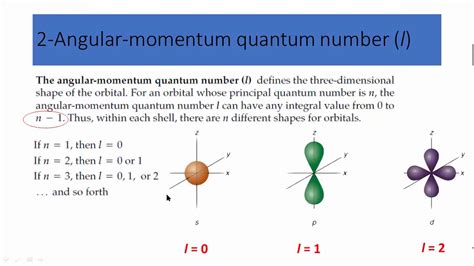
The angular quantum number, denoted by the symbol 'l', is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics and atomic physics. It plays a crucial role in describing the shape and orientation of atomic orbitals, which are the regions around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found. The angular quantum number is one of the four quantum numbers that are used to describe the energy, shape, and orientation of an electron's orbital. In this article, we will explore five ways the angular quantum number works and its significance in understanding the behavior of electrons in atoms.
Key Points
- The angular quantum number determines the shape of an atomic orbital, with different values of 'l' corresponding to different orbital shapes such as s, p, d, and f.
- The angular quantum number affects the energy of an electron in an atom, with higher values of 'l' generally corresponding to higher energy levels.
- The angular quantum number influences the magnetic properties of an atom, with different values of 'l' resulting in different magnetic moments.
- The angular quantum number is used to predict the chemical properties of an element, such as its reactivity and ability to form bonds with other atoms.
- The angular quantum number has applications in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and physics, where it is used to understand the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules.
Orbital Shape and Orientation
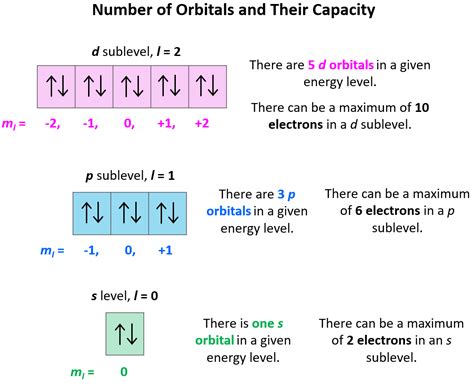
The angular quantum number is responsible for determining the shape and orientation of an atomic orbital. The value of ‘l’ can range from 0 to n-1, where n is the principal quantum number. Different values of ‘l’ correspond to different orbital shapes, such as s (l=0), p (l=1), d (l=2), and f (l=3). For example, the s-orbital has a spherical shape, while the p-orbital has a dumbbell shape. The angular quantum number also determines the orientation of the orbital in space, with different values of ‘l’ resulting in different orientations.
Energy Levels and Electron Configuration
The angular quantum number affects the energy of an electron in an atom. Electrons with higher values of ‘l’ generally have higher energy levels than those with lower values of ‘l’. This is because electrons with higher ‘l’ values are farther away from the nucleus and experience a weaker attractive force. The angular quantum number is also used to determine the electron configuration of an atom, which is the arrangement of electrons in different orbitals. The electron configuration is crucial in understanding the chemical properties of an element, such as its reactivity and ability to form bonds with other atoms.
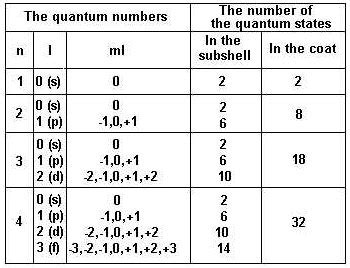
| Angular Quantum Number (l) | Orbital Shape | Energy Level |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | s | Lowest energy level |
| 1 | p | Higher energy level than s |
| 2 | d | Higher energy level than p |
| 3 | f | Higher energy level than d |
Magnetic Properties and Chemical Reactivity
The angular quantum number influences the magnetic properties of an atom, with different values of ‘l’ resulting in different magnetic moments. The magnetic moment is a measure of the strength and direction of an atom’s magnetic field. Atoms with unpaired electrons, which are electrons that do not have a partner electron with opposite spin, can exhibit magnetic properties. The angular quantum number is also used to predict the chemical reactivity of an element, which is its ability to form bonds with other atoms. Elements with unpaired electrons are generally more reactive than those with paired electrons.
Applications in Chemistry and Materials Science
The angular quantum number has numerous applications in chemistry and materials science. It is used to understand the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules, which is crucial in predicting the chemical properties of a substance. The angular quantum number is also used to design new materials with specific properties, such as superconductors and nanomaterials. In addition, it is used to understand the behavior of electrons in different environments, such as in solids, liquids, and gases.
What is the significance of the angular quantum number in atomic physics?
+The angular quantum number is significant in atomic physics because it determines the shape and orientation of atomic orbitals, affects the energy of an electron, and influences the magnetic properties of an atom.
How does the angular quantum number affect the chemical properties of an element?
+The angular quantum number affects the chemical properties of an element by determining the shape and orientation of its atomic orbitals, which in turn affects its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
What are some applications of the angular quantum number in materials science?
+The angular quantum number has applications in materials science, including the design of new materials with specific properties, such as superconductors and nanomaterials, and the understanding of the behavior of electrons in different environments.
In conclusion, the angular quantum number is a fundamental concept in atomic physics and chemistry, playing a crucial role in determining the shape and orientation of atomic orbitals, affecting the energy of an electron, and influencing the magnetic properties of an atom. Its applications in chemistry and materials science are numerous, and it continues to be an important area of research and study. By understanding the angular quantum number and its significance, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules, and develop new materials and technologies with specific properties.