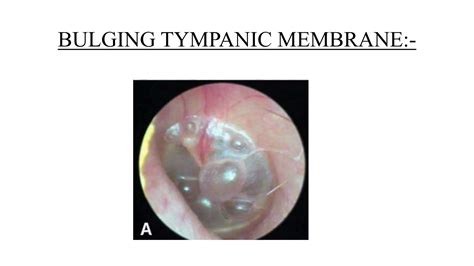
The tympanic membrane, also known as the eardrum, plays a crucial role in our auditory system. It is a thin, semi-transparent membrane that separates the external ear canal from the middle ear. In certain conditions, the tympanic membrane can become bulging, which can cause discomfort, hearing loss, and other complications. A bulging tympanic membrane is characterized by an outward protrusion of the membrane, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
One of the primary causes of a bulging tympanic membrane is otitis media, a type of ear infection that affects the middle ear. Otitis media can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or a combination of both. When the middle ear becomes infected, it can lead to an accumulation of fluid, which in turn causes the tympanic membrane to bulge. Other potential causes of a bulging tympanic membrane include Eustachian tube dysfunction, allergies, colds, and sinus infections. In some cases, a bulging tympanic membrane can also be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as a tumor or a cyst in the middle ear.
Key Points
- The tympanic membrane plays a critical role in our auditory system, and a bulging tympanic membrane can cause discomfort, hearing loss, and other complications.
- Otitis media is a primary cause of a bulging tympanic membrane, and it can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or a combination of both.
- Eustachian tube dysfunction, allergies, colds, and sinus infections are other potential causes of a bulging tympanic membrane.
- A bulging tympanic membrane can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as a tumor or a cyst in the middle ear.
- Treatment options for a bulging tympanic membrane include antibiotics, pain management, and surgical intervention in severe cases.
Causes and Risk Factors

A bulging tympanic membrane can be caused by a variety of factors, including otitis media, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and allergies. Otitis media is a common condition that affects the middle ear, and it can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or a combination of both. The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, plays a crucial role in regulating air pressure in the ear. When the Eustachian tube becomes blocked or dysfunctional, it can lead to an accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, causing the tympanic membrane to bulge.
Allergies, colds, and sinus infections can also contribute to a bulging tympanic membrane. In some cases, a bulging tympanic membrane can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as a tumor or a cyst in the middle ear. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a bulging tympanic membrane, such as ear pain, hearing loss, or discharge from the ear.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of a bulging tympanic membrane can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include ear pain, hearing loss, and discharge from the ear. In some cases, a bulging tympanic membrane can also cause vertigo, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. To diagnose a bulging tympanic membrane, a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination of the ear, using an otoscope to visualize the tympanic membrane.
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the condition. These tests can include a tympanogram, which measures the movement of the tympanic membrane, and a hearing test, which assesses the patient's hearing threshold. Imaging tests, such as a CT scan or an MRI, may also be necessary to rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing the bulging tympanic membrane.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Otoscopy | Visual examination of the tympanic membrane |
| Tympanogram | Measures the movement of the tympanic membrane |
| Hearing Test | Assesses the patient's hearing threshold |
| CT Scan or MRI | Rules out underlying conditions, such as a tumor or cyst |
Treatment Options
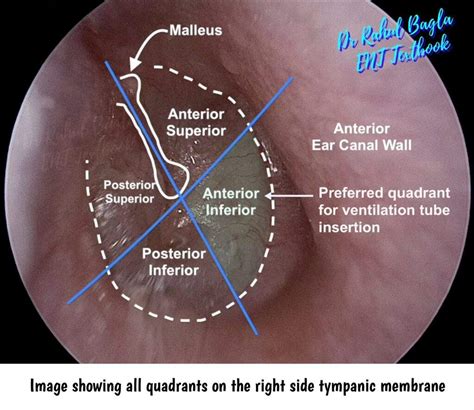
Treatment for a bulging tympanic membrane depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In cases where the condition is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear up the infection. Pain management may also be necessary to alleviate discomfort and reduce the risk of complications.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain the fluid from the middle ear or to repair any damage to the tympanic membrane. A myringotomy, which involves making a small incision in the tympanic membrane to drain the fluid, may be performed in some cases. In severe cases, a tympanoplasty, which involves repairing or replacing the tympanic membrane, may be necessary.
Prevention and Complications
Preventing a bulging tympanic membrane requires maintaining good ear hygiene, avoiding exposure to loud noises, and seeking medical attention if any symptoms of an ear infection or other condition occur. It is also essential to manage any underlying conditions, such as allergies or sinus infections, to reduce the risk of developing a bulging tympanic membrane.
If left untreated, a bulging tympanic membrane can lead to complications, such as hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus. In severe cases, the condition can also lead to more serious complications, such as a perforated eardrum, mastoiditis, or meningitis. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a bulging tympanic membrane to prevent long-term complications and promote optimal ear health.
What are the common causes of a bulging tympanic membrane?
+The common causes of a bulging tympanic membrane include otitis media, Eustachian tube dysfunction, allergies, colds, and sinus infections.
What are the symptoms of a bulging tympanic membrane?
+The symptoms of a bulging tympanic membrane include ear pain, hearing loss, discharge from the ear, vertigo, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
How is a bulging tympanic membrane diagnosed?
+A bulging tympanic membrane is diagnosed through a physical examination of the ear, using an otoscope to visualize the tympanic membrane, and additional tests, such as a tympanogram, hearing test, and imaging tests.
What are the treatment options for a bulging tympanic membrane?
+The treatment options for a bulging tympanic membrane include antibiotics, pain management, and surgical intervention, such as a myringotomy or tympanoplasty.
What are the potential complications of a bulging tympanic membrane?
+The potential complications of a bulging tympanic membrane include hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus, perforated eardrum, mastoiditis, and meningitis.
In conclusion, a bulging tympanic membrane is a complex condition that requires prompt medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and potential complications of this condition can help individuals seek medical attention and prevent long-term complications. By maintaining good ear hygiene, avoiding exposure to loud noises, and managing any underlying conditions, individuals can reduce the risk of developing a bulging tympanic membrane and promote optimal ear health.