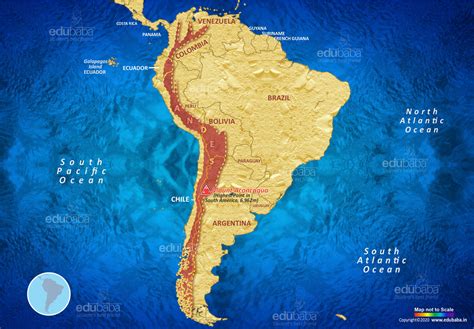
The Andes Mountain Range is one of the most impressive and awe-inspiring geographical features on the planet, stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) through seven countries in South America. This mountain range is not only a testament to the incredible forces of nature that have shaped our Earth but also home to a rich biodiversity, unique cultural heritage, and breathtaking landscapes. In this article, we will delve into five fascinating facts about the Andes Mountain Range, exploring its geological history, ecological significance, and the impact it has on the surrounding environment and human populations.
Key Points
- The Andes Mountain Range is the longest mountain range in the world, spanning over 7,000 kilometers.
- The highest peak in the Andes, Aconcagua, is also the highest peak outside of Asia, standing at 6,962 meters above sea level.
- The Andes are home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, deserts, and arctic tundras.
- The mountain range plays a crucial role in shaping the climate of South America, with the eastern and western sides experiencing vastly different weather patterns.
- The Andes have been inhabited by humans for thousands of years, with many indigenous communities still living in the region and preserving their unique cultural traditions.
Geological Formation and Characteristics
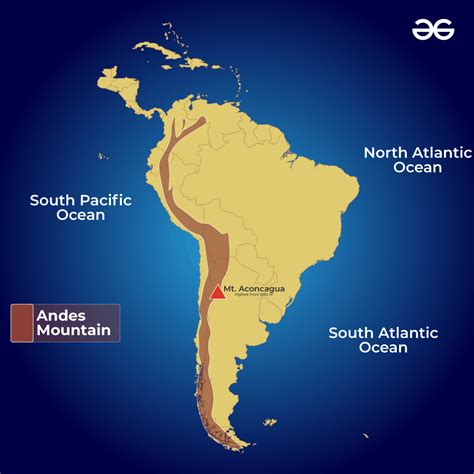
The Andes Mountain Range was formed as a result of the subduction of the Nazca Plate under the South American Plate, a process that began over 25 million years ago and continues to this day. This tectonic activity has pushed the Earth’s crust upwards, creating the towering mountain peaks that characterize the range. The Andes are divided into several sections, each with its unique geological features and characteristics. For example, the Cordillera Blanca in Peru is known for its stunning glaciers and snow-capped peaks, while the Atacama Desert in Chile is one of the driest places on Earth.
Ecological Significance and Biodiversity
The Andes Mountain Range is home to an incredible array of flora and fauna, with many species found nowhere else on the planet. The range’s diverse ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal life, from the majestic Andean condor to the tiny, iridescent hummingbirds that flit through the cloud forests. The Andes are also home to some of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on the planet, including the Amazon rainforest, which covers a significant portion of the eastern slope of the range. However, the region is also facing numerous environmental challenges, including deforestation, climate change, and habitat fragmentation, which threaten the very existence of these unique ecosystems.
| Country | Length of Andes Mountain Range (km) |
|---|---|
| Venezuela | 430 |
| Colombia | 1,239 |
| Ecuador | 790 |
| Peru | 1,821 |
| Bolivia | 840 |
| Chile | 2,880 |
| Argentina | 2,300 |
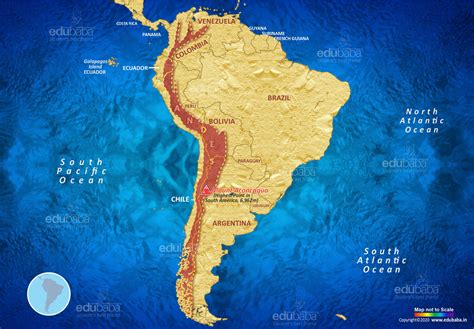
Cultural and Historical Significance

The Andes Mountain Range has been home to numerous indigenous cultures for thousands of years, each with their unique traditions, languages, and customs. The Inca Empire, which flourished in the 15th and 16th centuries, was one of the most powerful and sophisticated civilizations in the pre-Columbian Americas, with its capital, Cusco, located in the heart of the Andes. Today, many of these communities continue to thrive, preserving their cultural heritage and traditional ways of life, despite the challenges posed by modernization, urbanization, and environmental degradation.
Climate and Weather Patterns
The Andes Mountain Range plays a significant role in shaping the climate of South America, with the eastern and western sides experiencing vastly different weather patterns. The eastern slope of the range is generally wetter and more humid, with the Amazon rainforest receiving over 2,000 mm of rainfall per year. In contrast, the western slope is drier and more arid, with some areas receiving less than 100 mm of rainfall per year. This variation in climate has significant implications for agriculture, water management, and human settlement patterns in the region.
What is the highest peak in the Andes Mountain Range?
+The highest peak in the Andes Mountain Range is Aconcagua, located in Argentina, which stands at 6,962 meters above sea level.
What is the longest mountain range in the world?
+The Andes Mountain Range is the longest mountain range in the world, stretching over 7,000 kilometers through seven countries in South America.
What is the most biodiverse ecosystem in the Andes Mountain Range?
+The Amazon rainforest, which covers a significant portion of the eastern slope of the Andes, is one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet, supporting an incredible array of plant and animal life.
In conclusion, the Andes Mountain Range is a complex, fascinating, and awe-inspiring geographical feature that plays a critical role in shaping the climate, ecosystems, and human cultures of South America. As we continue to face the challenges of environmental degradation, climate change, and sustainable development, it is essential that we prioritize the conservation and management of this unique and fragile environment, preserving its natural beauty, biodiversity, and cultural significance for future generations.