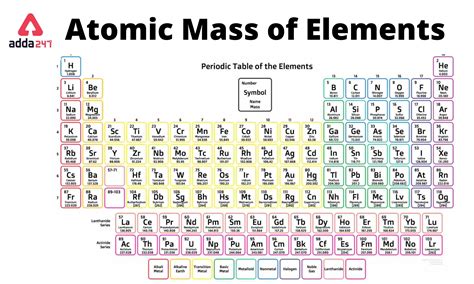
The atomic mass of an element is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and it plays a crucial role in understanding the properties and behavior of elements. On the periodic table, the atomic mass of an element is typically represented as a numerical value, which is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. In this article, we will delve into the concept of atomic mass, its significance, and how it is represented on the periodic table.
Key Points
- The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes.
- The atomic mass is typically represented on the periodic table as a numerical value.
- Understanding atomic mass is crucial for calculating the number of moles of an element, its molar mass, and its density.
- Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, resulting in different masses.
- The atomic mass unit (amu) is used to express the mass of an atom or molecule, with 1 amu being equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Understanding Atomic Mass
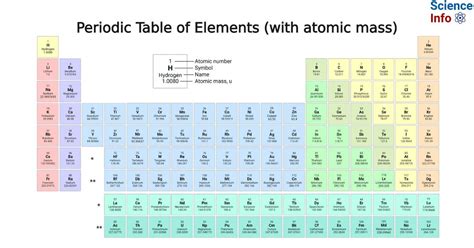
Atomic mass is a measure of the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. It is an average value, as most elements exist as a mixture of isotopes, each with a slightly different mass. The atomic mass of an element is calculated by summing the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes, weighted by their relative abundance. For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 u (unified atomic mass units), which is a weighted average of the masses of its three naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12 (98.93% abundance), carbon-13 (1.07% abundance), and carbon-14 (trace amounts).
Isotopes and Their Role in Atomic Mass
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number results in different masses for the isotopes. For instance, oxygen has three naturally occurring isotopes: oxygen-16 (99.76% abundance), oxygen-17 (0.0378% abundance), and oxygen-18 (0.2049% abundance). The atomic mass of oxygen is 15.9994 u, which is a weighted average of the masses of these isotopes.
| Isotope | Mass (u) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen-16 | 15.9949 | 99.76 |
| Oxygen-17 | 16.9991 | 0.0378 |
| Oxygen-18 | 17.9992 | 0.2049 |

Representation on the Periodic Table
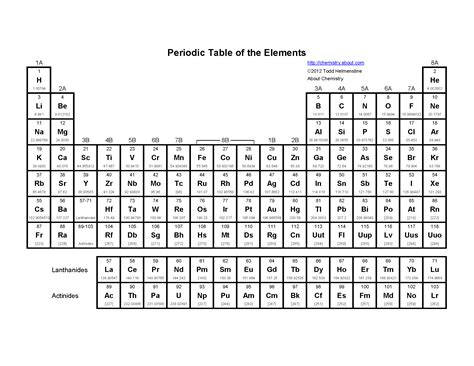
The atomic mass of an element is typically represented on the periodic table as a numerical value, usually in the bottom left or right corner of the element’s box. This value is usually expressed in unified atomic mass units (u) or atomic mass units (amu), with 1 u being equal to 1⁄12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. The atomic mass is usually rounded to the nearest whole number or to one decimal place, depending on the level of precision required.
Calculating Atomic Mass
To calculate the atomic mass of an element, the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes must be known, along with their relative abundances. The atomic mass is then calculated using the following formula: atomic mass = (mass of isotope 1 x abundance of isotope 1) + (mass of isotope 2 x abundance of isotope 2) +…. For example, the atomic mass of chlorine is calculated as follows: atomic mass = (34.9689 u x 0.7577) + (36.9659 u x 0.2423) = 35.453 u.
What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom, while the atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus.
Why is the atomic mass of an element a weighted average?
+The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average because most elements exist as a mixture of isotopes, each with a slightly different mass. The weighted average takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope.
How is the atomic mass of an element used in chemistry?
+The atomic mass of an element is used to calculate its molar mass, which is the mass of one mole of the element. This is particularly useful in chemical reactions, where the number of moles of reactants and products can be calculated using the atomic masses of the elements involved.
In conclusion, the atomic mass of an element is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and its representation on the periodic table provides a wealth of information about the element’s properties and behavior. By understanding the concept of atomic mass and how it is calculated, chemists and scientists can better appreciate the complexities of the periodic table and the relationships between elements.