When it comes to treating bacterial infections, two of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics are Augmentin and Amoxicillin. Both belong to the penicillin class of antibiotics but have distinct differences in their composition, effectiveness, and usage. Understanding these differences is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike to make informed decisions about treatment. In this article, we will delve into the comparison of Augmentin vs Amoxicillin, exploring their mechanisms of action, indications, side effects, and the scenarios in which one might be preferred over the other.
Key Points
- Augmentin is a combination antibiotic consisting of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, while Amoxicillin is a single-entity antibiotic.
- Augmentin is more effective against beta-lactamase-producing bacteria due to the presence of clavulanic acid.
- Amoxicillin is generally considered safer for use in pregnant women and has a narrower spectrum of activity compared to Augmentin.
- Side effects of Augmentin can include gastrointestinal disturbances, rash, and in rare cases, severe allergic reactions.
- The choice between Augmentin and Amoxicillin depends on the type of infection, patient's medical history, and potential for resistance.
Composition and Mechanism of Action

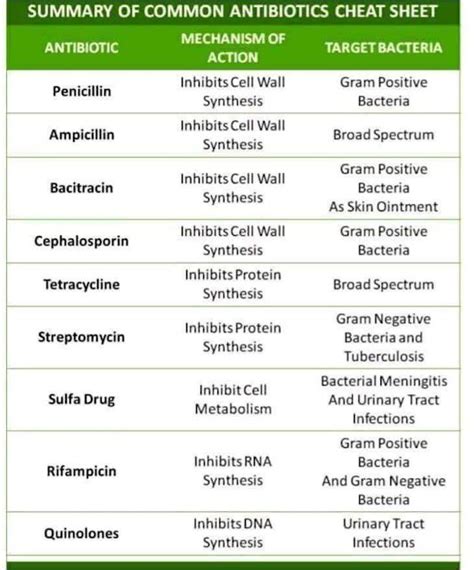
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death. It is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. However, its effectiveness can be compromised by bacteria that produce beta-lactamase enzymes, which can degrade amoxicillin and render it ineffective.
Augmentin, on the other hand, is a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that protects amoxicillin from degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, thereby extending its spectrum of activity to include beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. This makes Augmentin particularly useful for treating infections caused by bacteria that are resistant to amoxicillin alone.
Indications and Usage
Both Augmentin and Amoxicillin are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections. However, the choice between the two often depends on the suspected or confirmed causative organism and its likely resistance pattern. For example, Augmentin might be preferred for treating infections where beta-lactamase-producing organisms are suspected or confirmed, such as certain types of pneumonia or skin infections.
Amoxicillin, being a narrower-spectrum antibiotic, might be chosen for milder infections or in scenarios where the risk of resistance is lower, such as in the treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Both Augmentin and Amoxicillin can cause side effects, although the nature and severity can vary. Common side effects of both include gastrointestinal disturbances like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as the potential for allergic reactions. However, the addition of clavulanic acid in Augmentin can increase the risk of certain side effects, such as diarrhea and abdominal cramps, compared to amoxicillin alone.
In terms of safety, both antibiotics are generally considered safe when used appropriately. However, Amoxicillin is often preferred in pregnant women due to its longer history of safe use and narrower spectrum of activity, which may reduce the risk of disrupting the normal bacterial flora.
| Antibiotic | Spectrum of Activity | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | Narrower, susceptible to beta-lactamase degradation | Gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions |
| Augmentin | Broader, includes beta-lactamase-producing bacteria | Gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, increased risk of diarrhea |
Resistance and Future Directions

Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern worldwide, and both Augmentin and Amoxicillin are subject to resistance mechanisms. The overuse and misuse of these antibiotics can accelerate the development of resistance, making infections harder to treat. It is crucial, therefore, to use these antibiotics judiciously, following guidelines and always under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Future directions in antibiotic therapy may involve the development of new agents that can effectively combat resistant organisms. Additionally, strategies to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics, such as combination therapies or the use of adjuvant treatments, are areas of ongoing research.
What is the primary difference between Augmentin and Amoxicillin?
+The primary difference is the presence of clavulanic acid in Augmentin, which inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes and extends its spectrum of activity to include beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.
When should Augmentin be preferred over Amoxicillin?
+Augmentin should be preferred when the infection is suspected or confirmed to be caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, or in scenarios where resistance to amoxicillin is a concern.
Are there any safety concerns with using Augmentin in pregnant women?
+While Augmentin can be used in pregnancy, Amoxicillin is often preferred due to its longer history of safe use. However, the decision should always be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider, weighing the benefits against potential risks.
In conclusion, the choice between Augmentin and Amoxicillin depends on a nuanced understanding of their differences in composition, spectrum of activity, and potential side effects. By considering these factors, along with the specific needs of the patient and the characteristics of the infection, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing the risk of resistance and adverse effects.