Conduction, the process by which heat is transferred through a material object, is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering. It plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives, from the simplest household appliances to complex industrial systems. Understanding conduction is essential for designing efficient heating and cooling systems, as well as for ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic devices. In this article, we will delve into the world of conduction, exploring its principles, applications, and significance through 15 illustrative examples.
Key Points
- Conduction is a mode of heat transfer that occurs through direct contact between particles of matter.
- The efficiency of conduction depends on the material's thermal conductivity, density, and specific heat capacity.
- Conduction is crucial in the design of electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, to manage heat dissipation.
- Insulators, like foam and fiberglass, are used to reduce heat transfer via conduction in buildings and appliances.
- Conduction plays a significant role in geological processes, including the cooling of the Earth's core.
Principles of Conduction
Conduction is based on the transfer of thermal energy between adjacent molecules or electrons in a substance. The rate of heat transfer through conduction depends on the temperature difference between the two ends of the material, the cross-sectional area of the material, and its thermal conductivity. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals, are good conductors of heat, while those with low thermal conductivity, like wood or plastic, are poor conductors.
Factors Influencing Conduction
The efficiency of conduction is influenced by several factors, including the material’s thermal conductivity, its density, and its specific heat capacity. Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct heat, with higher values indicating better heat conduction. Density affects how closely packed the molecules are, which in turn affects the ease of heat transfer. Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the material by one degree Celsius.
Examples of Conduction
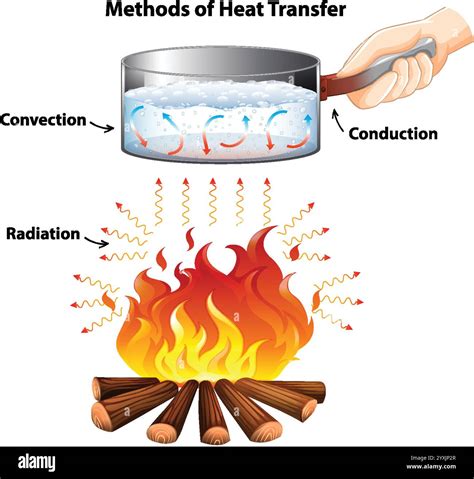
Here are 15 examples that illustrate the concept of conduction in various contexts:
- Touching a Hot Stove: When you accidentally touch a hot stove, the heat from the stove is conducted to your skin, causing a burn. This is an example of conduction through direct contact.
- Heating a Metal Rod: If you heat one end of a metal rod, the heat will be conducted to the other end, illustrating how conduction occurs within a solid material.
- Cooking with a Pot: The heat from the stove is conducted through the pot to the food, cooking it. This is an example of conduction through a solid object.
- Electronic Devices: Conduction is crucial in electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, to manage heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Building Insulation: Insulators, like foam and fiberglass, are used in buildings to reduce heat transfer via conduction, keeping the interior warm in winter and cool in summer.
- Geological Processes: Conduction plays a significant role in geological processes, including the cooling of the Earth's core and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Heat Sinks in Computers: Heat sinks are designed to conduct heat away from critical components in computers, such as the CPU and GPU, to prevent damage from overheating.
- Cooking Utensils: Metal cooking utensils, such as spatulas and whisks, conduct heat from the cookware to the food, facilitating cooking.
- Thermoses: Thermoses use vacuum insulation to reduce conduction and keep liquids at a consistent temperature for hours.
- Refrigerator Coils: The coils at the back of a refrigerator are designed to conduct heat from the inside of the fridge to the outside, cooling the contents.
- Heat Exchangers: Heat exchangers, used in power plants and HVAC systems, rely on conduction to transfer heat between two fluids without direct contact.
- Firefighter Gear: Firefighter suits and helmets are designed with materials that conduct heat away from the body, protecting firefighters from extreme temperatures.
- Medical Equipment: Some medical equipment, such as ultrasound machines, use conduction to apply heat or cold to the body for therapeutic purposes.
- Aerospace Applications: Conduction is critical in aerospace applications, such as in the design of rocket nozzles and heat shields, to manage extreme temperatures.
- High-Speed Rail: The brakes on high-speed trains use conduction to dissipate heat generated by friction, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Applications and Significance
Conduction has numerous applications across various industries, including electronics, construction, and manufacturing. Understanding conduction is essential for designing efficient systems, ensuring safety, and improving performance. In electronics, conduction is critical for managing heat dissipation and preventing component failure. In construction, insulation materials that reduce conduction are used to improve energy efficiency and comfort in buildings.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Copper | 386 |
| Aluminum | 237 |
| Steel | 50 |
| Wood | 0.13 |
| Fiberglass | 0.04 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, conduction is a vital process that underlies many aspects of our daily lives, from the functioning of electronic devices to the efficiency of heating and cooling systems in buildings. By understanding the principles of conduction and its applications, we can design more efficient, safe, and reliable systems. The 15 examples provided demonstrate the widespread relevance of conduction, highlighting its importance in various industries and everyday situations.
What is conduction, and how does it differ from other modes of heat transfer?
+Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles of matter. It differs from convection, which involves the movement of fluids, and radiation, which involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
How does the thermal conductivity of a material affect its ability to conduct heat?
+Materials with high thermal conductivity are better at conducting heat than those with low thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct heat, with higher values indicating better heat conduction.
What are some common applications of conduction in everyday life?
+Conduction is used in various applications, including electronic devices, cooking utensils, building insulation, and heat exchangers. It plays a crucial role in managing heat dissipation, ensuring safety, and improving performance in these systems.
How can conduction be optimized in system design?
+Conduction can be optimized in system design by selecting materials with appropriate thermal conductivity, ensuring good contact between surfaces, and minimizing thermal resistance. This can be achieved through careful material selection, design of heat transfer pathways, and optimization of system geometry.
What are the implications of conduction in geological processes?
+Conduction plays a significant role in geological processes, including the cooling of the Earth’s core and the formation of mountain ranges. It affects the Earth’s thermal budget, influencing climate patterns and geological activity.
How does conduction impact the design of electronic devices?
+Conduction is critical in the design of electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, to manage heat dissipation and prevent overheating. Materials with high thermal conductivity are used to conduct heat away from critical components, ensuring reliable operation and preventing damage.