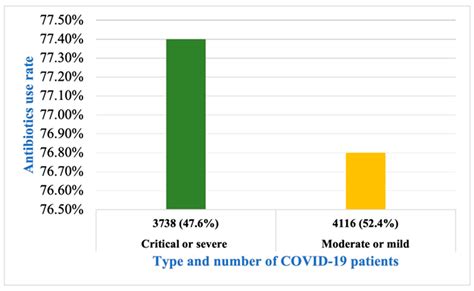
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an unprecedented global health crisis, with a significant impact on the way we approach infectious diseases. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges posed by this novel coronavirus, there has been considerable debate about the role of antibiotics in managing COVID-19. In this article, we will delve into the complex relationship between antibiotics and COVID-19, exploring the current state of knowledge, the potential benefits and risks, and the implications for clinical practice.
Understanding COVID-19 and Antibiotics

COVID-19 is a viral infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. As such, antibiotics, which are designed to target bacterial infections, are not effective against the virus itself. However, secondary bacterial infections can occur in some patients with COVID-19, particularly those with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems. In these cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the secondary infection, rather than the viral infection.
Current Guidelines and Recommendations
The World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and other reputable health organizations have issued guidelines and recommendations for the use of antibiotics in COVID-19 patients. These guidelines emphasize the importance of judicious antibiotic use, highlighting the need to balance the potential benefits of antibiotic treatment against the risks of antimicrobial resistance, side effects, and other adverse outcomes.
| Organization | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| WHO | Antibiotics should only be used in COVID-19 patients with suspected or confirmed bacterial co-infection. |
| CDC | Antibiotics should not be prescribed for COVID-19 patients without evidence of a secondary bacterial infection. |
Key Points
Key Points
- Antibiotics are not effective against COVID-19 itself, but may be used to treat secondary bacterial infections.
- Judicious antibiotic use is essential to minimize the risks of antimicrobial resistance and other adverse outcomes.
- Current guidelines and recommendations emphasize the importance of evidence-based decision-making when considering antibiotic treatment for COVID-19 patients.
- Secondary bacterial infections can occur in COVID-19 patients, particularly those with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems.
- Antibiotic treatment should only be initiated in COVID-19 patients with suspected or confirmed bacterial co-infection.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Despite the clear guidelines and recommendations, there are still misconceptions about the role of antibiotics in COVID-19 management. One common misconception is that antibiotics can prevent or treat COVID-19. This is not supported by scientific evidence, and the use of antibiotics for this purpose can contribute to the development of antimicrobial resistance.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making
When considering antibiotic treatment for COVID-19 patients, healthcare professionals must rely on evidence-based decision-making. This involves carefully evaluating the patient’s clinical presentation, laboratory results, and other relevant factors to determine the likelihood of a secondary bacterial infection. In cases where a bacterial co-infection is suspected or confirmed, antibiotics should be selected based on the suspected or confirmed pathogen, local antimicrobial resistance patterns, and the patient’s individual needs and circumstances.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | Presence of symptoms such as fever, cough, and shortness of breath. |
| Laboratory results | Presence of bacterial pathogens in respiratory or blood cultures. |
| Underlying health conditions | Presence of conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), diabetes, or immunocompromised state. |
What is the role of antibiotics in COVID-19 management?
+Antibiotics are not effective against COVID-19 itself, but may be used to treat secondary bacterial infections that can occur in some patients.
How should healthcare professionals decide when to use antibiotics in COVID-19 patients?
+Healthcare professionals should rely on evidence-based decision-making, carefully evaluating the patient's clinical presentation, laboratory results, and other relevant factors to determine the likelihood of a secondary bacterial infection.
What are the potential risks and benefits of antibiotic use in COVID-19 patients?
+The potential benefits of antibiotic use in COVID-19 patients include the treatment of secondary bacterial infections, while the potential risks include the development of antimicrobial resistance, side effects, and other adverse outcomes.
In conclusion, the use of antibiotics in COVID-19 management is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. By adhering to evidence-based guidelines and recommendations, healthcare professionals can ensure that antibiotics are used judiciously and effectively, minimizing the risks of antimicrobial resistance and other adverse outcomes. As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and updates in this rapidly changing field.