Altered mental status (AMS) is a condition characterized by a change in an individual's level of consciousness, which can manifest as confusion, disorientation, or a decreased ability to respond to environmental stimuli. This condition can be caused by a wide range of factors, including medical conditions, medications, and traumatic injuries. As a complex and multifaceted condition, AMS requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, incorporating the expertise of various healthcare professionals.
The diagnosis of AMS often involves a thorough physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests to identify underlying causes. Healthcare providers must consider the patient's age, medical history, and current symptoms to develop an effective treatment plan. In some cases, AMS may be a symptom of an underlying condition that requires immediate medical attention, such as a stroke or infection. In other cases, AMS may be caused by medications or substances that can be adjusted or discontinued to resolve the condition.
Key Points
- Altered mental status is a condition characterized by a change in level of consciousness, confusion, or disorientation.
- AMS can be caused by various factors, including medical conditions, medications, and traumatic injuries.
- Diagnosis involves a comprehensive physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests to identify underlying causes.
- Treatment plans must be tailored to the individual patient, considering age, medical history, and current symptoms.
- Early recognition and intervention are critical to preventing long-term consequences and improving patient outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors

AMS can be caused by a wide range of factors, including medical conditions, medications, and traumatic injuries. Some common causes of AMS include infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis, metabolic disorders, such as diabetes or liver disease, and traumatic brain injuries. Additionally, certain medications, such as sedatives or antidepressants, can cause AMS as a side effect. In some cases, AMS may be caused by a combination of factors, making diagnosis and treatment more complex.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing AMS. For example, individuals with a history of stroke or traumatic brain injury may be more likely to experience AMS. Additionally, individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or liver disease, may be more susceptible to AMS due to metabolic imbalances or other complications. Healthcare providers must consider the patient’s medical history and current symptoms to identify potential underlying causes of AMS.
| Medical Condition | Risk of AMS |
|---|---|
| Stroke | High |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | High |
| Diabetes | Moderate |
| Liver Disease | Moderate |
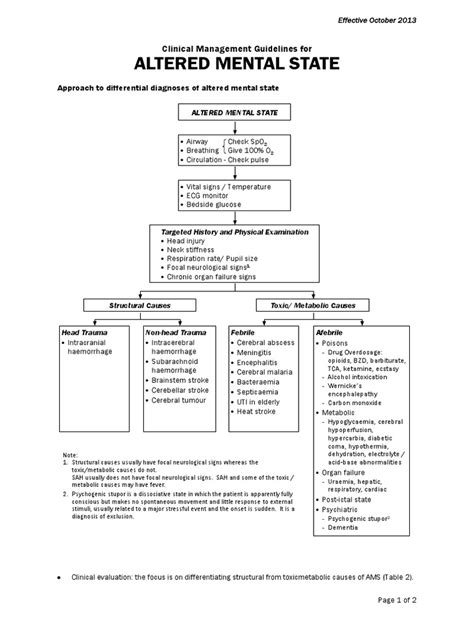
Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosis of AMS involves a comprehensive physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests to identify underlying causes. Healthcare providers must consider the patient’s age, medical history, and current symptoms to develop an effective treatment plan. In some cases, AMS may be a symptom of an underlying condition that requires immediate medical attention, such as a stroke or infection. In other cases, AMS may be caused by medications or substances that can be adjusted or discontinued to resolve the condition.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, such as complete blood counts, blood chemistry tests, and urinalyses, can help identify underlying causes of AMS. For example, a complete blood count can help diagnose infections or metabolic disorders, while blood chemistry tests can help identify electrolyte imbalances or other metabolic abnormalities. Urinalyses can help diagnose urinary tract infections or other conditions that may be contributing to AMS.
In addition to laboratory tests, imaging studies, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, may be used to evaluate the brain and identify potential causes of AMS. These studies can help diagnose traumatic brain injuries, strokes, or other conditions that may be contributing to AMS.
What are the common causes of altered mental status?
+Common causes of altered mental status include infections, metabolic disorders, traumatic brain injuries, and certain medications.
How is altered mental status diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of altered mental status involves a comprehensive physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests to identify underlying causes.
What is the treatment for altered mental status?
+Treatment for altered mental status depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, supportive care, or other interventions to address the underlying condition.
In conclusion, altered mental status is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers must consider the patient’s age, medical history, and current symptoms to develop an effective treatment plan. Early recognition and intervention are critical to preventing long-term consequences and improving patient outcomes. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for AMS, healthcare providers can provide high-quality care and improve patient outcomes.