The concept of forces is fundamental in physics, and understanding the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces is crucial for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects. Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object to change its state of motion, and they can be either balanced or unbalanced. In this article, we will delve into the world of forces, exploring the definitions, examples, and implications of balanced and unbalanced forces.
Understanding Balanced Forces

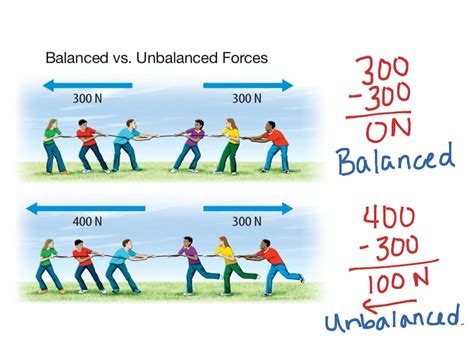
Balanced forces occur when the net force acting on an object is zero. This means that the forces acting on the object are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, resulting in no change in the object’s motion. When forces are balanced, the object is said to be in equilibrium, and it will maintain its state of motion unless an external force acts upon it. For example, consider a person standing still on the ground. The force of gravity is pulling the person down, but the ground is exerting an equal and opposite force upward, resulting in no net force and no change in motion.
Characteristics of Balanced Forces
There are several key characteristics of balanced forces that are essential to understand. Firstly, the net force acting on the object is zero, which means that the object is not accelerating. Secondly, the forces acting on the object are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, resulting in a state of equilibrium. Finally, balanced forces do not cause a change in the object’s motion, and the object will maintain its state of motion unless an external force acts upon it.
| Force Type | Force Direction | Force Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Gravity | Downward | Equal to the person's weight |
| Normal Force | Upward | Equal to the person's weight |

Understanding Unbalanced Forces

Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, occur when the net force acting on an object is not zero. This means that the forces acting on the object are not equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, resulting in a change in the object’s motion. When forces are unbalanced, the object will accelerate, either speeding up or slowing down, depending on the direction of the net force. For example, consider a car accelerating from rest. The force of the engine is greater than the force of friction, resulting in a net force that causes the car to accelerate forward.
Characteristics of Unbalanced Forces
There are several key characteristics of unbalanced forces that are essential to understand. Firstly, the net force acting on the object is not zero, which means that the object is accelerating. Secondly, the forces acting on the object are not equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, resulting in a change in the object’s motion. Finally, unbalanced forces cause a change in the object’s motion, and the object will accelerate until the forces become balanced again.
| Force Type | Force Direction | Force Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Force | Forward | Greater than the force of friction |
| Friction Force | Backward | Less than the force of the engine |
Key Points
- Balanced forces result in no change in motion, while unbalanced forces cause a change in motion.
- The net force acting on an object determines whether the forces are balanced or unbalanced.
- Forces can be either internal or external, and they can be classified as either contact or non-contact forces.
- Understanding the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces is crucial for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects.
- Real-world examples of balanced and unbalanced forces include a person standing still, a car accelerating from rest, and a ball rolling down a hill.
Real-World Applications of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
Balanced and unbalanced forces have numerous real-world applications, and understanding the difference between them is essential for predicting and analyzing the motion of objects. For example, in the field of engineering, understanding the forces acting on a bridge or a building is crucial for ensuring its stability and safety. In sports, understanding the forces acting on an athlete’s body is essential for optimizing performance and preventing injuries.
Practical Examples of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
There are numerous practical examples of balanced and unbalanced forces that illustrate their importance in everyday life. For example, a person standing still on the ground is an example of balanced forces, while a car accelerating from rest is an example of unbalanced forces. A ball rolling down a hill is another example of unbalanced forces, where the force of gravity is greater than the force of friction, resulting in a net force that causes the ball to accelerate downward.
What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?
+Balanced forces result in no change in motion, while unbalanced forces cause a change in motion. The net force acting on an object determines whether the forces are balanced or unbalanced.
Can an object be moving at a constant velocity and still have balanced forces acting on it?
+Yes, an object can be moving at a constant velocity and still have balanced forces acting on it. This occurs when the net force acting on the object is zero, resulting in no change in motion.
What are some real-world examples of balanced and unbalanced forces?
+Real-world examples of balanced forces include a person standing still on the ground, while examples of unbalanced forces include a car accelerating from rest, a ball rolling down a hill, and a person jumping up into the air.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces is crucial for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects. By recognizing the characteristics of balanced and unbalanced forces, we can better appreciate the complex interactions between objects and their environments, and we can apply this knowledge to real-world problems in fields such as engineering, sports, and everyday life. Whether we are designing a new bridge, optimizing an athlete’s performance, or simply understanding the world around us, the concepts of balanced and unbalanced forces play a vital role in our understanding of the physical world.