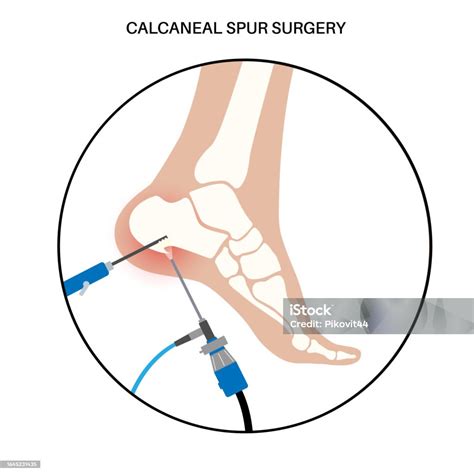
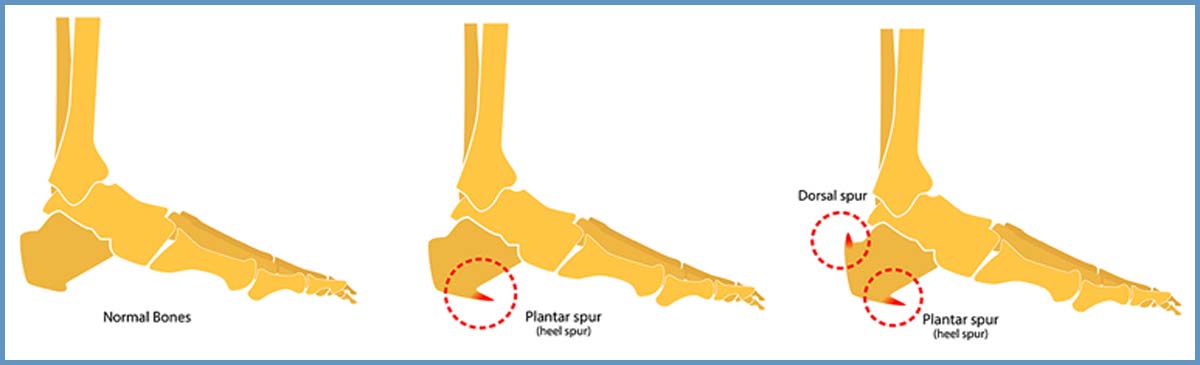
Calcaneal spur surgery, also known as heel spur surgery, is a medical procedure aimed at relieving pain and discomfort caused by a bony growth on the underside of the heel bone, known as the calcaneus. This condition, often associated with plantar fasciitis, can significantly impair an individual's quality of life, making everyday activities such as walking or standing painful. The decision to undergo surgery is typically considered after conservative treatments, including physical therapy, orthotics, and medication, have failed to provide adequate relief. Understanding the intricacies of calcaneal spur surgery, its indications, procedures, and outcomes is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients navigating this treatment path.
Key Points
- Calcaneal spur surgery is generally considered after failure of conservative treatments for heel pain and plantar fasciitis.
- The procedure involves removing the calcaneal spur and may include release of the plantar fascia to relieve tension.
- Minimally invasive and endoscopic techniques are increasingly used to reduce recovery time and minimize scarring.
- Patient selection and preoperative evaluation are critical for successful outcomes, including assessment of the spur size, location, and associated conditions.
- Postoperative care and rehabilitation are essential for optimal recovery, involving rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity.
Indications and Patient Selection

The primary indication for calcaneal spur surgery is persistent pain and dysfunction despite thorough conservative management. Patients with large spurs, significant plantar fascia thickening, or those who have failed to improve with at least 6-12 months of non-surgical treatments are typically considered candidates. The decision-making process involves a comprehensive evaluation, including clinical assessment, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI), and sometimes, diagnostic injections to confirm the source of pain.
Preoperative Evaluation and Preparation
A thorough preoperative evaluation is critical to ensure that surgery is the most appropriate next step. This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and review of imaging studies. The evaluation also considers the patient’s overall health, including any comorbid conditions that could impact surgical risk or recovery. Preparation for surgery may involve optimizing medical conditions, stopping certain medications, and arranging for postoperative support and rehabilitation.
| Preoperative Consideration | Importance |
|---|---|
| Medical Optimization | Reducing surgical risk and improving recovery |
| Smoking Cessation | Enhancing wound healing and reducing complications |
| Pain Management Expectations | Setting realistic postoperative pain management goals |
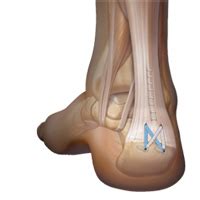
Surgical Techniques and Procedures
Calcaneal spur surgery can be performed through open or minimally invasive techniques. Traditional open surgery involves making an incision on the bottom of the heel to access and remove the spur. Minimally invasive and endoscopic approaches use smaller incisions and specialized instruments, potentially reducing recovery time and scarring. The choice of technique depends on the size and location of the spur, associated conditions such as plantar fasciitis, and the surgeon’s preference and experience.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Effective postoperative care and rehabilitation are crucial for optimal recovery and return to function. Immediately after surgery, patients are advised to rest, apply ice, and elevate the affected foot to reduce pain and swelling. A gradual rehabilitation program, including physical therapy, is essential to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Patients are typically non-weight bearing for several weeks, progressing to partial and then full weight-bearing as healing allows.
What are the potential risks and complications of calcaneal spur surgery?
+Potential risks and complications include infection, nerve damage, recurrence of the spur, and prolonged recovery. As with any surgery, there are also risks associated with anesthesia and the surgical procedure itself.
How long does it take to recover from calcaneal spur surgery?
+Recovery time can vary but generally involves several weeks of non-weight bearing, followed by a gradual return to activity over 2-6 months. Full recovery and return to preoperative activity levels may take up to a year or more in some cases.
Is calcaneal spur surgery always successful in relieving pain?
+While calcaneal spur surgery can be effective in relieving pain for many patients, success rates vary. Factors such as the size and location of the spur, associated conditions, and individual healing and rehabilitation can influence outcomes. Some patients may experience partial relief or require additional treatments for residual symptoms.
In conclusion, calcaneal spur surgery offers a viable treatment option for individuals suffering from persistent heel pain and plantar fasciitis who have not responded to conservative treatments. With careful patient selection, thorough preoperative evaluation, and appropriate postoperative care, surgery can provide significant relief and improve quality of life. However, it is essential to approach this decision with a comprehensive understanding of the procedure, its potential benefits, and risks, as well as the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care.