The activity series, also known as the reactivity series, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that ranks elements based on their ability to undergo displacement reactions. This series is crucial in understanding the behavior of elements in various chemical reactions, including single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions. The activity series is typically divided into two categories: the metal activity series and the nonmetal activity series. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the activity series, its significance, and its applications in chemistry.
Key Points
- The activity series ranks elements based on their ability to undergo displacement reactions.
- The metal activity series includes metals such as potassium, sodium, and calcium, which are highly reactive.
- The nonmetal activity series includes nonmetals such as fluorine, chlorine, and oxygen, which are also highly reactive.
- The activity series is used to predict the outcome of single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
- Understanding the activity series is essential in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and engineering.
Introduction to the Activity Series
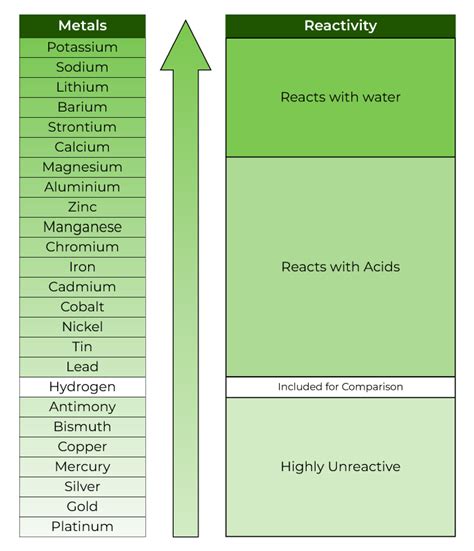
The activity series is a list of elements in order of their reactivity, with the most reactive elements at the top and the least reactive elements at the bottom. The series is based on the ability of an element to displace another element from a compound. For example, if element A can displace element B from a compound, then element A is more reactive than element B. The activity series is typically represented as a table or a list, with the most reactive elements on the left and the least reactive elements on the right.
Metal Activity Series
The metal activity series includes metals such as potassium, sodium, and calcium, which are highly reactive. These metals are capable of displacing other metals from their compounds, and they are often used as reducing agents in chemical reactions. The metal activity series is typically represented as follows:
| Metal | Reactivity |
|---|---|
| Potassium (K) | High |
| Sodium (Na) | High |
| Calcium (Ca) | Medium |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Medium |
| Aluminum (Al) | Low |
| Zinc (Zn) | Low |
| Tin (Sn) | Low |
| Lead (Pb) | Low |
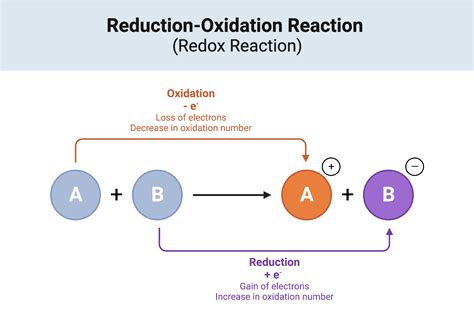
The metal activity series is used to predict the outcome of single displacement reactions, where one metal displaces another metal from a compound. For example, if potassium (K) is more reactive than sodium (Na), then potassium will displace sodium from a compound.
Nonmetal Activity Series
The nonmetal activity series includes nonmetals such as fluorine, chlorine, and oxygen, which are also highly reactive. These nonmetals are capable of displacing other nonmetals from their compounds, and they are often used as oxidizing agents in chemical reactions. The nonmetal activity series is typically represented as follows:
| Nonmetal | Reactivity |
|---|---|
| Fluorine (F) | High |
| Chlorine (Cl) | High |
| Oxygen (O) | Medium |
| Nitrogen (N) | Low |
| Carbon (C) | Low |
| Sulfur (S) | Low |
| Phosphorus (P) | Low |
The nonmetal activity series is used to predict the outcome of single displacement reactions, where one nonmetal displaces another nonmetal from a compound. For example, if fluorine (F) is more reactive than chlorine (Cl), then fluorine will displace chlorine from a compound.
Applications of the Activity Series

The activity series has numerous applications in chemistry and other fields. It is used to predict the outcome of single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions. The activity series is also used to determine the reactivity of elements, which is essential in understanding chemical bonding and chemical reactions.
Prediction of Reaction Outcomes
The activity series is used to predict the outcome of chemical reactions. For example, if a metal is more reactive than another metal, it will displace the less reactive metal from a compound. Similarly, if a nonmetal is more reactive than another nonmetal, it will displace the less reactive nonmetal from a compound.
Determination of Reactivity
The activity series is used to determine the reactivity of elements. Elements that are highly reactive are capable of displacing other elements from their compounds, while elements that are less reactive are not capable of doing so. The reactivity of elements is essential in understanding chemical bonding and chemical reactions.
What is the activity series in chemistry?
+The activity series is a list of elements in order of their reactivity, with the most reactive elements at the top and the least reactive elements at the bottom.
What are the applications of the activity series?
+The activity series has numerous applications in chemistry and other fields, including prediction of reaction outcomes, determination of reactivity, and understanding chemical bonding and chemical reactions.
How is the activity series used to predict reaction outcomes?
+The activity series is used to predict the outcome of chemical reactions by determining which element is more reactive and will displace the less reactive element from a compound.
In conclusion, the activity series is a fundamental concept in chemistry that ranks elements based on their ability to undergo displacement reactions. Understanding the activity series is essential in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and engineering. The activity series has numerous applications, including prediction of reaction outcomes, determination of reactivity, and understanding chemical bonding and chemical reactions.
Meta description: Discover the activity series in chemistry, a fundamental concept that ranks elements based on their reactivity, and learn about its applications in predicting reaction outcomes and determining reactivity. (147 characters)



