The Advanced Placement (AP) Government course is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and practices of government in the United States. As part of the course, students are required to be familiar with a range of foundational documents that have shaped the country's history, politics, and laws. These documents are not only essential for understanding the structure and function of the U.S. government but also play a critical role in the AP Government exam. Here, we will delve into the list of required documents, exploring their significance, relevance, and the role they play in the broader context of American government and politics.
Foundational Documents
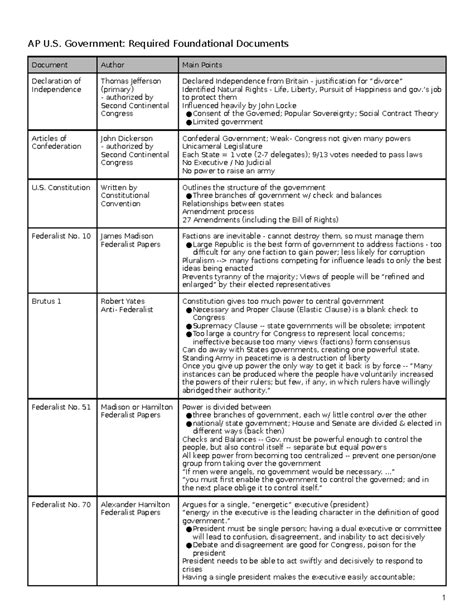
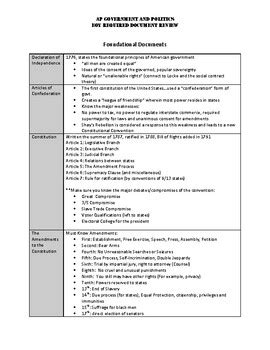
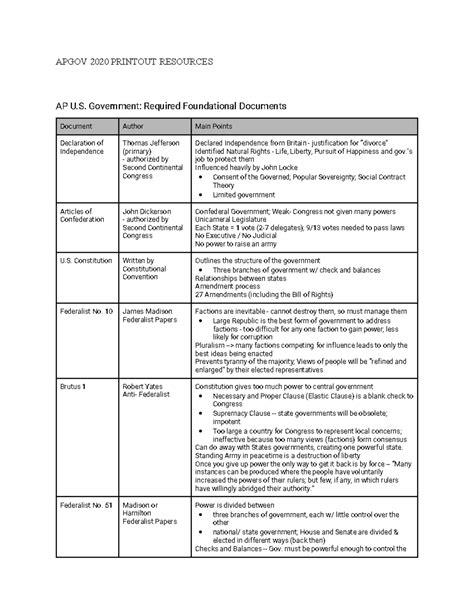
The foundational documents of the United States include the Declaration of Independence, the United States Constitution, and the Federalist Papers. These documents are the cornerstone of American democracy, outlining the principles of liberty, equality, and justice that have guided the nation since its inception. The Declaration of Independence, adopted in 1776, formally declared the 13 American colonies’ independence from Great Britain and established the principles of natural rights and consent of the governed. The United States Constitution, ratified in 1788, is the supreme law of the land, providing the framework for the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. The Federalist Papers, written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, are a series of essays that expound on the Constitution, its provisions, and the rationale behind its creation.
The Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence is a seminal document that not only announced the separation of the American colonies from Great Britain but also articulated the fundamental principles of equality and individual rights. Written by Thomas Jefferson, the Declaration is grounded in the Enlightenment ideas of John Locke, emphasizing the inherent rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. Its influence extends beyond the American Revolution, shaping political discourse and movements for independence and human rights globally.
The United States Constitution
The United States Constitution is the foundational legal document of the federal government and the supreme law of the land. It establishes the framework of the federal government, dividing power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, and outlines the relationship between the federal government and the states. The Constitution’s preamble sets forth the purposes of the document, including establishing justice, insuring domestic tranquility, providing for the common defense, promoting the general welfare, and securing the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity. The Constitution has been amended 27 times, with the Bill of Rights (the first ten amendments) guaranteeing fundamental rights and freedoms to individuals.
The Federalist Papers
The Federalist Papers are a collection of 85 articles and essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the pseudonym “Publius” to promote the ratification of the United States Constitution. These papers provide insight into the thinking of the Constitution’s framers, explaining the document’s provisions and the reasoning behind its structure. They address concerns about federal power, individual rights, and the potential for tyranny, offering a detailed defense of the Constitution’s principles and mechanisms, such as the system of checks and balances and the separation of powers.
| Document | Year | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration of Independence | 1776 | Declared independence from Great Britain, established principles of natural rights |
| United States Constitution | 1788 | Established the framework of the federal government and individual rights |
| Federalist Papers | 1787-1788 | Expounded on the Constitution, its provisions, and rationale |
Key Supreme Court Cases

Beyond the foundational documents, the AP Government course also emphasizes the importance of landmark Supreme Court cases that have interpreted the Constitution and shaped the legal landscape of the United States. Cases such as Marbury v. Madison (1803), which established judicial review; Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which declared segregation in public schools unconstitutional; and Roe v. Wade (1973), which addressed the issue of abortion and a woman’s right to privacy, are pivotal in understanding the evolution of constitutional law and its impact on American society.
Marbury v. Madison
Marbury v. Madison is a landmark case that established the principle of judicial review, granting the Supreme Court the power to declare laws and government actions unconstitutional. This decision, written by Chief Justice John Marshall, has had a profound impact on the system of checks and balances, allowing the judiciary to act as a check on the other branches of government.
Brown v. Board of Education
Brown v. Board of Education marked a significant turning point in the civil rights movement, overturning the “separate but equal” doctrine established by Plessy v. Ferguson in 1896. The Supreme Court’s unanimous decision held that segregation in public schools is inherently unequal, paving the way for the desegregation of public facilities and the advancement of civil rights for African Americans.
Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade is a controversial case that addressed the issue of abortion, ruling that a woman’s right to privacy extends to her decision to have an abortion. The case has been at the center of political and social debates regarding reproductive rights, privacy, and the role of the government in personal health decisions.
| Case | Year | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Marbury v. Madison | 1803 | Established judicial review |
| Brown v. Board of Education | 1954 | Declared segregation in public schools unconstitutional |
| Roe v. Wade | 1973 | Addressed the issue of abortion and the right to privacy |
Key Points
- The foundational documents of the United States, including the Declaration of Independence, the United States Constitution, and the Federalist Papers, are essential for understanding American government and politics.
- Landmark Supreme Court cases such as Marbury v. Madison, Brown v. Board of Education, and Roe v. Wade have significantly shaped the interpretation of the Constitution and the legal landscape of the United States.
- Understanding these documents and cases is critical for analyzing contemporary political, legal, and social issues in the United States.
- The principles of natural rights, individual liberties, and the system of checks and balances are foundational to American democracy and continue to influence political discourse and decision-making.
- The evolution of constitutional law, as reflected in Supreme Court decisions, demonstrates the dynamic nature of the U.S. legal system and its capacity to address changing societal values and challenges.
In conclusion, the study of required documents in the AP Government course provides a rich and nuanced understanding of the principles, structures, and practices of the U.S. government. By examining the foundational documents and landmark Supreme Court cases, students gain insights into the historical development of American democracy, the interpretation of the Constitution, and the ongoing debates and challenges that shape the country's political landscape. This knowledge is not only essential for the AP Government exam but also for engaging with the complexities of American government and politics in a thoughtful and informed manner.
What is the significance of the Declaration of Independence in American history?
+The Declaration of Independence is significant because it formally declared the 13 American colonies’ independence from Great Britain and established the principles of natural rights and consent of the governed, which have been foundational to American democracy.
How does the system of checks and balances work in the U.S. government?
+The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of the federal government from becoming too powerful. Each branch has certain powers that it can use to check the actions of the other branches, ensuring that power is distributed evenly and that no branch can dominate the others.
What is the importance of landmark Supreme Court cases in shaping American law and society?
+Landmark Supreme Court cases are important because they interpret the Constitution and federal laws, setting precedents that guide lower court decisions and influence the development of American law and society. These cases often address critical issues, such as individual rights, equality, and the role of government, and their decisions can have profound impacts on the lives of Americans.