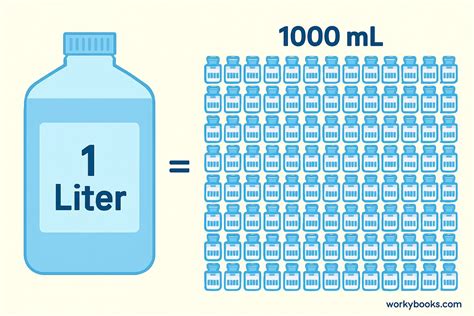
The relationship between liters and milliliters is a fundamental concept in the metric system, which is used internationally for scientific, culinary, and everyday applications. Understanding this conversion is crucial for precision in various fields, including chemistry, cooking, and medicine. At its core, the metric system is designed to be straightforward and easy to use, with each unit of measurement building upon the last in a logical and consistent manner.
One of the key features of the metric system is its use of prefixes to denote different orders of magnitude. For liquids, the base unit of measurement is the liter (L), with 1 liter being equivalent to 1000 milliliters (mL). This means that to convert liters to milliliters, one simply multiplies the number of liters by 1000. Conversely, to convert milliliters to liters, one divides the number of milliliters by 1000. This conversion factor is essential for recipes, chemical reactions, and any scenario where the precise measurement of liquids is required.
Key Points
- 1 liter is equal to 1000 milliliters, providing a standard conversion rate between these two units of volume.
- The metric system's use of prefixes allows for easy conversion between different units, with each prefix representing a specific power of ten.
- Understanding the conversion between liters and milliliters is crucial for accuracy in cooking, chemistry, and other fields where precise measurements are necessary.
- This conversion applies universally, regardless of the substance being measured, as long as it is a liquid.
- Knowledge of this conversion can help avoid mistakes in measurement, which can have significant consequences in certain applications, such as pharmaceuticals or industrial manufacturing.
The Importance of Precision in Measurement
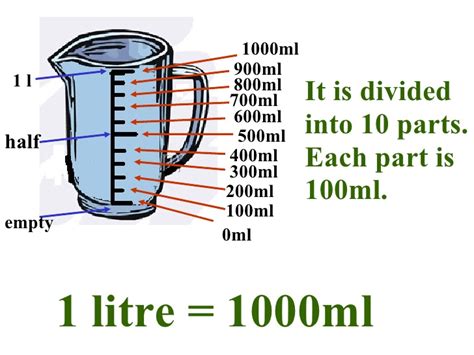
Precision in measurement is vital in many areas, including science, engineering, and healthcare. In these fields, small discrepancies in measurement can lead to significant differences in outcomes. For instance, in chemistry, the ratio of reactants can dramatically affect the yield and purity of the product. Similarly, in cooking, the balance of ingredients can alter the flavor, texture, and nutritional content of a dish. The conversion between liters and milliliters, therefore, plays a critical role in ensuring that recipes and chemical reactions are executed correctly.
Applications of the Metric System
The metric system, with its logical and consistent structure, has found widespread adoption globally. Its use simplifies international communication and trade, as it provides a common language for scientific and commercial activities. In the context of liters and milliliters, this means that a recipe developed in one country can be easily replicated in another, without the need for complicated conversions between different systems of measurement.
| Unit of Measurement | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| 1 Liter (L) | 1000 Milliliters (mL) |
| 1 Milliliter (mL) | 0.001 Liters (L) |

Practical Applications and Examples
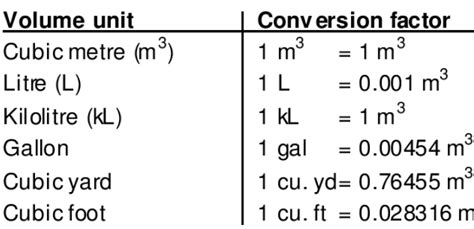
In practical terms, understanding that 1 liter equals 1000 milliliters is essential for everyday tasks. For example, when following a recipe that calls for 2 liters of water, knowing that this is equivalent to 2000 milliliters can help in accurately measuring the ingredient, especially when the measuring tools available are marked in milliliters. Similarly, in a laboratory setting, converting between liters and milliliters is crucial for preparing solutions and conducting experiments with precision.
Education and Training
Education plays a critical role in ensuring that individuals understand and can apply the metric system correctly. From a young age, students are introduced to the basics of measurement, including the relationship between liters and milliliters. As they progress in their studies, especially in sciences and culinary arts, the importance of accurate conversions becomes more apparent. Training programs for professionals, such as chefs and laboratory technicians, also emphasize the need for precision in measurement, underscoring the significance of the liter to milliliter conversion.
In conclusion, the relationship between liters and milliliters is a fundamental aspect of the metric system, with far-reaching implications for accuracy and precision in various fields. By understanding and applying this conversion correctly, individuals can ensure that their measurements are accurate, whether in the kitchen, the laboratory, or any other setting where liquids are measured.
Why is the metric system preferred over other systems of measurement?
+The metric system is preferred due to its simplicity, logic, and ease of use. It is based on the decimal system, making conversions between units straightforward. This simplicity facilitates international communication and trade, as it provides a common language for scientific and commercial activities.
How does the conversion between liters and milliliters apply in cooking?
+In cooking, the conversion between liters and milliliters is crucial for following recipes accurately. Many recipes list ingredients in milliliters, especially for liquids, while others might use liters. Knowing that 1 liter equals 1000 milliliters allows cooks to adjust ingredient quantities correctly, ensuring the desired taste, texture, and consistency of the dish.
What are the implications of incorrect conversions between liters and milliliters in a laboratory setting?
+In a laboratory setting, incorrect conversions between liters and milliliters can have significant implications, including inaccurate experimental results, wasted resources, and potential safety hazards. For chemical reactions, the ratio of reactants is critical, and small discrepancies can lead to unforeseen outcomes, affecting the yield, purity, and properties of the product.