Capital goods are a fundamental component of any economy, playing a crucial role in the production of goods and services. These are durable goods used in the production process to manufacture other goods and services. Unlike consumer goods, which are intended for personal consumption, capital goods are utilized by businesses and organizations to generate revenue and promote economic growth. The concept of capital goods dates back to the early days of industrialization, where the primary focus was on the development and utilization of machinery and equipment to enhance productivity and efficiency.
The definition of capital goods encompasses a wide range of products, including machinery, equipment, buildings, and infrastructure. These goods are characterized by their durability and long lifespan, often requiring significant investment and maintenance. The primary purpose of capital goods is to facilitate the production process, increase productivity, and reduce costs. For instance, a manufacturing company may invest in new machinery to improve production efficiency, while a construction company may purchase heavy equipment to facilitate the building process.
Key Points
- Capital goods are durable goods used in the production process to manufacture other goods and services.
- These goods are utilized by businesses and organizations to generate revenue and promote economic growth.
- Capital goods encompass a wide range of products, including machinery, equipment, buildings, and infrastructure.
- The primary purpose of capital goods is to facilitate the production process, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
- Examples of capital goods include manufacturing machinery, construction equipment, and commercial vehicles.
Characteristics of Capital Goods

Capital goods possess several distinct characteristics that set them apart from consumer goods. One of the primary characteristics is their durability, which enables them to withstand the rigors of repeated use and last for an extended period. Capital goods are also often highly specialized, designed to perform specific tasks or functions within the production process. Additionally, these goods typically require significant investment, maintenance, and repair, which can be a substantial cost for businesses and organizations.
Another key characteristic of capital goods is their ability to increase productivity and efficiency. By investing in capital goods, businesses can streamline their production processes, reduce labor costs, and improve product quality. For example, a company that manufactures textiles may invest in automated weaving machines to increase production capacity and reduce labor costs. Similarly, a logistics company may purchase fleet management software to optimize routes and reduce fuel consumption.
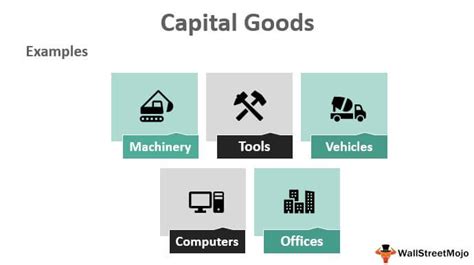
Examples of Capital Goods
Capital goods can be found in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and transportation. Some common examples of capital goods include manufacturing machinery, such as lathes and drills, construction equipment, such as cranes and bulldozers, and commercial vehicles, such as trucks and buses. Other examples include office equipment, such as computers and printers, and agricultural machinery, such as tractors and plows.
| Category | Examples of Capital Goods |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Machinery, equipment, and tools |
| Construction | Heavy equipment, such as cranes and bulldozers |
| Transportation | Commercial vehicles, such as trucks and buses |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and plows |
Economic Importance of Capital Goods

Capital goods play a vital role in the economy, as they are essential for the production of goods and services. The demand for capital goods is derived from the demand for consumer goods, as businesses and organizations invest in capital goods to meet the demand for their products. The production of capital goods also has a multiplier effect on the economy, as it creates jobs, stimulates economic growth, and increases tax revenue.
The economic importance of capital goods is also reflected in their contribution to GDP (Gross Domestic Product). In many countries, the production of capital goods accounts for a significant portion of GDP, highlighting the critical role they play in the economy. Furthermore, the development and utilization of capital goods have been instrumental in driving economic growth and industrialization throughout history.
Impact of Capital Goods on Productivity
The impact of capital goods on productivity is significant, as they enable businesses to streamline their production processes, reduce labor costs, and improve product quality. By investing in capital goods, companies can increase their productivity, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. This, in turn, can lead to increased competitiveness, improved profitability, and enhanced economic growth.
For instance, a study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that the adoption of new technologies and capital goods in the manufacturing sector led to a significant increase in productivity and efficiency. Similarly, a report by the International Labor Organization highlighted the importance of capital goods in improving working conditions, reducing labor costs, and promoting economic growth.
What are capital goods, and how do they differ from consumer goods?
+Capital goods are durable goods used in the production process to manufacture other goods and services, whereas consumer goods are intended for personal consumption. Capital goods are characterized by their durability, specialization, and ability to increase productivity and efficiency.
What are some examples of capital goods, and how are they used in different industries?
+Examples of capital goods include manufacturing machinery, construction equipment, commercial vehicles, and agricultural machinery. These goods are used in various industries, such as manufacturing, construction, transportation, and agriculture, to facilitate the production process, increase productivity, and reduce costs.
How do capital goods contribute to economic growth and productivity?
+Capital goods play a vital role in the economy, as they are essential for the production of goods and services. The production of capital goods has a multiplier effect on the economy, creating jobs, stimulating economic growth, and increasing tax revenue. By investing in capital goods, businesses can increase their productivity, reduce waste, and improve efficiency, leading to increased competitiveness, improved profitability, and enhanced economic growth.
In conclusion, capital goods are a critical component of any economy, enabling businesses and organizations to produce goods and services efficiently and effectively. The definition, characteristics, and examples of capital goods highlight their importance in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and transportation. By understanding the role of capital goods in the economy and their impact on productivity, businesses and policymakers can make informed decisions to promote economic growth, improve efficiency, and increase competitiveness.