Cancer, a term that encompasses a broad range of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells, affects millions of people worldwide. The complexity and variability of cancer types, coupled with ongoing research and advancements in medical science, mean that understanding cancer requires a multifaceted approach. This article aims to delve into key aspects of cancer, providing insights into its prevalence, types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest research findings.
Understanding Cancer: Prevalence and Impact

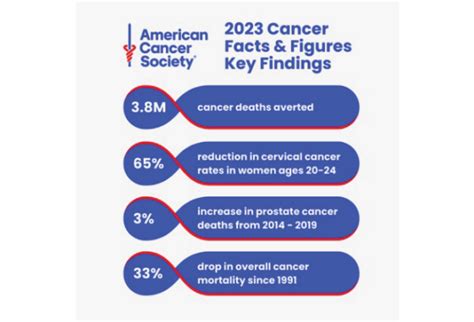
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, with the World Health Organization (WHO) reporting that it was responsible for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020. The prevalence of cancer varies significantly across different regions, with factors such as lifestyle, environmental exposures, and access to healthcare playing crucial roles. For instance, lung, breast, and colorectal cancers are among the most common types worldwide, each having distinct risk factors and screening methods. The economic burden of cancer is also substantial, with costs including not only treatment expenses but also lost productivity and the impact on families and communities.
Key Points
- Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, with nearly 10 million deaths in 2020.
- The prevalence of cancer varies by region, influenced by lifestyle, environment, and healthcare access.
- Lung, breast, and colorectal cancers are among the most common types globally.
- Early detection and screening can significantly improve survival rates for many cancer types.
- Research into cancer causes, prevention, and treatment is ongoing, with a focus on personalized medicine and immunotherapy.
Cancer Types and Risk Factors
There are over 100 different types of cancer, each with its unique set of risk factors and characteristics. For example, tobacco use is a major risk factor for lung cancer, while genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection strategies. Furthermore, certain infections, like human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B, can lead to specific types of cancer, highlighting the importance of vaccination and infection control measures.
| Cancer Type | Risk Factors | Screening/Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | Tobacco use, exposure to radon and asbestos | Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) |
| Breast Cancer | Genetic mutations (BRCA1, BRCA2), family history, radiation exposure | Mammography, clinical breast exam, MRI |
| Colorectal Cancer | Family history, diet low in fiber and high in fat, lack of physical activity | Colonoscopy, fecal occult blood test (FOBT), sigmoidoscopy |

Treatment Options and Research Directions
Treatment for cancer depends on the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health. Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, has emerged as a promising area of research, with checkpoint inhibitors being one of the notable developments. Additionally, there is a growing focus on precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to the specific genetic characteristics of the patient’s cancer.
Future Perspectives and Challenges
Despite the progress made in understanding and treating cancer, significant challenges remain. These include the development of drug resistance, the high cost of new therapies, and the need for more effective treatments for certain types of cancer. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges through innovative approaches, such as combining different therapies, exploring new targets for treatment, and improving our understanding of the complex biology of cancer. Moreover, there is a growing recognition of the importance of addressing the social determinants of health and ensuring equitable access to cancer care and preventive services globally.
What are the most common symptoms of cancer?
+Common symptoms include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, pain, and changes in the skin. However, many cancers may not show symptoms in the early stages, emphasizing the importance of screening and early detection.
How can cancer be prevented?
+Prevention strategies include avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, being physically active, and protecting against certain infections through vaccination. Early screening and detection are also crucial for reducing the risk of cancer-related deaths.
What role does genetics play in cancer development?
+Genetics can play a significant role, with certain genetic mutations increasing the risk of developing specific types of cancer. Genetic testing can help identify individuals at higher risk, allowing for early interventions and preventive measures.
In conclusion, cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. As research continues to unravel the mysteries of cancer, there is hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by this disease. The journey towards conquering cancer is long and challenging, but with persistence, innovation, and collaboration, we can make significant strides in the fight against this global health threat.