a tight seal between adjacent cells. Adherens junctions, on the other hand, are involved in cell-cell adhesion and are critical for maintaining tissue structure and organization. They are composed of cadherin proteins, which bind to each other and to the cytoskeleton, providing mechanical strength to tissues. Gap junctions, which are composed of connexin proteins, allow for the direct exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between adjacent cells.
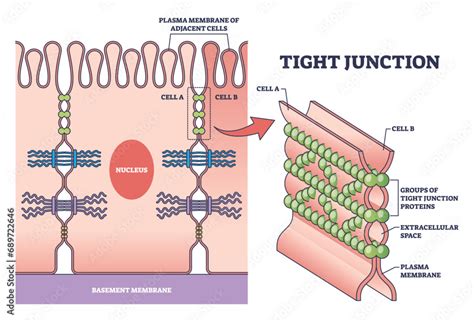
Tight Junctions
Tight junctions are the most apical junctions and are responsible for maintaining the barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues. They are composed of a complex network of proteins, including occludin, claudin, and zonulin, which form a tight seal between adjacent cells. Tight junctions are critical for maintaining the integrity of the epithelial and endothelial tissues, and their dysregulation has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer and inflammatory bowel disease. For example, a study published in the journal Nature found that the loss of tight junctions in epithelial cells leads to increased permeability and inflammation, which can contribute to the development of cancer.
Adherens Junctions
Adherens junctions are involved in cell-cell adhesion and are critical for maintaining tissue structure and organization. They are composed of cadherin proteins, which bind to each other and to the cytoskeleton, providing mechanical strength to tissues. Adherens junctions are also involved in signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, and survival. For example, a study published in the journal Cell found that the activation of adherens junctions in epithelial cells leads to the activation of signaling pathways that regulate cell growth and differentiation.
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are composed of connexin proteins and allow for the direct exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between adjacent cells. Gap junctions are critical for maintaining tissue homeostasis and are involved in various physiological processes, including the regulation of ion balance, metabolism, and cell signaling. For example, a study published in the journal Science found that the loss of gap junctions in cardiac tissue leads to impaired ion balance and cardiac dysfunction.
| Type of Junction | Function |
|---|---|
| Tight Junctions | Maintain barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues |
| Adherens Junctions | Involved in cell-cell adhesion and maintain tissue structure and organization |
| Gap Junctions | Allow for the direct exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between adjacent cells |
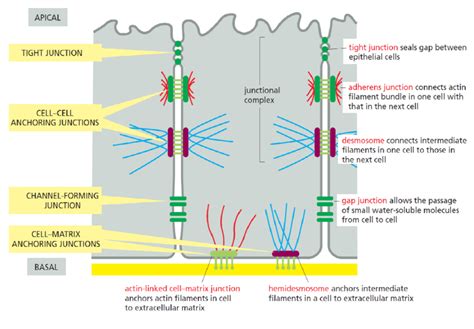
Regulation of Cell-Cell Junctions
The regulation of cell-cell junctions is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of multiple signaling pathways and proteins. Various signaling molecules, including growth factors, cytokines, and hormones, can regulate the formation and maintenance of cell-cell junctions. For example, the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway has been shown to regulate the formation of tight junctions in epithelial cells. Additionally, the regulation of cell-cell junctions is also influenced by the cytoskeleton, which provides mechanical support and regulates the dynamics of junctional proteins.
Signaling Pathways
Various signaling pathways, including the PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK, and NF-κB pathways, can regulate the formation and maintenance of cell-cell junctions. These signaling pathways can activate or inhibit the expression of junctional proteins, as well as regulate their activity and localization. For example, a study published in the journal Journal of Cell Biology found that the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway regulates the formation of tight junctions in epithelial cells by phosphorylating and activating the tight junction protein occludin.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton provides mechanical support and regulates the dynamics of junctional proteins. The actin cytoskeleton, in particular, plays a critical role in regulating the formation and maintenance of cell-cell junctions. For example, a study published in the journal Journal of Cell Science found that the disruption of the actin cytoskeleton leads to impaired tight junction formation and increased permeability in epithelial cells.
What are the main types of cell-cell junctions?
+The main types of cell-cell junctions are tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions.
What is the function of tight junctions?
+Tight junctions are responsible for maintaining the barrier function of epithelial and endothelial tissues.
What is the role of adherens junctions in tissue structure and organization?
+Adherens junctions are involved in cell-cell adhesion and are critical for maintaining tissue structure and organization.
What is the function of gap junctions?
+Gap junctions allow for the direct exchange of ions, metabolites, and signaling molecules between adjacent cells.
How are cell-cell junctions regulated?
+Cell-cell junctions are regulated by various signaling pathways and proteins, as well as the cytoskeleton.
Meta Description: Cell-cell junctions are complex structures that play a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity and facilitating communication between adjacent cells. Learn about the types, functions, and significance of cell-cell junctions in human health and disease. (147 characters)