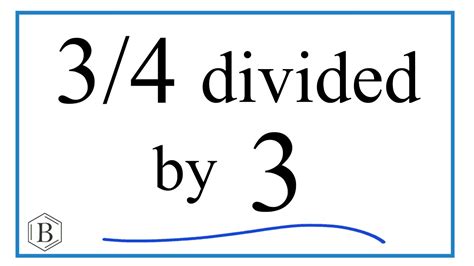
The concept of dividing 3 by a number that doesn't neatly fit into it can lead to interesting mathematical explorations, especially when considering different mathematical frameworks and interpretations. The division operation, fundamentally, is about distributing a quantity into equal parts. However, when we talk about dividing 3 by a number that does not divide 3 without leaving a remainder in standard arithmetic, we venture into territories that require an understanding of various mathematical concepts and structures.
Introduction to Mathematical Frameworks
Mathematics provides several frameworks for handling division in non-standard scenarios, including modular arithmetic, fractions, and extensions of the real number system such as the complex numbers. Each of these frameworks offers a way to interpret and perform division operations in a manner that is consistent within its own rules and applications.
Modular Arithmetic
In modular arithmetic, numbers “wrap around” upon reaching a certain value, called the modulus. For example, if we are working modulo 4, the sequence of numbers starting from 0 would be 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. In this context, dividing 3 by 4 doesn’t yield a fraction but rather looks for a multiplicative inverse of 4 modulo some number. However, since 4 and 3 are relatively prime (their greatest common divisor is 1), we can find a multiplicative inverse of 3 modulo 4, but not directly a division of 3 by 4 in the traditional sense.
| Modulus | Multiplicative Inverse of 3 |
|---|---|
| 4 | 3 (since 3*3 mod 4 = 1) |
Fractions and Real Numbers

In the real number system, division can be more straightforwardly defined, including dividing by numbers that don’t evenly divide into 3. For example, dividing 3 by 4 yields 3⁄4, a fraction that represents the quotient. This fraction can also be expressed as a decimal, 0.75, offering another way to understand the division result.
Complex Numbers
Extending into the complex number system, which includes all numbers of the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit (satisfying i^2 = -1), provides even more flexibility. However, dividing 3 by a complex number doesn’t directly apply to the simple case of dividing 3 by a real number unless the complex number has a real component that can be considered in the context of division.
Key Points
- Division in modular arithmetic involves finding multiplicative inverses and may not directly apply to dividing a number by another in the traditional sense.
- The real number system, including fractions and decimals, offers a more conventional approach to dividing numbers that don't divide evenly.
- Complex numbers provide an extension of the real number system but aren't directly relevant to simple division problems unless dealing with complex quotients.
- Understanding different mathematical frameworks is crucial for approaching division problems that don't fit standard arithmetic operations.
- Each framework provides its own set of rules and applications for handling division, making mathematics a versatile and powerful tool for problem-solving.
Considering these mathematical frameworks, it becomes apparent that the question of dividing 3 by 4 (or any other number that doesn't divide 3 without a remainder) opens up discussions on the nature of numbers and operations. Whether through modular arithmetic, fractions, or an understanding of the real and complex number systems, mathematics offers a variety of lenses through which to view and solve division problems, each with its own set of assumptions and applications.
What is the difference between dividing 3 by 4 in modular arithmetic versus the real number system?
+In modular arithmetic, dividing 3 by 4 looks for a multiplicative inverse of 4 modulo some number, which doesn't directly translate to the traditional division operation. In contrast, the real number system allows for a straightforward division, resulting in a fraction (3/4) or decimal (0.75), which represents the quotient directly.
How do complex numbers extend our understanding of division operations?
+Complex numbers provide a framework for dealing with division operations that involve imaginary components. While they don't directly apply to simple division problems like dividing 3 by 4, they offer a broader context for understanding division in mathematical operations, especially in algebra and calculus.
What is the significance of understanding different mathematical frameworks for division operations?
+Understanding different mathematical frameworks for division operations allows for a deeper appreciation of the flexibility and power of mathematics. Each framework provides its own tools and perspectives, enabling mathematicians and problem-solvers to approach division problems from multiple angles, depending on the context and requirements of the problem.
As we explore the various ways to divide 3, it becomes clear that mathematics is not just about numbers and operations but about the contexts, frameworks, and interpretations we apply to those numbers and operations. The division of 3 by 4, or any other number, is not just a simple arithmetic problem but an invitation to delve into the richness and diversity of mathematical thought.