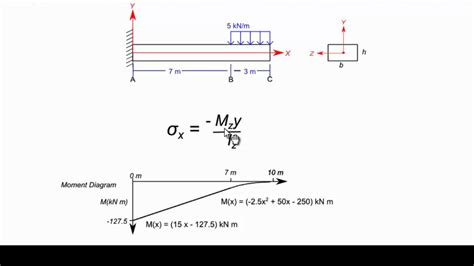
The bending stress equation is a fundamental concept in the field of mechanical engineering, particularly in the design and analysis of beams and other structural elements. It is used to calculate the maximum stress that occurs in a beam when it is subjected to a bending moment, which is a measure of the force that causes the beam to bend. The equation is crucial in determining the safety and integrity of a structure, as excessive bending stress can lead to failure.
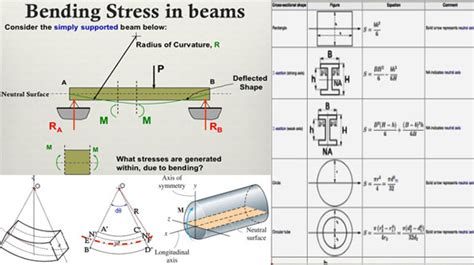
The bending stress equation is typically represented as σ = (M \* c) / I, where σ is the bending stress, M is the bending moment, c is the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber, and I is the moment of inertia of the beam's cross-sectional area. This equation is derived from the principles of mechanics of materials and is widely used in the design of beams, columns, and other structural elements.
Key Points
- The bending stress equation is used to calculate the maximum stress in a beam due to bending.
- The equation is σ = (M \* c) / I, where σ is the bending stress, M is the bending moment, c is the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber, and I is the moment of inertia.
- The bending moment (M) is a measure of the force that causes the beam to bend.
- The distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber (c) is a critical parameter in determining the bending stress.
- The moment of inertia (I) is a measure of the beam's resistance to bending and is dependent on the beam's cross-sectional area and shape.
Derivation of the Bending Stress Equation
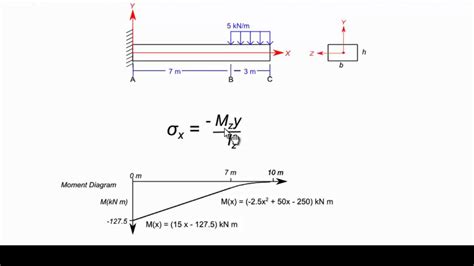
The derivation of the bending stress equation involves several key assumptions and simplifications. One of the primary assumptions is that the beam is subjected to a pure bending moment, which means that there are no external forces or moments acting on the beam other than the bending moment. Additionally, it is assumed that the beam is made of a homogeneous, isotropic material, and that the bending moment is applied gradually and slowly.
The bending stress equation can be derived by considering the equilibrium of a small element of the beam. The element is subjected to a normal stress (σ) and a shear stress (τ), which are functions of the distance from the neutral axis. By applying the principles of equilibrium and compatibility, the bending stress equation can be derived as σ = (M \* c) / I.
Factors Affecting Bending Stress
There are several factors that can affect the bending stress in a beam, including the magnitude of the bending moment, the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber, and the moment of inertia of the beam’s cross-sectional area. The bending moment is a measure of the force that causes the beam to bend, and it is typically calculated using the beam’s loading and support conditions.
The distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber (c) is a critical parameter in determining the bending stress. The neutral axis is the line that passes through the center of the beam and is perpendicular to the plane of bending. The extreme fiber is the point on the beam that is farthest from the neutral axis, and it is typically the point of maximum stress.
| Parameter | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bending Moment (M) | N-m | Measure of the force that causes the beam to bend |
| Distance from Neutral Axis to Extreme Fiber (c) | m | Distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber |
| Moment of Inertia (I) | m^4 | Measure of the beam's resistance to bending |
| Bending Stress (σ) | Pascal (Pa) | Maximum stress that occurs in the beam due to bending |
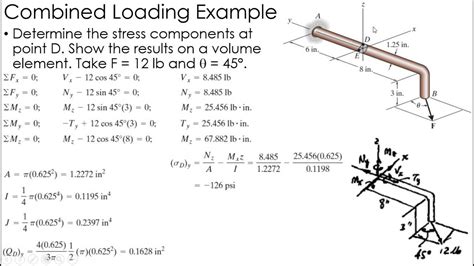
Applications of the Bending Stress Equation
The bending stress equation has numerous applications in the field of mechanical engineering, including the design of beams, columns, and other structural elements. It is used to determine the maximum stress that occurs in a beam due to bending, and to ensure that the beam can withstand the applied loads without failing.
The bending stress equation is also used in the analysis of complex structures, such as bridges and buildings. It is used to determine the maximum stress that occurs in the structure due to various loads, including dead loads, live loads, and environmental loads.
Limitations of the Bending Stress Equation
While the bending stress equation is a powerful tool for designing and analyzing beams and other structural elements, it has several limitations. One of the primary limitations is that it assumes a pure bending moment, which means that there are no external forces or moments acting on the beam other than the bending moment.
Additionally, the bending stress equation assumes that the beam is made of a homogeneous, isotropic material, and that the bending moment is applied gradually and slowly. In reality, beams are often subjected to complex loads and boundary conditions, which can affect the accuracy of the bending stress equation.
What is the bending stress equation?
+The bending stress equation is σ = (M \* c) / I, where σ is the bending stress, M is the bending moment, c is the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber, and I is the moment of inertia.
What are the factors that affect the bending stress in a beam?
+The factors that affect the bending stress in a beam include the magnitude of the bending moment, the distance from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber, and the moment of inertia of the beam's cross-sectional area.
What are the limitations of the bending stress equation?
+The limitations of the bending stress equation include the assumption of a pure bending moment, the assumption of a homogeneous, isotropic material, and the assumption that the bending moment is applied gradually and slowly.
In conclusion, the bending stress equation is a fundamental concept in the field of mechanical engineering, and it is widely used in the design and analysis of beams and other structural elements. While it has several limitations, it is a powerful tool for determining the maximum stress that occurs in a beam due to bending, and for ensuring that the beam can withstand the applied loads without failing.