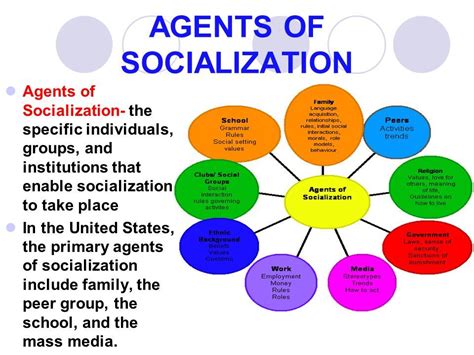
The concept of socialisation refers to the process through which individuals learn and internalise the norms, values, and behaviours of the society they live in. This process is crucial for the development of a person's identity, worldview, and social skills. Agents of socialisation are the individuals, groups, or institutions that play a significant role in shaping our socialisation. These agents can be formal or informal and can have a profound impact on our lives, influencing how we think, feel, and behave. In this article, we will delve into the world of agents of socialisation, exploring their types, roles, and significance in shaping our social reality.
Key Points
- Family is the primary agent of socialisation, responsible for initial socialisation and laying the foundation for future social interactions.
- Schools and education systems serve as secondary agents of socialisation, teaching formal knowledge and social norms.
- Peers and friendship groups are significant agents of socialisation during adolescence and early adulthood, influencing social behaviour and identity formation.
- Mass media, including television, social media, and the internet, play a crucial role in shaping cultural values, social attitudes, and consumer behaviour.
- Community and social institutions, such as religious organisations and voluntary groups, contribute to socialisation by providing a sense of belonging and social identity.
Types of Agents of Socialisation

Agents of socialisation can be broadly categorised into primary and secondary agents. Primary agents are those that are responsible for our initial socialisation, while secondary agents become more influential as we grow older and interact with a wider range of social groups. The primary agents of socialisation include family, caregivers, and close relatives, who teach us basic social skills, values, and norms from a young age. Secondary agents, on the other hand, include schools, peers, mass media, and social institutions, which become more significant as we progress through different stages of life.
Family as an Agent of Socialisation
Family is the most important primary agent of socialisation. It is within the family setting that we first learn about social norms, values, and expectations. Parents, caregivers, and siblings play a significant role in shaping our early socialisation, teaching us how to communicate, interact with others, and behave in a socially acceptable manner. The family also influences our language, customs, and cultural practices, laying the foundation for our future social interactions. For instance, a study by Sociologist George Herbert Mead found that children who are exposed to positive reinforcement and social interaction within the family are more likely to develop healthy self-esteem and social skills.
| Agent of Socialisation | Role | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Primary socialisation, teaching basic social skills and values | Foundation for future social interactions and identity formation |
| Schools | Secondary socialisation, teaching formal knowledge and social norms | Shaping cognitive development, social behaviour, and cultural values |
| Peers | Secondary socialisation, influencing social behaviour and identity formation | Significant during adolescence and early adulthood, shaping social attitudes and consumer behaviour |

Secondary Agents of Socialisation
Secondary agents of socialisation become more influential as we progress through different stages of life. Schools, for example, play a crucial role in teaching formal knowledge, social norms, and values. Educators and peers within the school setting can significantly influence our social behaviour, attitudes, and identity formation. Mass media, including television, social media, and the internet, also play a significant role in shaping our cultural values, social attitudes, and consumer behaviour. Furthermore, community and social institutions, such as religious organisations and voluntary groups, contribute to socialisation by providing a sense of belonging and social identity.
The Impact of Mass Media on Socialisation
Mass media has become an increasingly important agent of socialisation in modern society. The internet, social media, and television can shape our cultural values, social attitudes, and consumer behaviour, often in subtle yet profound ways. For instance, a study by the American Psychological Association found that exposure to violent media can increase aggressive behaviour in children and adolescents. Similarly, social media platforms can influence our self-esteem, body image, and social relationships, highlighting the need for critical media literacy and responsible media consumption.
In conclusion, agents of socialisation play a vital role in shaping our social reality, influencing how we think, feel, and behave. By understanding the different types of agents of socialisation and their roles in the socialisation process, we can gain valuable insights into the complex and dynamic nature of socialisation. As we navigate the complexities of modern society, it is essential to recognise the significance of agents of socialisation and their impact on our individual and collective behaviour.
What is the primary agent of socialisation?
+The primary agent of socialisation is the family, which teaches basic social skills, values, and norms from a young age.
How does mass media influence socialisation?
+Mass media, including television, social media, and the internet, can shape cultural values, social attitudes, and consumer behaviour, often in subtle yet profound ways.
What is the role of schools in socialisation?
+Schools play a crucial role in teaching formal knowledge, social norms, and values, shaping cognitive development, social behaviour, and cultural values.