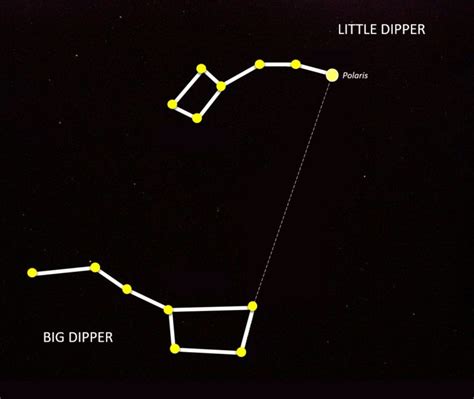
The Big Dipper, one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky, has been a source of fascination for astronomers and stargazers alike for centuries. This group of seven bright stars, part of the larger constellation Ursa Major, holds a special place in the lore of astronomy due to its unique shape and the North Star, also known as Polaris, that it helps to locate. Let's delve into some interesting facts about the Big Dipper, exploring its composition, its role in navigation, and its cultural significance.
Formation and Composition

The Big Dipper is composed of seven main stars: Dubhe, Merak, Phecda, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar, and Alkaid. These stars form a ladle-like shape, with four stars making up the “bowl” of the dipper and three forming the “handle.” Interestingly, these stars are not as close to each other as they appear from Earth; they are merely aligned from our vantage point, a phenomenon known as a “asterism.” Each of these stars has its own unique characteristics, such as color, size, and luminosity, contributing to the distinctiveness of the Big Dipper.
Astronomical Significance
Astronomically, the Big Dipper plays a crucial role in identifying other stars and constellations in the night sky. By drawing an imaginary line through the two stars at the end of the “bowl” (Dubhe and Merak), one can find the North Star (Polaris), which is nearly aligned with the Earth’s axis of rotation. This makes the Big Dipper an indispensable tool for navigation, as it can be used to determine direction and, by extension, latitude. The North Star’s stability and the Big Dipper’s visibility throughout much of the year in the Northern Hemisphere have made them invaluable for navigation throughout history.
| Star Name | Distance from Earth | Apparent Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Dubhe | 124 light-years | 1.79 |
| Merak | 79 light-years | 2.34 |
| Phecda | 84 light-years | 2.44 |
| Megrez | 58 light-years | 3.32 |
| Alioth | 81 light-years | 1.77 |
| Mizar | 78 light-years | 2.23 |
| Alkaid | 100 light-years | 1.86 |

Cultural and Historical Significance

Culturally and historically, the Big Dipper has been interpreted in many different ways across various societies. In ancient Greek mythology, the constellation Ursa Major, which includes the Big Dipper, was associated with Callisto and her son Arcas, who were transformed into bears by the god Zeus to save them from the wrath of his wife, Hera. In many indigenous cultures of North America, the Big Dipper is seen as a bear or a buffalo, while in some Asian cultures, it is associated with a ladle or a chariot. These diverse interpretations reflect the Big Dipper’s significance as a navigational aid and its appearance in the night sky across different latitudes.
Key Points
- The Big Dipper is part of the Ursa Major constellation and is used to locate the North Star (Polaris).
- It consists of seven main stars: Dubhe, Merak, Phecda, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar, and Alkaid, which form a ladle-like shape.
- The distance of these stars from Earth varies, ranging from about 58 to 124 light-years.
- The Big Dipper has significant cultural and historical importance, appearing in the mythology and folklore of many societies worldwide.
- Its role in navigation is paramount, as it can be used to determine direction and, by extension, latitude, making it an indispensable tool for travelers and explorers.
Conclusion and Forward Look
In conclusion, the Big Dipper is more than just a recognizable pattern of stars in the night sky; it holds a wealth of information about our universe, from the distances and characteristics of its constituent stars to its role in navigation and cultural symbolism. As we continue to explore the cosmos, understanding and appreciating celestial bodies like the Big Dipper not only deepens our connection to the universe but also underscores the complexity and beauty of the natural world around us.
What are the main stars that make up the Big Dipper?
+The Big Dipper is composed of seven main stars: Dubhe, Merak, Phecda, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar, and Alkaid.
Why is the Big Dipper important for navigation?
+The Big Dipper is crucial for navigation because it can be used to locate the North Star (Polaris), which is nearly aligned with the Earth’s axis of rotation, thereby helping to determine direction and latitude.
What are some cultural interpretations of the Big Dipper?
+The Big Dipper has been interpreted in many different ways across cultures, including as a bear, a buffalo, a ladle, or a chariot, reflecting its significance and visibility in the night sky.