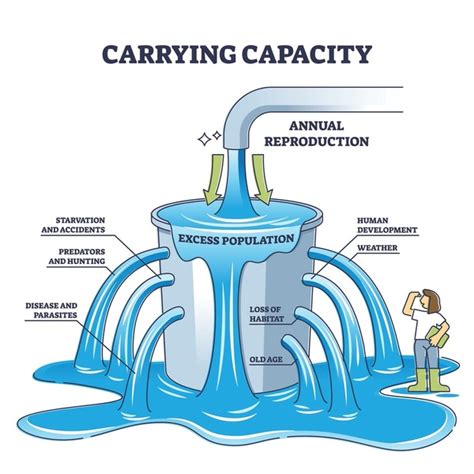
The concept of carrying capacity is a fundamental principle in ecology, referring to the maximum number of individuals of a species that an environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment. This concept is crucial for understanding the dynamics of populations and the impact of human activities on the environment. To illustrate this concept, let's consider a comprehensive example that demonstrates the various aspects of carrying capacity, including its calculation, factors influencing it, and the consequences of exceeding it.
Key Points
- Carrying capacity is the maximum population size an environment can sustain.
- It is influenced by factors such as food availability, habitat size, and environmental conditions.
- Calculating carrying capacity involves understanding the resource limitations of an environment.
- Exceeding carrying capacity can lead to resource depletion, increased mortality, and decreased population growth.
- Understanding and managing carrying capacity is essential for conservation and sustainable development.
Understanding Carrying Capacity

Carrying capacity is determined by the availability of resources such as food, water, shelter, and space. For example, in a forest ecosystem, the carrying capacity for deer might be limited by the availability of food (such as leaves and twigs) and water. If the deer population grows beyond the carrying capacity, the environment may become degraded, leading to reduced food availability, increased competition among deer for the limited resources, and potentially even starvation or the spread of diseases.
Factors Influencing Carrying Capacity
Several factors can influence the carrying capacity of an environment. These include climate change, which can alter the availability of resources such as water and food; habitat destruction, which reduces the available space and resources for species; and pollution, which can degrade the quality of resources like water and air. For instance, a change in climate might reduce the carrying capacity of a forest by altering the types of plants that can grow there, thus affecting the food supply for herbivores.
| Factor | Effect on Carrying Capacity |
|---|---|
| Climate Change | Can reduce resource availability through altered precipitation patterns and temperature changes. |
| Habitat Destruction | Directly reduces available space and resources, leading to a decrease in carrying capacity. |
| Pollution | Can degrade resource quality, making them less usable or even harmful to species. |
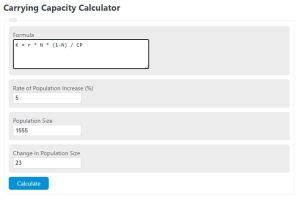
Calculating Carrying Capacity
Calculating carrying capacity involves understanding the resource limitations of an environment and how they impact population growth. This can be done using various models and formulas, such as the logistic growth equation, which describes how a population grows over time in an environment with limited resources. The equation is dN/dt = rN(1 - N/K), where N is the population size, r is the intrinsic growth rate, and K is the carrying capacity.
Consequences of Exceeding Carrying Capacity
When a population exceeds the carrying capacity of its environment, several negative consequences can occur. These include resource depletion, where the population consumes resources faster than they can be replenished; increased mortality, as competition for limited resources leads to malnutrition and disease; and decreased population growth, as the population reaches its limits and may even begin to decline. For example, if a deer population exceeds the carrying capacity of its forest habitat, the deer may overgraze, leading to a decline in vegetation, which in turn can lead to malnutrition and increased mortality among the deer.
Understanding and managing carrying capacity is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable development. By recognizing the limits of an environment and taking steps to maintain populations within those limits, we can work to preserve biodiversity and ensure the long-term health of ecosystems. This requires a nuanced understanding of ecological principles, careful planning, and sometimes, difficult decisions about how to balance human needs with environmental constraints.
What is the significance of carrying capacity in ecology?
+Carrying capacity is significant because it determines the maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely, thus helping in understanding population dynamics and the impact of human activities on the environment.
How does climate change affect carrying capacity?
+Climate change can alter the availability of resources such as food and water, thus affecting the carrying capacity of an environment. It can lead to a reduction in carrying capacity by changing precipitation patterns, altering species distributions, and affecting the quality and quantity of habitats.
What are the consequences of exceeding carrying capacity?
+Exceeding carrying capacity can lead to resource depletion, increased mortality, and decreased population growth. It can also result in environmental degradation, loss of biodiversity, and in severe cases, the collapse of ecosystems.
In conclusion, carrying capacity is a critical concept in ecology that highlights the importance of understanding the limits of environmental resources and the impact of population growth on ecosystems. By recognizing these limits and taking action to manage populations within them, we can work towards a more sustainable future for both human societies and the natural world.