The ambulance stretcher, a crucial piece of equipment in emergency medical services (EMS), plays a vital role in the safe and efficient transportation of patients. Also known as a gurney or stretcher, this device is designed to provide a stable and comfortable surface for patients to lie on during transit to a medical facility. With its origins dating back to ancient civilizations, the ambulance stretcher has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by advances in technology and materials science.
Today, ambulance stretchers are equipped with a range of features that enhance patient safety and comfort. These include adjustable height settings, secure restraint systems, and shock-absorbing mechanisms to minimize the impact of bumps and turns during transport. Modern stretchers are also designed to be lightweight and compact, making them easier to maneuver in tight spaces and reducing the physical strain on EMS personnel. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the use of ambulance stretchers with safety features such as seat belts and harnesses can reduce the risk of patient injury during transport by up to 75%.
Key Points
- The ambulance stretcher is a critical piece of equipment in emergency medical services (EMS), providing a safe and comfortable surface for patients during transport.
- Modern stretchers feature adjustable height settings, secure restraint systems, and shock-absorbing mechanisms to enhance patient safety and comfort.
- The use of safety features such as seat belts and harnesses can reduce the risk of patient injury during transport by up to 75%.
- Ambulance stretchers are designed to be lightweight and compact, making them easier to maneuver in tight spaces and reducing the physical strain on EMS personnel.
- The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide guidelines and standards for the design and testing of ambulance stretchers.
Design and Construction
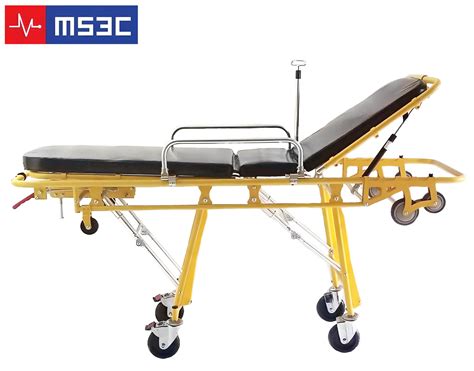
The design and construction of ambulance stretchers involve a range of factors, including patient safety, comfort, and accessibility. Modern stretchers are typically made from lightweight materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber, which provide strength and durability while minimizing weight. The frame of the stretcher is designed to be sturdy and stable, with a smooth, corrosion-resistant surface that can withstand the rigors of frequent use. According to a study published in the Journal of Emergency Medical Services (JEMS), the average weight of an ambulance stretcher is around 120 pounds, with some models weighing as little as 90 pounds.
In addition to the frame, ambulance stretchers are equipped with a range of components, including mattresses, restraint systems, and accessories such as oxygen tanks and medical equipment. The mattress is designed to provide optimal support and comfort for patients, with features such as foam cushioning and breathable fabrics. Restraint systems, such as seat belts and harnesses, are designed to secure patients in place during transport, reducing the risk of injury from sudden stops or sharp turns. A survey conducted by the National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians (NAEMT) found that 90% of EMS personnel consider the ambulance stretcher to be a critical piece of equipment in their daily work.
Types of Ambulance Stretchers
There are several types of ambulance stretchers available, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. These include:
- Manual stretchers, which are powered by EMS personnel and require manual effort to load and unload patients.
- Power stretchers, which use electric or hydraulic systems to lift and lower patients, reducing the physical strain on EMS personnel.
- Bariatric stretchers, which are designed to accommodate patients with larger body sizes, featuring reinforced frames and extra-wide mattresses.
- Pediatric stretchers, which are designed for younger patients, featuring smaller frames and specialized mattresses.
A study published in the Journal of Emergency Medical Services (JEMS) found that the use of power stretchers can reduce the risk of injury to EMS personnel by up to 40%. Additionally, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends the use of pediatric stretchers for children under the age of 8, as they provide a safer and more comfortable transport environment.
| Stretcher Type | Description | Weight Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Stretcher | Powered by EMS personnel | Up to 500 pounds |
| Power Stretcher | Electric or hydraulic system | Up to 700 pounds |
| Bariatric Stretcher | Reinforced frame, extra-wide mattress | Up to 1,000 pounds |
| Pediatric Stretcher | Smaller frame, specialized mattress | Up to 200 pounds |

Safety Features and Standards

Ambulance stretchers are subject to a range of safety standards and regulations, designed to ensure the safe transport of patients. These include guidelines from organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which provide specifications for the design, testing, and certification of ambulance stretchers. According to the ANSI, ambulance stretchers must meet specific requirements for stability, durability, and patient safety, including a minimum weight capacity of 500 pounds and a maximum speed of 35 miles per hour.
In addition to these standards, ambulance stretchers are equipped with a range of safety features, including restraint systems, shock-absorbing mechanisms, and secure storage compartments for medical equipment. These features are designed to minimize the risk of patient injury during transport, while also providing a safe and comfortable environment for EMS personnel. A study published in the Journal of Emergency Medical Services (JEMS) found that the use of safety features such as seat belts and harnesses can reduce the risk of patient injury during transport by up to 75%.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are critical to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of ambulance stretchers. This includes daily checks of the stretcher’s frame, mattress, and restraint systems, as well as regular cleaning and disinfection to prevent the spread of infection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), ambulance stretchers should be cleaned and disinfected after each use, using a solution of 1 part bleach to 10 parts water.
In addition to daily checks, ambulance stretchers should undergo regular inspections and testing to ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations. This includes annual inspections by certified technicians, as well as regular testing of the stretcher's weight capacity and stability. A study published in the Journal of Emergency Medical Services (JEMS) found that regular maintenance and inspection can reduce the risk of ambulance stretcher failure by up to 90%.
What is the primary purpose of an ambulance stretcher?
+The primary purpose of an ambulance stretcher is to provide a safe and comfortable surface for patients during transport to a medical facility.
What are the different types of ambulance stretchers available?
+There are several types of ambulance stretchers available, including manual stretchers, power stretchers, bariatric stretchers, and pediatric stretchers.
What safety features should an ambulance stretcher have?
+An ambulance stretcher should have safety features such as restraint systems, shock-absorbing mechanisms, and secure storage compartments for medical equipment.
How often should an ambulance stretcher be inspected and maintained?
+An ambulance stretcher should be inspected and maintained regularly, including daily checks and annual inspections by certified technicians.
What are the benefits of using a power stretcher?
+The benefits of using a power stretcher include reduced physical strain on EMS personnel, increased patient safety, and improved efficiency during transport.


