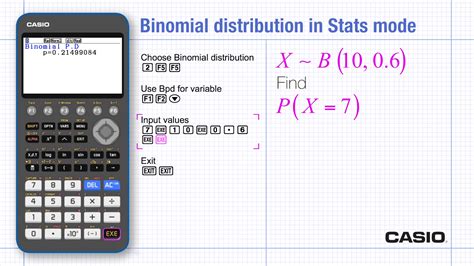
The binomial probability distribution function (PDF) is a fundamental concept in statistics, used to model the probability of obtaining exactly k successes in n independent trials, where the probability of success in each trial is p. Understanding the binomial PDF is crucial for analyzing and interpreting data in various fields, including medicine, social sciences, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the world of binomial distributions, exploring five essential tips for working with binomial PDFs, and providing a comprehensive guide for professionals and researchers seeking to enhance their statistical analysis skills.
Key Points
- Understanding the binomial coefficient and its role in calculating probabilities
- Recognizing the importance of identifying the number of trials, probability of success, and number of successes
- Utilizing the binomial probability formula to calculate probabilities for different scenarios
- Visualizing binomial distributions using graphs and charts to gain insight into the data
- Applying binomial distributions to real-world problems, such as quality control and medical research
Tip 1: Understanding the Binomial Coefficient
The binomial coefficient, often denoted as “n choose k” or C(n, k), plays a vital role in calculating binomial probabilities. It represents the number of ways to choose k successes from n trials, without regard to order. The formula for the binomial coefficient is n! / (k! * (n-k)!)}, where! denotes the factorial function. For instance, if we want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 3 heads in 5 coin tosses, we need to calculate C(5, 3), which equals 10. This value is then used in the binomial probability formula to obtain the desired probability.
Calculating Binomial Probabilities
To calculate binomial probabilities, we use the formula P(X = k) = C(n, k) * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k), where P(X = k) is the probability of obtaining exactly k successes, n is the number of trials, k is the number of successes, p is the probability of success, and (1-p) is the probability of failure. For example, if we want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 2 successes in 4 trials, with a probability of success p = 0.6, we would use the formula: P(X = 2) = C(4, 2) * 0.6^2 * (1-0.6)^(4-2). Plugging in the values, we get P(X = 2) = 6 * 0.36 * 0.16 = 0.3456.
| Number of Trials (n) | Number of Successes (k) | Probability of Success (p) | Binomial Probability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.3456 |
| 5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.3087 |
| 6 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2458 |

Tip 2: Identifying the Number of Trials, Probability of Success, and Number of Successes

Before calculating binomial probabilities, it’s crucial to identify the number of trials (n), the probability of success (p), and the number of successes (k). These values are essential components of the binomial probability formula. In real-world applications, the number of trials may represent the number of patients in a clinical trial, the probability of success may represent the effectiveness of a treatment, and the number of successes may represent the number of patients who respond to the treatment. For instance, in a medical study, we may want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 15 responses to a new treatment in a sample of 20 patients, with a probability of response p = 0.75. In this case, n = 20, k = 15, and p = 0.75.
Real-World Applications
Binomial distributions have numerous real-world applications, including quality control, medical research, and social sciences. In quality control, binomial distributions can be used to model the probability of defective products in a manufacturing process. In medical research, binomial distributions can be used to model the probability of response to a new treatment. In social sciences, binomial distributions can be used to model the probability of success in a survey or poll. By understanding how to apply binomial distributions to real-world problems, you can gain valuable insights into the data and make informed decisions.
Tip 3: Utilizing the Binomial Probability Formula
The binomial probability formula is a powerful tool for calculating probabilities in binomial distributions. By plugging in the values of n, k, and p, you can obtain the probability of different outcomes. However, it’s essential to ensure that the values are accurate and relevant to the problem at hand. Additionally, it’s crucial to consider the assumptions of the binomial distribution, including independence of trials and a fixed probability of success. For example, if we want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 10 successes in 15 trials, with a probability of success p = 0.5, we would use the formula: P(X = 10) = C(15, 10) * 0.5^10 * (1-0.5)^(15-10). Plugging in the values, we get P(X = 10) = 3003 * 0.0009766 * 0.0009766 = 0.0215.
Tip 4: Visualizing Binomial Distributions
Visualizing binomial distributions can provide valuable insights into the data. By plotting the probability of different outcomes, you can gain a better understanding of the distribution and identify patterns or trends. There are several ways to visualize binomial distributions, including histograms, bar charts, and probability plots. For instance, a histogram can be used to display the probability of different outcomes in a binomial distribution, while a probability plot can be used to display the cumulative probability of different outcomes. By visualizing binomial distributions, you can gain a deeper understanding of the data and make more informed decisions.
Tip 5: Applying Binomial Distributions to Real-World Problems

Binomial distributions have numerous real-world applications, including quality control, medical research, and social sciences. By understanding how to apply binomial distributions to real-world problems, you can gain valuable insights into the data and make informed decisions. For example, in a medical study, you may want to calculate the probability of getting exactly 20 responses to a new treatment in a sample of 25 patients, with a probability of response p = 0.8. In this case, you would use the binomial probability formula to obtain the probability of different outcomes and visualize the results using a histogram or probability plot.
What is the binomial probability formula?
+The binomial probability formula is P(X = k) = C(n, k) \* p^k \* (1-p)^(n-k), where P(X = k) is the probability of obtaining exactly k successes, n is the number of trials, k is the number of successes, p is the probability of success, and (1-p) is the probability of failure.
How do I calculate the binomial coefficient?
+The binomial coefficient, often denoted as "n choose k" or C(n, k), can be calculated using the formula n! / (k! \* (n-k)!)}, where! denotes the factorial function.
What are some real-world applications of binomial distributions?
+Binomial distributions have numerous real-world applications, including quality control, medical research, and social sciences. By understanding how to apply binomial distributions to real-world problems, you can gain valuable insights into the data and make informed decisions.
Meta description: Learn how to work with binomial probability distribution functions (PDFs) and discover five essential tips for calculating probabilities, identifying key components, and applying binomial distributions to real-world problems.