When considering the mathematical operation of division, particularly with the expression "4 ways to divide 2," it's essential to understand that division is a fundamental operation in mathematics that represents the process of sharing or grouping a certain quantity into equal parts. The expression itself might seem straightforward, but it opens up discussions on the interpretation of division, especially in the context of integers and fractions. In this article, we will delve into the concept of dividing 2 in different mathematical contexts, exploring the multifaceted nature of division.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic concept of division and its application to integers and fractions.
- Exploring division in the context of whole numbers, where 2 can be divided by 1 and 2 itself.
- Delving into fractional division, where 2 can be divided by fractions to yield different results.
- Considering the role of negative numbers in division, further expanding the ways 2 can be divided.
- Appreciating the conceptual understanding of division as a mathematical operation that can be applied in various ways.
Division in Whole Numbers
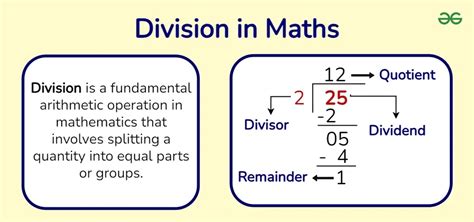
In the realm of whole numbers, division is often considered in terms of factors. For the number 2, the factors are 1 and 2 itself. Thus, 2 can be divided by 1 and 2, yielding 2 and 1, respectively. This represents the basic understanding of division in the context of integers, where we look for numbers that divide into another without leaving a remainder.
Division by Fractions
When we introduce fractions into the equation, the concept of division expands. Dividing by a fraction is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. Therefore, 2 divided by 1⁄2 (or 0.5) equals 2 * 2 = 4. Similarly, 2 divided by 1⁄4 equals 2 * 4 = 8. This demonstrates how fractions can significantly alter the outcome of division operations, providing a broader range of results when dividing 2.
| Divisor | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 1/2 | 4 |
| 1/4 | 8 |
Division and Negative Numbers
Introducing negative numbers into division further complicates and enriches our understanding. When dividing 2 by -1, the result is -2. Similarly, dividing 2 by -2 yields -1. This aspect of division underscores the significance of sign rules in mathematics, affecting the outcome of division operations and expanding the “ways” 2 can be divided when considering negative divisors.
Conceptual Understanding of Division
The conceptual depth of division is not limited to its operational aspects but also includes understanding its role in mathematical structures and its implications in problem-solving. Recognizing that division can represent sharing, scaling, or finding the rate of change in certain contexts adds layers to how we interpret and apply division in mathematics and real-world scenarios.
What is the basic concept of division in mathematics?
+Division is a mathematical operation that represents the process of sharing or grouping a certain quantity into equal parts. It is denoted by the division sign (÷) or the fraction bar.
How does dividing by fractions work?
+Dividing by a fraction is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal. For example, dividing 2 by 1/2 means multiplying 2 by 2, which equals 4.
What role do negative numbers play in division operations?
+Negative numbers in division operations follow specific sign rules. For instance, dividing a positive number by a negative number yields a negative result, and vice versa. This expands the outcomes when dividing 2 by considering negative divisors.
In conclusion, the expression “4 ways to divide 2” serves as a catalyst for exploring the multifaceted nature of division in mathematics. From the straightforward division of whole numbers to the more complex scenarios involving fractions and negative numbers, each context provides unique insights into the operation of division. Understanding these different aspects not only enhances one’s mathematical proficiency but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the conceptual richness and versatility of division as a fundamental mathematical operation.



