The natural world is comprised of various components that interact and influence one another, creating complex ecosystems. These components can be broadly categorized into two groups: biotic and abiotic. Understanding the differences between these components is essential for grasping the intricacies of ecological systems and the relationships within them. In this article, we will delve into the world of biotic and abiotic components, exploring their definitions, examples, and significance in maintaining the delicate balance of nature.
Biotic Components: The Living Organisms

Biotic components refer to the living organisms that inhabit an ecosystem. These can range from tiny microorganisms like bacteria and fungi to larger, more complex organisms such as plants, animals, and humans. Biotic components are further divided into three main categories: producers, consumers, and decomposers. Producers, primarily plants and certain bacteria, are capable of producing their own food through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food web. Consumers, which include animals, feed on other organisms, transferring energy from one level to the next. Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. The interactions among these biotic components are crucial for the survival and functioning of ecosystems.
Types of Biotic Components
Within the biotic category, organisms can be classified based on their roles and characteristics. For instance, autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food, whereas heterotrophs rely on consuming other organisms for energy. Another classification is based on the organism’s position in the food chain, with primary consumers being herbivores that directly feed on producers, and secondary consumers being carnivores that feed on primary consumers. This complex web of relationships highlights the interdependence of biotic components within an ecosystem.
| Category | Examples | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Producers | Plants, Algae, Certain Bacteria | Produce food through photosynthesis |
| Consumers | Animals (Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores) | Feed on other organisms for energy |
| Decomposers | Fungi, Bacteria | Break down dead organic matter, recycle nutrients |
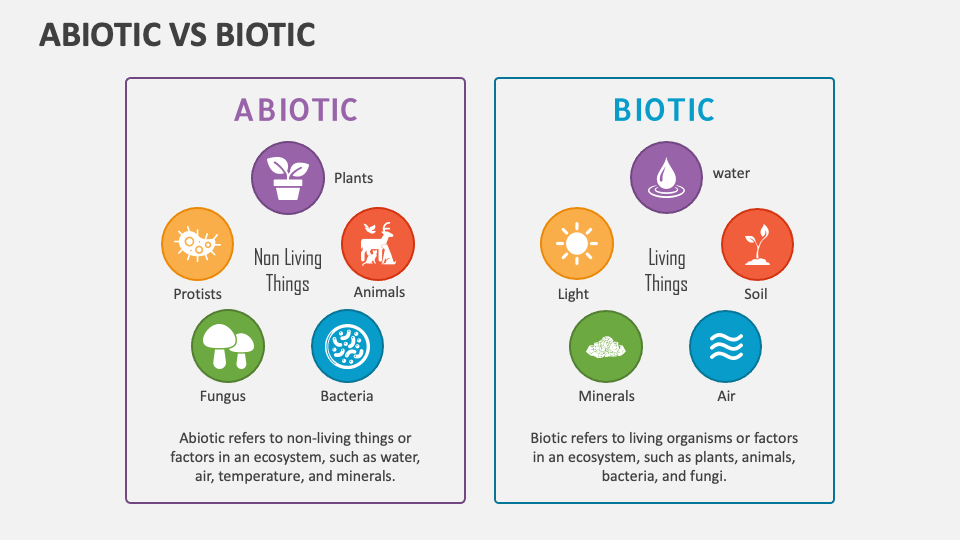
Abiotic Components: The Non-Living Factors
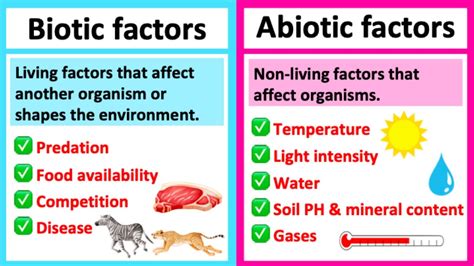
Abiotic components, on the other hand, are non-living factors that influence the ecosystem. These components can be physical or chemical in nature and play a vital role in shaping the environment and affecting the biotic components. Examples of abiotic components include temperature, humidity, light, soil, water, and air quality. These factors can impact the growth, reproduction, and survival of living organisms, thus influencing the structure and function of ecosystems.
Influence of Abiotic Components
The influence of abiotic components on ecosystems can be profound. For instance, temperature affects the metabolic rates of organisms, influencing their activity levels and distribution. Light is essential for photosynthesis, impacting the productivity of ecosystems. Soil quality affects plant growth, which in turn influences the entire food web. Understanding these abiotic factors is essential for managing ecosystems and predicting how they might respond to changes, such as those induced by climate change.
Key Points
- Biotic components are living organisms that include producers, consumers, and decomposers, interacting to form complex ecosystems.
- Abiotic components are non-living factors such as temperature, humidity, and light that significantly influence the ecosystem and its biotic components.
- The balance between biotic and abiotic components is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the health and resilience of ecosystems.
- Understanding these components and their interactions is vital for ecological conservation and management practices.
- Human activities can significantly impact both biotic and abiotic components, necessitating careful consideration and sustainable practices to protect ecosystems.
In conclusion, the interplay between biotic and abiotic components is fundamental to the functioning and resilience of ecosystems. As we navigate the challenges of environmental conservation and sustainability, recognizing the intricate relationships within ecosystems and the impact of human activities on these delicate balances is of paramount importance. By fostering a deeper understanding of biotic and abiotic components and their roles in ecological systems, we can work towards preserving the natural world for future generations.
What is the primary difference between biotic and abiotic components in an ecosystem?
+The primary difference is that biotic components are living organisms, whereas abiotic components are non-living factors that influence the ecosystem.
How do abiotic components influence the biotic components of an ecosystem?
+Abiotic components such as temperature, light, and water availability can affect the growth, reproduction, and survival of living organisms, thus influencing the structure and function of ecosystems.
Why is understanding biotic and abiotic components important for ecological conservation?
+Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies, predicting ecosystem responses to environmental changes, and managing ecosystems sustainably.



