Kinetic friction is a fundamental concept in physics that opposes the motion of an object when it is in contact with another surface. Calculating kinetic friction is essential in understanding various phenomena, from the motion of vehicles to the behavior of objects on different surfaces. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate kinetic friction, discussing the underlying principles, formulas, and practical applications.
Key Points
- The kinetic friction coefficient (μk) is a critical parameter in calculating kinetic friction.
- The normal force (Fn) and the kinetic friction coefficient (μk) are essential in determining the kinetic friction force (Fk).
- Experimental methods, such as the inclined plane and the horizontal motion experiment, can be used to calculate kinetic friction.
- Theoretical models, like the Coulomb friction model, provide a framework for understanding kinetic friction.
- Real-world applications, including vehicle braking and object motion on inclined planes, rely on accurate calculations of kinetic friction.
Understanding Kinetic Friction
Kinetic friction occurs when an object is in motion and is in contact with another surface. The force of kinetic friction (Fk) opposes the motion of the object and is typically smaller than the force of static friction. The kinetic friction coefficient (μk) is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the strength of the kinetic friction force. The value of μk depends on the materials in contact and can be determined experimentally or theoretically.
Method 1: Using the Kinetic Friction Formula
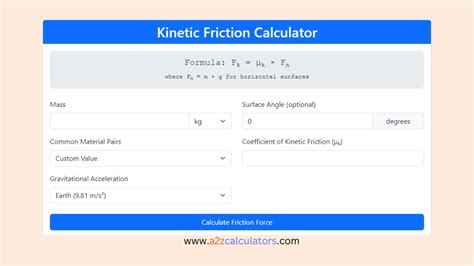
The kinetic friction force (Fk) can be calculated using the formula Fk = μk * Fn, where μk is the kinetic friction coefficient and Fn is the normal force. The normal force (Fn) is the force exerted by the surface on the object, perpendicular to the surface. By rearranging the formula, we can solve for μk: μk = Fk / Fn. This method requires knowledge of the kinetic friction force (Fk) and the normal force (Fn), which can be measured experimentally.
| Quantity | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fk | N (Newtons) | Kinetic friction force |
| μk | Dimensionless | Kinetic friction coefficient |
| Fn | N (Newtons) | Normal force |

Method 2: Inclined Plane Experiment
The inclined plane experiment is a classic method for measuring kinetic friction. By placing an object on an inclined plane and measuring the angle at which the object begins to slide, we can calculate the kinetic friction coefficient (μk). The formula for μk in this case is μk = tan(θ), where θ is the angle of the inclined plane. This method provides a straightforward way to measure kinetic friction and can be used for a variety of materials.
Method 3: Horizontal Motion Experiment
The horizontal motion experiment involves measuring the force required to keep an object moving at a constant velocity on a horizontal surface. By using a spring scale or a force sensor, we can measure the force of kinetic friction (Fk) and calculate the kinetic friction coefficient (μk) using the formula μk = Fk / Fn. This method provides a direct measurement of kinetic friction and can be used to study the effects of different surface materials and velocities.
Method 4: Coulomb Friction Model
The Coulomb friction model is a theoretical framework for understanding kinetic friction. The model states that the kinetic friction force (Fk) is proportional to the normal force (Fn) and the kinetic friction coefficient (μk). The formula for Fk in this case is Fk = μk * Fn. The Coulomb friction model provides a useful framework for understanding kinetic friction and can be used to predict the behavior of objects on different surfaces.
Method 5: Analytical Calculations
For complex systems, analytical calculations can be used to calculate kinetic friction. This method involves using mathematical models to simulate the behavior of objects on different surfaces. By solving the equations of motion and incorporating the kinetic friction force (Fk), we can calculate the kinetic friction coefficient (μk) and predict the behavior of the system. This method requires advanced mathematical skills and can be used to study a wide range of phenomena, from vehicle braking to object motion on inclined planes.
What is the difference between static and kinetic friction?
+Static friction occurs when an object is at rest, while kinetic friction occurs when an object is in motion. The force of static friction is typically larger than the force of kinetic friction.
How can I measure kinetic friction in a real-world scenario?
+You can measure kinetic friction by using an inclined plane or a horizontal motion experiment. These methods provide a straightforward way to measure kinetic friction and can be used for a variety of materials.
What is the significance of kinetic friction in everyday life?
+Kinetic friction plays a crucial role in many everyday phenomena, from vehicle braking to object motion on inclined planes. Understanding kinetic friction is essential for designing and optimizing systems, such as braking systems and conveyor belts.
In conclusion, calculating kinetic friction is essential for understanding various phenomena in physics and engineering. The five methods discussed in this article provide a range of approaches for measuring and calculating kinetic friction, from experimental methods to theoretical models. By understanding kinetic friction, we can design and optimize systems, predict the behavior of objects on different surfaces, and improve our understanding of the natural world.