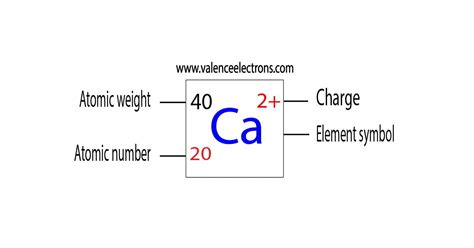
Calcium ions, denoted as Ca²⁺, play a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes. The positive two charge of a calcium ion is a result of the loss of two electrons from a neutral calcium atom, which has an atomic number of 20. This ionization process occurs when a calcium atom, with its electronic configuration of [Ar] 4s², loses two electrons from its outermost energy level, resulting in a stable configuration with a positive charge.
Chemical Properties of Calcium Ions

The positive two charge of calcium ions makes them highly reactive, particularly in aqueous solutions. They tend to form stable compounds with anions such as chloride (Cl⁻), phosphate (PO₄³⁻), and carbonate (CO₃²⁻). The chemical properties of calcium ions are also influenced by their ionic radius, which is approximately 99 picometers. This relatively small size allows calcium ions to participate in various biochemical reactions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and bone mineralization.
Biological Significance of Calcium Ions
In living organisms, calcium ions are essential for maintaining proper cellular function and overall health. They play a critical role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as secondary messengers to regulate various cellular processes. Calcium ions are also involved in the regulation of muscle contraction, with the troponin-tropomyosin complex relying on calcium binding to initiate muscle contraction. Additionally, calcium ions are a key component of bone tissue, where they are deposited in the form of hydroxyapatite to provide structural support and rigidity.
| Biological Process | Role of Calcium Ions |
|---|---|
| Muscle Contraction | Regulation of muscle contraction through troponin-tropomyosin complex |
| Nerve Impulse Transmission | Modulation of neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity |
| Bone Mineralization | Deposition of calcium ions in the form of hydroxyapatite to provide structural support |
Key Points
- Calcium ions have a positive two charge, resulting from the loss of two electrons from a neutral calcium atom.
- The chemical properties of calcium ions are influenced by their ionic radius and reactivity in aqueous solutions.
- Calcium ions play a critical role in biological processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and bone mineralization.
- The regulation of calcium ion concentrations is essential for maintaining proper cellular function and overall health.
- Calcium ions act as secondary messengers in signal transduction pathways, regulating various cellular processes.
Chemical Reactions Involving Calcium Ions
Calcium ions participate in various chemical reactions, including precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions. One notable example is the reaction between calcium ions and phosphate ions to form calcium phosphate, a key component of bone tissue. This reaction is highly exothermic, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Ions
The thermodynamic properties of calcium ions are influenced by their ionic radius, charge, and hydration energy. The standard electrode potential of calcium ions is approximately -2.87 volts, indicating a strong tendency to lose electrons and form a stable compound. The hydration energy of calcium ions is also relatively high, resulting in a strong interaction with water molecules and influencing their chemical reactivity.
| Thermodynamic Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Standard Electrode Potential | -2.87 volts |
| Hydration Energy | -1925 kJ/mol |
| Entropy Change | 57.3 J/mol·K |
Conclusion
In conclusion, calcium ions play a vital role in various biological and chemical processes. Their positive two charge, resulting from the loss of two electrons from a neutral calcium atom, makes them highly reactive and essential for maintaining proper cellular function and overall health. The chemical properties of calcium ions, including their ionic radius, reactivity, and hydration energy, influence their participation in various biochemical reactions and regulate critical cellular processes. As domain experts in biochemistry and physical chemistry, it is essential to continue exploring the complex properties and functions of calcium ions to further our understanding of their importance in living organisms.
What is the charge of a calcium ion?
+A calcium ion has a positive two charge, denoted as Ca²⁺.
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
+Calcium ions regulate muscle contraction through the troponin-tropomyosin complex, acting as a trigger for muscle contraction.
What is the standard electrode potential of calcium ions?
+The standard electrode potential of calcium ions is approximately -2.87 volts.